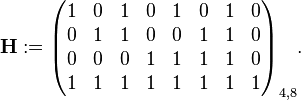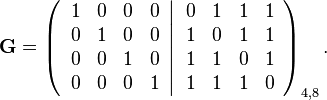Hamming code
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In telecommunication, a Hamming code is a linear error-correcting code named after its inventor, Richard Hamming. Hamming codes can detect up to two simultaneous bit errors, and correct single-bit errors; thus, reliable communication is possible when the Hamming distance between the transmitted and received bit patterns is less than or equal to one. By contrast, the simple parity code cannot correct errors, and can only detect an odd number of errors.
In mathematical terms, Hamming codes are a class of binary linear codes. For each integer m > 2 there is a code with parameters: [2m − 1,2m − m − 1,3]. The parity-check matrix of a Hamming code is constructed by listing all columns of length m that are pair-wise independent.
Because of the simplicity of Hamming codes, they are widely used in computer memory (RAM). In particular, a single-error-correcting and double-error-detecting variant commonly referred to as SECDED.
Contents |
[edit] History
Hamming worked at Bell Labs in the 1940s on the Bell Model V computer, an electromechanical relay-based machine with cycle times in seconds. Input was fed in on punch cards, which would invariably have read errors. During weekdays, special code would find errors and flash lights so the operators could correct the problem. During after-hours periods and on weekends, when there were no operators, the machine simply moved on to the next job.
Hamming worked on weekends, and grew increasingly frustrated with having to restart his programs from scratch due to the unreliability of the card reader. Over the next few years he worked on the problem of error-correction, developing an increasingly powerful array of algorithms. In 1950 he published what is now known as Hamming Code, which remains in use in some applications today.
[edit] Codes predating Hamming
A number of simple error-detecting codes were used before Hamming codes, but none were as effective as Hamming codes in the same overhead of space.
[edit] Parity
Parity adds a single bit that indicates whether the number of 1 bits in the preceding data was even or odd. If an odd number of bits is changed in transmission, the message will change parity and the error can be detected at this point. (Note that the bit that changed may have been the parity bit itself!) The most common convention is that a parity value of 1 indicates that there is an odd number of ones in the data, and a parity value of 0 indicates that there is an even number of ones in the data. In other words: The data and the parity bit together should contain an even number of 1s.
Parity checking is not very robust, since if the number of bits changed is even, the check bit will be valid and the error will not be detected. Moreover, parity does not indicate which bit contained the error, even when it can detect it. The data must be discarded entirely and re-transmitted from scratch. On a noisy transmission medium, a successful transmission could take a long time or may never occur. However, while the quality of parity checking is poor, since it uses only a single bit, this method results in the least overhead. Furthermore, parity checking does allow for the restoration of an erroneous bit when its position is known.
[edit] Two-out-of-five code
[edit] Hamming codes
If more error-correcting bits are included with a message, and if those bits can be arranged such that different incorrect bits produce different error results, then bad bits could be identified. In a 7-bit message, there are seven possible single bit errors, so three error control bits could potentially specify not only that an error occurred but also which bit caused the error.
Hamming studied the existing coding schemes, including two-of-five, and generalized their concepts. To start with, he developed a nomenclature to describe the system, including the number of data bits and error-correction bits in a block. For instance, parity includes a single bit for any data word, so assuming ASCII words with 7-bits, Hamming described this as an (8,7) code, with eight bits in total, of which 7 are data. The repetition example would be (3,1), following the same logic. The information rate is the second number divided by the first, for our repetition example, 1/3.
Hamming also noticed the problems with flipping two or more bits, and described this as the "distance" (it is now called the Hamming distance, after him). Parity has a distance of 2, as any two bit flips will be invisible. The (3,1) repetition has a distance of 3, as three bits need to be flipped in the same triple to obtain another code word with no visible errors. A (4,1) repetition (each bit is repeated four times) has a distance of 4, so flipping two bits can be detected, but not corrected. When three bits flip in the same group there can be situations where the code corrects towards the wrong code word.
Hamming was interested in two problems at once; increasing the distance as much as possible, while at the same time increasing the information rate as much as possible. During the 1940s he developed several encoding schemes that were dramatic improvements on existing codes. The key to all of his systems was to have the parity bits overlap, such that they managed to check each other as well as the data.
[edit] General algorithm
Although any number of algorithms can be created, the following general algorithm positions the parity bits at powers of two to ease calculation of which bit was flipped upon detection of incorrect parity.
- All bit positions that are powers of two are used as parity bits. (positions 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, etc.), see A000079 at the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences.
- All other bit positions are for the data to be encoded. (positions 3, 5, 6, 7, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 17, etc.), see A057716 at the On-Line Encyclopedia of Integer Sequences.
- Each parity bit calculates the parity for some of the bits in the code word. The position of the parity bit determines the sequence of bits that it alternately checks and skips.
- Position 1 (n=1): skip 0 bits (0=n−1), check 1 bit (n), skip 1 bit (n), check 1 bit (n), skip 1 bit (n), etc. (1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,...)
- Position 2 (n=2): skip 1 bit (1=n−1), check 2 bits (n), skip 2 bits (n), check 2 bits (n), skip 2 bits (n), etc. (2,3,6,7,10,11,14,15,...)
- Position 4 (n=4): skip 3 bits (3=n−1), check 4 bits (n), skip 4 bits (n), check 4 bits (n), skip 4 bits (n), etc. (4,5,6,7,12,13,14,15,20,21,22,23,...)
- Position 8 (n=8): skip 7 bits (7=n−1), check 8 bits (n), skip 8 bits (n), check 8 bits (n), skip 8 bits (n), etc. (8-15,24-31,40-47,...)
- Position 16 (n=16): skip 15 bits (15=n−1), check 16 bits (n), skip 16 bits (n), check 16 bits (n), skip 16 bits (n), etc. (16-31,48-63,80-95,...)
- Position 32 (n=32): skip 31 bits (31=n−1), check 32 bits (n), skip 32 bits (n), check 32 bits (n), skip 32 bits (n), etc. (32-63,96-127,160-191,...)
- General rule for position n: skip n−1 bits, check n bits, skip n bits, check n bits...
- And so on.
In other words, the parity bit at position 2k checks bits in positions having bit k set in their binary representation. Conversely, for instance, bit 13, i.e. 1101(2), is checked by bits 1000(2) = 8, 0100(2)=4 and 0001(2) = 1.
This general rule can be shown visually:
-
Bit position 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 ... Encoded data bits p1 p2 d1 p3 d2 d3 d4 p4 d5 d6 d7 d8 d9 d10 d11 p5 d12 d13 d14 d15 Parity
bit
coveragep1 X X X X X X X X X X p2 X X X X X X X X X X p3 X X X X X X X X X p4 X X X X X X X X p5 X X X X X
Shown are only 20 encoded bits (5 parity, 15 data) but the pattern continues indefinitely. The key thing about Hamming Codes that can easily be seen from visual inspection is that any given bit has a unique parity bit coverage. For example, the only bit covered by p3 and p4 only is bit 12 (d8). It is this unique bit coverage that lets a Hamming Code correct any single-bit error, and at the same time allows the code to detect (but not correct) any two-bit error. For example, if bits 1 (p1) & 2 (p2) were flipped then this would be confused with bit 3 (d1) being flipped since the parity bit coverage of bit 3 is the same as bits 1 & 2.
[edit] Hamming codes with additional parity (SECDED)
Hamming codes have a minimum distance of 3, which means that the code can detect and correct a single error, but a double bit error is indistinguishable from a different code with a single bit error. Thus, they can detect double-bit errors only if correction is not attempted.
By including an extra parity bit, it is possible to increase the minimum distance of the Hamming code to 4. This gives the code the ability to detect and correct a single error and at the same time detect (but not correct) a double error. (It could also be used to detect up to 3 errors but not correct any.)
This code system is popular in computer memory systems, where it is known as SECDED ("single error correction, double error detection"). Particularly popular is the (72,64) code, a truncated (127,120) Hamming code plus an additional parity bit, which has the same space overhead as a (9,8) parity code.
[edit] Hamming(7,4) code
In 1950, Hamming introduced the (7,4) code. It encodes 4 data bits into 7 bits by adding three parity bits. Hamming(7,4) can detect and correct single-bit errors but can only detect double-bit errors.
[edit] Construction of G and H
The matrix  is called a (Canonical) generator matrix of a linear (n,k) code,
is called a (Canonical) generator matrix of a linear (n,k) code,
and  is called a parity-check matrix.
is called a parity-check matrix.
This is the construction of G and H in standard (or systematic) form. Regardless of form, G and H for linear block codes must satisfy
 , an all-zeros matrix [Moon, p.89].
, an all-zeros matrix [Moon, p.89].
Since (7,4,3)=(n,k,d)=[2m − 1, 2m−1-m, 3]. The parity-check matrix H of a Hamming code is constructed by listing all columns of length m that are pair-wise independent.
Thus H is a matrix whose left side is all of the nonzero n-tuples where order of the n-tuples in the columns of matrix does not matter. The right hand side is just the (n-k)-identity matrix.
So G can be obtained from H by taking the transpose of the left hand side of H with the identity k-identity matrix on the left hand side of G.
The code generator matrix  and the parity-check matrix
and the parity-check matrix  are:
are:

and

Finally, these matrices can be mutated into equivalent non-systematic codes by the following operations [Moon, p. 85]:
- Column permutations (swapping columns)
- Elementary row operations (replacing a row with a linear combination of rows)
[edit] Encoding
Example
From the above matrix we have 2k=24=16 codewords. The codewords 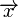 of this binary code can be obtained from
of this binary code can be obtained from 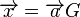 . With
. With 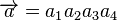 with ai exist in F2 ( A field with two elements namely 0 and 1).
with ai exist in F2 ( A field with two elements namely 0 and 1).
Thus the codewords are all the 4-tuples (k-tuples).
Therefore,
(1,0,1,1) gets encoded as (1,0,1,1,0,1,0).
[edit] Hamming(8,4) code
The Hamming(7,4) can easily be extended to an (8,4) code by adding an extra parity bit on top of the (7,4) encoded word (see Hamming(7,4)). This can be summed up with the revised matrices:
and
Note that H is not in standard form. To obtain G, elementary row operations can be used to obtain an equivalent matrix to H in systematic form:
For example, the first row in this matrix is the sum of the second and third rows of H in non-systematic form. Using the systematic construction for Hamming codes from above, the matrix A is apparent and the systematic form of G is written as
The non-systematic form of G can be row reduced (using elementary row operations) to match this matrix.
The addition of the fourth row effectively computes the sum of all the codeword bits (data and parity) as the fourth parity bit.
For example, 1011 is encoded into 01100110 where blue digits are data; red digits are parity from the Hamming(7,4) code; and the green digit is the parity added by Hamming(8,4). The green digit makes the parity of the (7,4) code even.
Finally, it can be shown that the minimum distance has increased from 3, as with the (7,4) code, to 4 with the (8,4) code. Therefore, the code can be defined as Hamming(8,4,4).
[edit] Hamming(11,7) code
Consider the 7-bit data word "0110101". To demonstrate how Hamming codes are calculated and used to detect an error, see the tables below. They use d to signify data bits and p to signify parity bits.
Firstly the data bits are inserted into their appropriate positions and the parity bits calculated in each case using even parity. The diagram to the right shows which of the four parity bits cover which data bits.
-
Calculation of Hamming code parity bits p1 p2 d1 p3 d2 d3 d4 p4 d5 d6 d7 Data word (without parity): 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 p1 1 0 1 0 1 1 p2 0 0 1 0 0 1 p3 0 1 1 0 p4 0 1 0 1 Data word (with parity): 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1
The new data word (with parity bits) is now "10001100101". We now assume the final bit gets corrupted and turned from 1 to 0. Our new data word is "10001100100"; and this time when we analyze how the Hamming codes were created we flag each parity bit as 1 when the even parity check fails.
-
Checking of parity bits (switched bit highlighted) p1 p2 d1 p3 d2 d3 d4 p4 d5 d6 d7 Parity check Parity bit Received data word: 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 p1 1 0 1 0 1 0 Fail 1 p2 0 0 1 0 0 0 Fail 1 p3 0 1 1 0 Pass 0 p4 0 1 0 0 Fail 1
The final step is to evaluate the value of the parity bits (remembering the bit with lowest index is the least significant bit, i.e., it goes furthest to the right). The integer value of the parity bits is 11, signifying that the 11th bit in the data word (including parity bits) is wrong and needs to be flipped.
-
p4 p3 p2 p1 Binary 1 0 1 1 Decimal 8 2 1 Σ = 11
Flipping the 11th bit changes 10001100100 back into 10001100101. Removing the Hamming codes gives the original data word of 0110101.
Note that in this case, as parity bits do not check each other, if a single parity bit check fails while all others succeed, then the bit error occurred in this parity bit and not any bit it checks.
Finally, suppose two bits change, at positions x and y. If x and y have the same bit at the 2k position in their binary representations, then the parity bit corresponding to that position checks them both, and so will remain the same. However, some parity bit must be altered, because x ≠ y, and so some two corresponding bits differ in x and y. Thus, the Hamming code detects all two bit errors — however, it cannot distinguish them from 1-bit errors.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- Moon, Todd K. (2005). Error Correction Coding. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0-471-64800-0. http://www.neng.usu.edu/ece/faculty/tmoon/eccbook/book.html.
- MacKay, David J.C. (September 2003). Information Theory, Inference and Learning Algorithms. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-64298-1. http://www.inference.phy.cam.ac.uk/mackay/itila/book.html.
- D.K. Bhattacharryya, S. Nandi. "An efficient class of SEC-DED-AUED codes". 1997 International Symposium on Parallel Architectures, Algorithms and Networks (ISPAN '97): 410–415. doi:10.1109/ISPAN.1997.645128.