Electronic signature
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| This article may contain original research or unverified claims. Please improve the article by adding references. See the talk page for details. (August 2008) |
| The examples and perspective in this article may not represent a worldwide view of the subject. Please improve this article or discuss the issue on the talk page. |
| This article includes a list of references or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it has insufficient inline citations. Please help to improve this article by introducing more precise citations where appropriate. (July 2008) |
A signature is a stylized script associated with a person. It is comparable to a seal. In commerce and the law, a signature on a document is an indication that the person adopts the intentions recorded in the document. An electronic signature is any legally recognised electronic means that indicates that a person adopts the contents of an electronic message.[1] It may be an electronic transmission of the document which contains the signature, as in the case of facsimile transmissions, or it may be encoded message, such as telegraphy using morse code. Increasingly, encrypted digital signatures are used in e-commerce and in regulatory filings as digital signatures are more secure than a simple generic electronic signature.[2][3][4] The concept itself is not new, with common law jurisdictions having recognized telegraph signatures as far back as the mid-19th century and faxed signatures since the 1980s.
In many countries, including the United States, the European Union and Australia, electronic signatures (when recognised under the law of each jurisdiction) have the same legal consequences as the more traditional forms of executing of documents.[5]
Contents |
[edit] History
Since well before the American Civil War began in 1861, morse code was used to send messages electronically by telegraphy. Some of these messages were agreements to terms that were intended as enforceable contracts. An early acceptance of the enforceability of telegraphic messages as electronic signatures came from the New Hampshire Supreme Court in 1869.[citation needed]
In the 1980s, many companies and even some individuals began using fax machines for high-priority or time-sensitive delivery of documents. Although the original signature on the original document was on paper, the image of the signature and its transmission was electronic.[6]
Courts in various jurisdictions have decided that enforceable electronic signatures can include agreements made by email, entering a personal identification number (PIN) into a bank ATM, signing a credit or debit slip with a digital pen pad device (an application of graphics tablet technology) at a point of sale, installing software with a clickwrap software license agreement on the package , and signing electronic documents online.[citation needed]
The first agreement signed electronically by two sovereign nations was a Joint Communiqué recognizing the growing importance of the promotion of electronic commerce, signed by the United States and Ireland in 1998.[7]
[edit] Enforceability of electronic signatures
| This section needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding reliable references (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (July 2008) |
In the United States, the definition of what qualifies as an electronic signature is wide and is set out in the Uniform Electronic Transactions Act ("UETA") released by the National Conference of Commissioners on Uniform State Laws (NCCUSL) in 1999.[8]. It was influenced by ABA committee white papers and the uniform law promulgated by NCCUSL. Under UETA, the term means "an electronic sound, symbol, or process, attached to or logically associated with a record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record." This definition and many other core concepts of UETA are echoed in the U.S. ESign Act of 2000[1] 46 US states, the District of Columbia, and the US Virgin Islands have enacted UETA.[9]
Canadian law (PIPEDA) attempts to clarify the situation by first defining a generic electronic signature as "a signature that consists of one or more letters, characters, numbers or other symbols in digital form incorporated in, attached to or associated with an electronic document", then defining a secure electronic signature as an electronic signature with specific properties. PIPEDA's secure electronic signature regulations refine the definition as being a digital signature applied and verified in a specific manner.
In the European Union, the EU Directive on Electronic Signatures or the EU Electronic Signatures Directive was published in the EC Official Journal, as Directive 1999/93/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 13 December 1999 on a Community framework for electronic signatures (OJ No L 13 p.12 19/1/2000).[10]
[edit] Legal definitions
Various laws have been passed internationally to facilitate commerce by the use of electronic records and signatures in interstate and foreign commerce. The intent is to ensure the validity and legal effect of contracts entered into electronically. For instance,
- PIPEDA definitions
- (1) An electronic signature is an "a signature that consists of one or more letters, characters, numbers or other symbols in digital form incorporated in, attached to or associated with an electronic document";
- (2) A secure electronic signature is as an electronic signature that
- (a) is unique to the person making the signature;
- (b) the technology or process used to make the signature is under the sole control of the person making the signature;
- (c) the technology or process can be used to identify the person using the technology or process; and
- (d) the electronic signature can be linked with an electronic document in such a way that it can be used to determine whether the electronic document has been changed since the electronic signature was incorporated in, attached to or associated with the electronic document.
- ESIGN Act Sec 106 definitions
- [11]
- (2) ELECTRONIC- The term 'electronic' means relating to technology having electrical, digital, magnetic, wireless, optical, electromagnetic, or similar capabilities.
- (4) ELECTRONIC RECORD- The term 'electronic record' means a contract or other record created, generated, sent, communicated, received, or stored by electronic means.
- (5) ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE- The term 'electronic signature' means an electronic sound, symbol, or process, attached to or logically associated with a contract or other record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record.
- GPEA Sec 1710 definitions
- (1) ELECTRONIC SIGNATURE.—the term "electronic signature" means a method of signing an electronic message that—
- (A) identifies and authenticates a particular person as the source of the electronic message; and
- (B) indicates such person's approval of the information contained in the electronic message.
- UETA Sec 2 definitions
- (5) "Electronic" means relating to technology having electrical, digital, magnetic, wireless, optical, electromagnetic, or similar capabilities.
- (6) "Electronic agent" means a computer program or an electronic or other automated means used independently to initiate an action or respond to electronic records or performances in whole or in part, without review or action by an individual.
- (7) "Electronic record" means a record created, generated, sent, communicated, received, or stored by electronic means.
- (8) "Electronic signature" means an electronic sound, symbol, or process attached to or logically associated with a record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record.
- Federal Reserve 12 CFR 202 definitions
- refers to the ESIGN Act
- Commodity Futures Trading Commission 17 CFR Part 1 Sec. 1.3 definitions
- (tt) Electronic signature means an electronic sound, symbol, or process attached to or logically associated with a record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record.
- Food and Drug Administration 21 CFR Sec. 11.3 definitions
- (5) Digital signature means an electronic signature based upon cryptographic methods of originator authentication, computed by using a set of rules and a set of parameters such that the identity of the signer and the integrity of the data can be verified.
- (7) Electronic signature means a computer data compilation of any symbol or series of symbols executed, adopted, or authorized by an individual to be the legally binding equivalent of the individual's handwritten signature.
[edit] Legal test of electronic signatures
In law, if a signature on a contract or other document is contested, the signature must meet certain tests before a court will uphold them if contested. These requirements vary by jurisdiction, but various sorts of signatures, some entirely electronic Telex addresses (for example, ABC Company sends a Telex to XYZ Company making an offer at a particular price. The offer was held to be binding when the 'signature' was challenged.), telegrams (for example, "I ACCEPT, SMITH" even though Smith never actually touched the telegraph key), and faxes of documents, even in some cases where the original was not signed by the sender.
A central question in such cases is forgery and spoofing of assent, and in these decisions, courts have held that forgery and spoofing can be in practice ruled out. Nevertheless, it is easily possible, for many electronic methods of signature, or imputed signature, to forge or spoof assent. The rapidly rising problem of identity theft illustrates the ease of such forgeries.
Often, businesses rely on other means to attempt to ensure an electronic signature is correct, including talking with the signing person directly or over the phone before an electronic signing, having an ongoing business relationship, and receiving payment or other indications of intent to do business that do not rely solely on a signed document. This is good business practice even in the paper world, as forgeries have been common there since time immemorial. Fraud is a common issue in all signature situations, and neither type of signature (paper or electronic) provides fully effective anti-fraud protections.
None of the electronic signatures in these examples are digital signatures in that there is no cryptographic assurance of the sender's identity, and no integrity check on the text received. However, all are electronic signatures, and all have been found legally binding in some circumstances, but proving the validity of a digital signature in a court of law is much easier than proving the validity of a simple electronic signature.
[edit] Laws regarding use of electronic signatures
- Canada - PIPEDA, its regulations, and the Canada Evidence Act.
- China - Law of the People’s Republic of China on Electronic Signature (effective April 1, 2005)
- Costa Rica - Digital Signature Law 8454 (2005)
- Croatia 2002, updated 2008
- Czech Republic - Zákon o elektronickém podpisu 227/2000Sb.
- European Union - Electronic Signature Directive (1999/93/EC) - detailed information on implementation within the EU is set out in the Digital Signatures and the Law.
- India - Information Technology Act
- Japan - Law Concerning Electronic Signatures and Certification Services, 2000
- Mexico - E-Commerce Act [2000]
- Poland - Ustawa o podpisie elektronicznym (Dziennik Ustaw z 2001 r. Nr 130 poz. 1450) [[1]]
- Slovakia - Zákon č.215/2002 o elektronickom podpise
- Slovenia Slovene Electronic Commerce and Electronic Signature Act
- South Africa - The Electronic Communications and Transactions Act 25, 2002
- Republika Srpska (entity of the Bosnia and Herzegovina) 2005
- Turkey - Electronic Signature Law* U.S. - Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act
- UK - s.7 Electronic Communications Act 2000
- U.S. - Uniform Electronic Transactions Act - adopted by 48 states
- U.S. - Digital Signature And Electronic Authentication Law
- U.S. - Government Paperwork Elimination Act (GPEA)
- U.S. - The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC)
[edit] Pseudo-legal use of imputed electronic signatures
| This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (July 2008) |
Some web sites and software EULAs contain terms that assert that various electronic and other actions give rise to legally effective signatures. For example, a web page might announce that, by accessing the site at all, you have agreed to a certain set of terms and conditions. A software product might assert, in its packaging or on an early installation screen, that by using it you have agreed to licensing terms. These may or may not have been discernible prior to sale, and may or may not be completely displayed even at installation. Such licenses often include such restrictions as a prohibition of reviewing the product for publication (electronic or otherwise) without prior permission of the publisher/distributor, or prohibition on studying the product (i.e., reverse engineering) for an otherwise lawful purpose such as producing data files in a compatible format. Some such claims would appear to be contrary to patent law (which requires public disclosure as a condition of granting a patent) or to copyright law which does the same for works available to the public, or to contract law which requires informed knowing assent to reasonable contract terms as a condition of enforceability in court. Only if all such covered matters are trade secrets would many such clauses appear sustainable, but even so a condition of trade secrecy is maintenance of the secret by the holder. This may not be met in the case of a widely distributed product offered for sale to anyone.
The legal status of such claims is uncertain. In the US, only two states have adopted a new revision of the Uniform Commercial Code which authorize such licensing restrictions, with disclosure after purchase. The validity of such terms remains uncertain, despite the views of many EULA authors. Analogies to the physical world in which contracts and signatures are written, signed, and stored in tangible form suggest that analogous terms would not be acceptable. In the UK, Regulation 9 of the Electronic Commerce Regulations 2002 (SI 2002/2013) requires that a purchaser is able to determine in advance “the different technical steps to follow to conclude the contract.”
[edit] Cryptographic signatures
| This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (July 2008) |
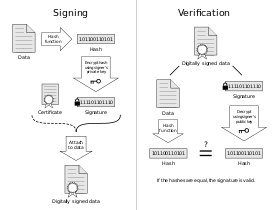
An electronic signature may incorporate a digital signature if it uses cryptographic methods to assure, at the least, both message integrity and authenticity. For example, a proposed contract accepted by a vendor and returned via email to the purchaser after being digitally signed. In fact, in modern practice, a digital signature of some text is always electronically processed in some sense, for the cryptographic mechanisms are impracticable without computers. In theory however, this is not required. Because of the use of message integrity mechanisms, any changes to a digitally signed document will be readily detectable if tested for, and the attached signature cannot then be taken as valid.
It is important to understand the cryptographic signatures are much more than an error checking technique akin to checksum algorithms, or even high reliability error detection and correction algorithms such as Reed-Solomon. These can offer no assurance that the text has not been tampered with, as all can be regenerated as needed by a tamperer. In addition, no message integrity protocols include error correction, for to do so would destroy the tampering detection feature.
Popular electronic signature standards include the OpenPGP standard supported by PGP and GnuPG, and some of the S/MIME IETF standards. All current cryptographic digital signature schemes require that the recipient have a way to obtain the sender's public key with assurances of some kind that the public key and sender identity properly belong together, and that message integrity measures (also digital signatures) which assure that neither the attestation nor the value of the public key can be surreptitiously changed. A secure channel is not typically required.
A digitally signed text may also be encrypted for protection during transmission, but this is not required when most digital signature protocols have been properly carried out. Confidentiality requirements will be the guiding consideration.
[edit] Digitally captured signatures
| This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (July 2008) |
An emerging form of electronic signatures is defined as “Biometric Signature” or “Dynamic Signature”. The term stands for handwritten signatures that are digitized throughout the writing process – including static characteristics and biometric (dynamic) signals”. Instead of replacing the handwritten signature these kind of e-signing solutions seek to transfer the signing ceremony into the digital world. “Biometric Signatures” require a hardware device for signature capturing and a software which is able to combine the signature data, encrypt it and allows to detect later manipulation by creating a hash value.
At the time when the first versions of electronic signature laws were created in the mid 90s this sort of technology was almost unknown. In 1999 the European Directive about a framework for electronic signatures opened a broader technological approach to electronic signatures. Law makers are gradually reflecting “biometric signatures” now as well.
A lot of digitized signatures today are taken with a low resolution. One example is the capturing devices that courier services are using. They capture a rather pixilated image of a signature that is usually not applicable for a later verification. Signatures taken on these devices may easily be claimed to be a forgery. Non-repudiation can only be achieved when the biometric characteristics of a signature are captured too, and when this information is securely bound to the signed document. The additional verification of dynamic signals offers a higher level in security. A signature with a similar image like the reference signature may be detected as falsification because differences in their creation characteristics are discovered.
In order to understand what is necessary to trust a signature it is important to keep in mind that forensic experts rely on the holistic analysis of signatures, i.e. they look at and take into account the paper features, type of stylus, the ink flow and “visible” pressure. Most forensic experts exposed to the analysis of dynamic signatures tend to forget to apply the same principles. The equivalent holistic approach for dynamic signatures must take into account which device was used for signature capture, the device features and maybe even the signing environment and the co-relations to the signing process.
Signatures may be digitized during the signing process instead of scanning them from paper using a wide range of instruments: pen pads (with and without LC display), special pens and Tablet PCs. They allow a gradual move from paper-based documentation to electronic forms and straight-through-processing as well as upgrading the quality of signature verification in general. A proper comparison of static signature characteristics and dynamic signature signals requires a digitizing instrument that is taking a sufficient amount of time signals. It also has to be able to differentiate between various pressure levels and to provide an appropriate resolution rate. These requirements are also reflected in the standard for the interchange of biometric signature data (ISO/IEC FDIS 19794-7).
- Forensic experts require precise information on the relation of force applied and pressure levels. Manufactures must make available this sort of “pressure curve chart” to vendors of signature verification software and to the forensic experts.
- A reliable capturing device has to record the same pressure levels in all segments of the capturing area with the same precision when the same force is being applied.
- When capturing signatures on different tablets of the same type from the same manufacturer signal data must not exceed a certain tolerance level, otherwise an analysis or verification would have to be adjusted to each device.
- The ergonomics of the writing tablet must reflect the typical signing situation and ideally provide for a “paper-like” surface (which imitates the writing feeling on paper as close as possible).
- The capturing technology must exclude the capturing of unwanted “overspill” information such as signals from a thumb ball that touched the capturing surface while signing.
- In addition, for non-repudiation, security and auditing purposes, the capturing device must provide a unique serial number, a device id number and trustworthy of the communication between device (firmware) and device driver (operating system).
[edit] Biometric signatures
| This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (August 2008) |
Another approach is to attach some biometric measurement to a document as evidence of signature. For instance, fingerprints or iris patterns or and geometry (finger lengths and palm size) or even retinal patterns. All of these are collected using electronic sensors of some kind. Since each of these physical characteristics has claims to uniqueness among humans, each is to some extent useful as a signature method. Unfortunately, each is easily spoofable by a replay of the electronic signal produced and submitted to the computer system responsible for 'affixing' a signature to a document. Wiretapping techniques often suffice. In the particular case of fingerprints, a Japanese professor and some graduate students managed to spoof all of the commercially available fingerprint readers available to them with some ordinary kitchen chemistry (gummy bear candy gel) and a little ingenuity. No actual fingers were needed to successfully spoof every reading device.
In addition, some German journalists at a CeBit conference were able to fool several iris pattern scanners with improvised masks.
Biometric measurements of this type are useless as passwords, as they can't be changed if compromised, but might be serviceable as electronic signatures of a kind except that, to date, they have been so easily spoofable that they can carry little assurance that the person who purportedly signed a document was actually the person who did.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ a b US ESIGN Act of 2000
- ^ The University of Virginia
- ^ State of WI
- ^ National Archives of Australia
- ^ See US Federal Rules of Evidence 1001, 1002, and 1003. Federal Rules of Evidence (LII 2006 ed.)
- ^ The History of eSign
- ^ http://www.asil.org/ilib/ilib0104.htm#04 International Law in brief
- ^ http://www.law.upenn.edu/bll/ulc/fnact99/1990s/ueta99.htm
- ^ http://www.nccusl.org/Update/uniformact_factsheets/uniformacts-fs-ueta.asp
- ^ Directive 1999/93/EC
- ^ Analysis of the ESIGN Act
[edit] Further reading
| This section may require cleanup to meet Wikipedia's quality standards. Please improve this section if you can. (May 2008) |
For books in English on electronic signatures, see:
- Stephen Mason (2007). Electronic Signatures in Law (2nd ed.). Haywards Heath: Tottel. ISBN 978-1-84592-425-6
- Dennis Campbell (Ed.) (2005). E-Commerce and the Law of Digital Signatures. Oceana Publications.
- Lorna Brazell (2004). Electronic Signatures Law and Regulation. Sweet & Maxwell.
- M. H. M Schellenkens (2004). Electronic Signatures Authentication Technology from a Legal Perspective. TMC Asser Press.
For journals on electronic signatures, see:
- Stephen Mason (Ed.). Digital Evidence and Electronic Signature Law Review. Includes translations of electronic signature cases from Europe, Brazil, China and Colombia into English.
[edit] External links
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of |
- Introduction to cryptography from the PGP international website
- OpenOffice Electronic Signatures and Security specification (OpenOffice format), also in pdf format. Incorporates standards for document format and XML Digital Signatures. Includes a comparison of document signature software and features from Adobe (Acrobat), Microsoft (Word) and Mozilla.
- E-Sign Final Report (2005, European Union)
- 21 CFR Part 11 Electronic Records; Electronic Signatures; Final Rule Electronic Submissions; Establishment of Public Docket; Notice - as published in the Federal Register / Vol. 62, No. 54 / Thursday, March 20, 1997
- Judicial Studies Board Digital Signature Guidelines