Eritrea
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| This article contains Ethiopic text. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, boxes, or other symbols instead of Ethiopic characters. |
| State of Eritrea
Hagere Ertra
ሃገረ ኤርትራ دولة إرتريا Dawlat Iritriya |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Anthem: Ertra, Ertra, Ertra |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Asmara |
|||||
| Official languages | Tigrinya[1] | |||||
| Demonym | Eritrean | |||||
| Government | Transitional government | |||||
| - | President | Isaias Afewerki | ||||
| Independence | ||||||
| - | from Italy | November 1941 | ||||
| - | from Ethiopia de facto | 24 May 1991 | ||||
| - | from Ethiopia de jure | 24 May 1993 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 117,600 km2 (100th) 45,405 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | negligible | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | July 2005 estimate | 4,401,009 (118th) | ||||
| - | 2002 census | 4,298,270 | ||||
| - | Density | 37/km2 (165th) 96/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $3.743 billion[2] | ||||
| - | Per capita | $748[2] | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2008 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $1.479 billion[2] | ||||
| - | Per capita | $295[2] | ||||
| HDI (2007) | ▬ 0.483 (low) (157th) | |||||
| Currency | Nakfa (ERN) |
|||||
| Time zone | EAT (UTC+3) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | not observed (UTC+3) | ||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Internet TLD | .er | |||||
| Calling code | 291 | |||||
| 1 | Working languages: Tigrigna, Arabic, English [2], [3]. | |||||
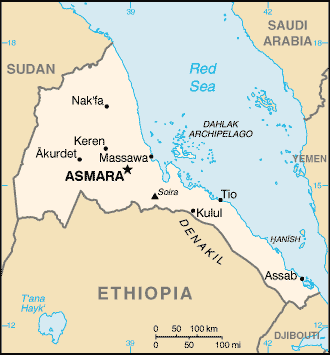
Eritrea (IPA: /ˌɛrɨˈtreɪə/, /ˌɛrɨˈtriːə/) (Ge'ez: ኤርትራ ʾErtrā, Arabic: إرتريا Iritriya), officially the State of Eritrea, is a country in Northeast Africa. It is bordered by Sudan in the west, Ethiopia in the south, and Djibouti in the southeast. The east and northeast of the country have an extensive coastline on the Red Sea, directly across from Saudi Arabia and Yemen. The Dahlak Archipelago and several of the Hanish Islands are part of Eritrea. Its size is just under 118,000 km² with an estimated population of 4,400,000. The capital is Asmara.
Italy conquered Eritrea and the Italian government formally consolidated it into a colony on January 1, 1890. In 1936 it became a province of Italian East Africa (Africa Orientale Italiana), along with Ethiopia and Italian Somaliland. The British expelled the Italians in 1941[3] and continued to administer the territory under a UN Mandate until 1951 when Eritrea was federated with Ethiopia as per UN resolution 390(A) adopted in December 1950.
Increasing unrest and resistance in Eritrea against the federation with Ethiopia eventually led to a decision by the Ethiopian government to annex Eritrea as its 14th province in 1962. An Eritrean independence movement formed in the early 1960s which later erupted into a 31-year long war against successive Ethiopian governments that ended in 1991. Following a UN supervised referendum in Eritrea dubbed UNOVER in which the Eritrean people overwhelmingly voted for independence from Ethiopia, Eritrea declared its independence and gained international recognition in 1993.[4] Eritrea is a single-party state - whilst its constitution, adopted in 1997, stipulates that the state is a presidential republic with a unicameral parliamentary democracy, it has yet to be implemented. According to the government[5], this is due to the prevailing border conflict with Ethiopia which began in May 1998. English is also used in all of the government's international communication and is the language of instruction in all education beyond the fifth grade.[6]
Contents |
[edit] Pre-History
One of the oldest hominids, representing a possible link between Homo erectus and an archaic Homo sapiens, was found in Buya (Eritrean Danakil) in 1995 by Italian scientists. The cranium was dated to over 1 million years old.[7] Furthermore, in 1999, the Eritrean Research Project Team, discovered some of the earliest remains of humans using tools to harvest marine resources. The site contained obsidian tools dated to the paleolithic era, over 125,000 years old.[8] Epipaleolithic or mesolithic cave paintings in central and northern Eritrea attest to early hunter-gatherers in this region. A US paleontologist, William Sanders of the University of Michigan, also discovered a possible missing link between ancient and modern elephants in the form of the fossilized remains of a pig-sized creature in Eritrea. The fossil which is 27 million years old pushes the origins of elephants and mastodons five million years further into the past and asserts that modern elephants originated in Africa. Also mixed with Arab, Indian,Caucasian, Egyptian.
[edit] Pre-colonial civilization
The oldest written reference to the territory now known as Eritrea is the chronicled expedition launched to the fabled Punt (or Ta Netjeru, meaning land of the Gods) by the Ancient Egyptians in the twenty-fifth century BC under Pharaoh Sahure. Later sources from the Pharaoh Hatshepsut in the fifteenth century BC present a more detailed portrayal of an expedition in search of frankincense. The geographical location of the missions to Punt is described as roughly corresponding to the southern west coast of the Red Sea. The name Eritrea is a rendition of the ancient Greek name Ερυθραία, Erythraía, the "Red Land" The earliest evidence of agriculture, urban settlement and trade in Eritrea was found in the western region of the country consisting of archeological remains dating back to 3500 BC in sites called the Gash group. Based on the archaeological evidence, there seems to have been a connection between the peoples of the Gash group and the civilizations of the Nile Valley namely Ancient Egypt and Nubia.[9]
In the highlands, in the capital city Asmara's suburbs, scores of ancient sites have been documented, including Sembel, Mai Chiot, Ona Gudo, Mai Temenai, Weki Duba, and Mai Hutsa. Mostly dating to the early and mid-1st millennium BCE (800 to 350 BCE), these communities consisted of small towns, villages, and hamlets built of stone. The proximity of these ancient communities to gold mines suggest that part of their prosperity was linked to the mining and processing of gold. Around the mid-1st millennium, several sites with Sabaean remains (inscriptions, artifacts, monuments, etc.) seem to emerge in the central highlands, for example, at Keskese. [10] Between the eighth and fifth century BCE, a kingdom known as D'mt was supposedly established in what is today Eritrea and northern Ethiopia (Tigray).[11][12][13] After D'mt's decline around the fifth century BC, the state of Aksum arose in much of Eritrea and the northern Ethiopian Highlands. It grew during the fourth century BC and came into prominence during the first century AD, minting its own coins by the third century, and converting in the fourth century to Christianity, thereby becoming the second official Christian state (after Armenia), and the first country to feature the cross on its coins. According to Mani, it grew to be one of the four greatest civilizations in the world, on a par with China, Persia, and Rome. In the seventh century, with the advent of Islam across the Red Sea in Arabia and the Arab invasion and subsequent destruction of Adulis, Aksum's trade and power on the Red Sea began to decline and the empire gradually diminished and was overtaken by smaller rival kingdoms.
During the medieval period, contemporary with and following the gradual disintegration of the Aksumite state between the 9th and 10th centuries, several states as well as tribal and clan lands emerged in the area known today as Eritrea. Between the eighth and thirteenth century, northern and northwestern Eritrea had largely come under the domination of the Beja, a Cushitic people from northeastern Sudan.[14] The Beja brought Islam to large parts of Eritrea and connected the region to the greater Islamic world. Christians of the Axumite era continued nonetheless to inhabit these areas and retain their religion. In the main highland area and adjacent coastline of what were previously Moslem (Beja) ruled areas, a Christian Kingdom called Midir Bahr or Midri Bahri (Tigrinya for land of the sea) arose, ruled by the Bahr negus or Bahr negash, ("ruler of the sea") emerged in the 15th century.[15] The southeastern parts of Eritrea, inhabited by the independent Afar since ancient times, came to form part of the Islamic sultanate of Adal in the early 13th century. Parts of the southwestern lowlands of Eritrea were under the dominion of the then Christian/animist Funj sultanate of Sinnar.
An invading force of the Turkish Ottoman Empire, under Suleiman I, conquered Massawa in 1557 from the Christians, building what is now considered the "old town" of Massawa on Batsi island. They also conquered the towns of Hergigo, and Debarwa, the capital city of the contemporary Christian Bahr negus (ruler), Yeshaq before being repulsed back to the coast by 1578. The Ottomans remained in control of the important ports of Massawa and Hergigo and their environs, and maintained their dominion over the coastal areas for nearly 300 years, absorbing the coastal areas of the disintegrated Adal sultanate as vassals in the 16th century. The Funj sultanate of Sinnar converted to Islam in the 16th century but maintained independent control of the southwestern areas of Eritrea until being absorbed into the Ottoman Empire in the early 19th century. With the feudal rule of the Bahr negash in the predominantly Christian highland interior severely weakened from the 17th century up until modern times, the area became dubbed Mereb Mellash by locals and neighboring Ethiopians alike, meaning "beyond the Mereb" (in Tigrinya). This name defined the territory as being north of the Mareb River which to this day is a natural boundary between the modern states of Eritrea and Ethiopia.[16] Roughly the same area also came to be referred to as Hamasien, a name that survived until modern times, designating a much smaller area (province) immediately surrounding the capital Asmara, until being absorbed into the new administrative divisions in 1994. In these areas, feudal authority was particularly weak or nonexistent, and the autonomy of the landowning peasantry was particularly strong; a kind of "Republic" was prevalent, governed by local customary laws legislated by elected elder's councils (shimagile). [17] In 1770, the Scottish researcher James Bruce describes Hamasien and Abyssinia as "different countries who are often fighting" (SUKE, p. 25).
[edit] Colonialism
Italian colonisation began arguably with the purchase of the locality of Assab by a Roman Catholic priest by the name of Giuseppe Sapetto acting on behalf of a Genovese shipping company called "Rubattino" who bought the land from the Afar Sultan of Obock (a vassal of the Ottomans) in 1869. This happened in the same year as the opening of the Suez Canal.[18] With the approval of the Italian parliament and King Umberto I of Italy (later succeeded by his son Victor Emmanuel III), the government of Italy bought the Rubattino company's holdings and expanded its possessions northward along the Red Sea coast toward and beyond Massawa, encroaching on and quickly expelling previous 'Egyptian' possessions but meeting stiffer resistance in the Eritrean highlands from the invading army of the Emperor Yohannes IV of Ethiopia.

[edit] Colonia "Primigenia"
Italy declared Eritrea a territory of Italy as of New Years Day 1890. The Kingdom of Italy ruled Eritrea from 1890 to 1941.
Approximately 100.000 Italian colonists settled during the 1930s in the Colonia Primigenia (as was called Eritrea by the Italians, meaning that they considered Eritrea their first and most important colony), mainly in Asmara.
Between 1936 and 1941, dictator Benito Mussolini briefly created the Italian Empire, with the short-lived union of Eritrea, Ethiopia and Italian Somaliland. Eritrea enjoyed considerable industrialization and development of modern infrastructure during Italian rule (such as roads and the Eritrean Railway).
The Italians remained the colonial power in Eritrea throughout the lifetime of fascism and the beginnings of World War II, when they were defeated by Allied forces in 1941, and Eritrea came under British administration.[18]
In the Peace Treaty of February 1947 Italy surrendered all her colonies, including Eritrea. While under British trusteeship, the United Nations decided after a lengthy inquiry regarding the status of Eritrea, to federate it with Ethiopia in 1950.[19]
[edit] Struggle for independence
Barely 10 years into the federation with Ethiopia, in 1961, the 30-year Eritrean Struggle for Independence began, following the Ethiopian Emperor Haile Selassie I's dissolution of the federation and shutting down of Eritrea's parliament.
The Emperor declared Eritrea the fourteenth province of Ethiopia in 1962.[20] Eritreans formed the Eritrean Liberation Front (ELF) and rebelled.
The ELF was initially a conservative grass-roots movement dominated by Muslim lowlanders and thus received backing from Arab socialist governments such as Syria and Egypt. Ethiopia's imperial government received support from the United States which had established a radio listening base (the Kagnew base) in Eritrea's Ethiopian-occupied capital, Asmara. Internal divisions within the ELF based on religion, ideology, ethnicity, clan and, sometimes, personalities, led to the weakening and factioning of the ELF from which sprung the Eritrean People's Liberation Front.

The EPLF professed Marxism and egalitarian values devoid of gender, religion, or ethnic bias. Its leadership was educated in China. It came to be supported by a growing Eritrean diaspora. Bitter fighting broke out between the ELF and EPLF during the late 1970s and 1980s for dominance over Eritrea. The ELF continued to dominate the Eritrean landscape well into the 1970s when the struggle for independence neared victory due to Ethiopia's internal turmoil caused by a socialist revolution against the monarchy there. The ELF's gains suffered when Ethiopia's ailing US-backed Emperor was deposed and replaced by the Derg, a Marxist military junta with backing from the Soviet Union and other communist countries, who continued the Ethiopian policy of repressing Eritrean "separatists" with increased military assistance and fervor. Nevertheless, the Eritrean resistance, which saw itself forced to retreat from most of the Eritrean countryside it had previously occupied, became instead entrenched in the northern parts of the country around the Sudanese border from where the most important supply lines came. The heavily bombarded and embattled northern town of Nakfa came to symbolize the Eritrean struggle. (The Eritrean currency is named after it.)[21] The numbers of the EPLF swelled in the 1980s. The EPLF relied largely on armaments captured from the Ethiopian army itself as well as financial and political support from the Eritrean diaspora and the cooperation of neighboring states hostile to Ethiopia's government Somalia and Sudan (although the support of the latter turned into hostility in agreement with Ethiopia during the Gaafar Nimeiry administration between 1971 and 1985) as well as Ethiopian resistance and separatist movements. Drought, famine, and intensive offensives launched by the Ethiopian army on Eritrea took a heavy toll on the population — more than half a million fled to Sudan as refugees. In 1985, Eritrean elite commandos infiltrated the Ethiopian- and Soviet-held air force base in Asmara and destroyed all 30 fighter jets there, suffering only one casualty. In 1988, a massive Ethiopian military offensive against Eritrean rebels backfired with a third of the Ethiopian army annihilated in the northern Eritrean town of Afabet.[22] Following the decline of the Soviet Union in 1989 and diminishing support for the Ethiopian war, Eritrean rebels advanced further, capturing the port of Massawa and putting the Ethiopian and Soviet naval capabilities there out of action. By 1990 and early 1991 virtually all Eritrean territory had been liberated by the EPLF except for the capital, whose only connection with the rest of government-held Ethiopia during the last year of the war was by an air-bridge. In 1991, the Ethiopian army finally capitulated and its leader Mengistu Hailemariam fled to Zimbabwe where he resides to this day. Eritrean rebels entered the capital Asmara and began to govern Eritrea on May 24, 1991. The new Ethiopian government consisting of a coalition of Ethiopian resistance and separatist movements allied with Eritrea's rebels, conceded to Eritrea's demands to have an internationally (UN) supervised referendum dubbed UNOVER to be held in Eritrea, which ended in April 1993 with an overwhelming vote by Eritreans for independence. Independence was declared on May 24, 1993.[23]
[edit] Independence
Upon Eritrea's declaration of independence, the leader of the EPLF, Isaias Afewerki, became Eritrea's first Provisional President, and the Eritrean People's Liberation Front (later renamed the People's Front for Democracy and Justice, or PFDJ) created a government.[24]
Faced with limited economic resources and a country shattered by decades of war, the government embarked on a reconstruction and defense effort, later called the Warsai Yikalo Program, based on the labour of national servicemen and women. It is still ongoing and deploys the enlisted into a combination of duties ranging from military service to construction projects, health care, teaching and training/education as well as agricultural work to improve the country's food security.[25]
The government also attempts to tap into the resources of the Eritreans living abroad by levying a 2% tax on the gross income of those who wish to gain full economic rights and access as citizens in Eritrea (land ownership, business licenses and other privileges for nationals etc),[26] while at the same time encouraging tourism and investment both from Eritreans living abroad and other foreign investors. This has been complicated by Eritrea's tumultuous relations with its neighbours, lack of stability and subsequent political problems.
Eritrea severed diplomatic relations with Sudan in 1994, citing that the latter was hosting Islamic terrorist groups to destabilize Eritrea, and both countries entered into an acrimonious relationship, each accusing the other of hosting various opposition rebel groups or "terrorists" and soliciting outside support to destabilize the other. Diplomatic relations were resumed in 2005 following a reconciliation agreement reached with the help of Qatar's negotiation in 1999.[27][28] Eritrea now plays a prominent role in the internal Sudanese peace and reconciliation effort.[29]
Perhaps the conflict with the deepest impact on independent Eritrea has been the renewed hostility with Ethiopia. In 1998, a border war with Ethiopia over the town of Badme occurred. The Eritrean-Ethiopian War ended in 2000 with a negotiated agreement known as the Algiers Agreement, which assigned an independent, UN-associated boundary commission known as the Eritrea-Ethiopia Boundary Commission (EEBC), whose task was to clearly identify the border between the two countries and issue a final and binding ruling. Along with the agreement the UN established a temporary security zone consisting of a 25-kilometre demilitarized buffer zone within Eritrea, running along the length of the disputed border between the two states and patrolled by UN troops in the mission named UNMEE. Ethiopia was to withdraw to positions held before the outbreak of hostilities in May 1998. The peace agreement would be completed with the implementation of the Border Commission's ruling, also ending the task of the peacekeeping mission of UNMEE. The EEBC's verdict came in April 2002, which awarded Badme to Eritrea. However, Ethiopia refused to withdraw its military from positions in the disputed areas, including Badme, and also refused to implement the EEBC's ruling, and the dispute is ongoing.[30]
Eritrea's diplomatic relations with Djibouti were briefly severed during the border war with Ethiopia in 1998 due to a dispute over Djibouti's intimate relation with Ethiopia during the war but were restored and normalized in 2000. [31] Relations are again tense due to a renewed border dispute.[32] Similarly, Eritrea and Yemen had a border conflict between 1996 to 1998 over the Hanish islands and the maritime border, which was resolved in 2000 by the Permanent Court of Arbitration in the Hague.
[edit] Regions and districts
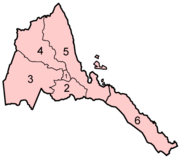
Eritrea is divided into six regions (zobas) and subdivided into districts ("sub-zobas"). The geographical extent of the regions is based on their respective hydrological properties. This a dual intent on the part of the Eritrean government: to provide each administration with sufficient control over its agricultural capacity, and to eliminate historical intra-regional conflicts.
The regions, followed by the sub-region, are:
| No. | Region (ዞባ) | Sub-region (ንኡስ ዞባ) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Central (ዞባ ማእከል) |
Berikh, Ghala-Nefhi, Semienawi Mibraq, Serejaka, Debubawi Mibraq, Semienawi Mi'erab, Debubawi Mi'erab |
| 2 | Southern (ዞባ ደቡብ) |
Adi Keyh, Adi Quala, Areza, Debarwa, Dekemhare, Mai Ayni, Mai Mne, Mendefera, Segeneiti, Senafe, Tserona |
| 3 | Gash-Barka (ዞባ ጋሽ ባርካ) |
Agordat, Barentu, Dghe, Forto, Gogne, Haykota, Logo-Anseba, Mensura, Mogolo, Molki, Guluj, Shambuko, Tesseney, La'elay Gash |
| 4 | Anseba (ዞባ ዓንሰባ) |
Adi Tekelezan, Asmat, Elabered, Geleb, Hagaz, Halhal, Habero, Keren City, Kerkebet, Sel'a |
| 5 | Northern Red Sea (ዞባ ሰሜናዊ ቀይሕ ባሕሪ) |
Afabet, Dahlak, Ghel'alo, Foro, Ghinda, Karura, Massawa, Nakfa, She'eb |
| 6 | Southern Red Sea (ዞባ ደቡባዊ ቀይሕ ባሕሪ) |
Are'eta, Central Dankalia, Southern Dankalia, Assab |
[edit] Politics and government

Eritrea is a single-party state, run by the People's Front for Democracy and Justice (PFDJ).[33] Other political groups are not allowed to organise, although the non-implemented Constitution of 1997 provided for the existence of multi-party politics. The National Assembly of 150 seats (of which 75 were occupied by EPLF). National elections have been periodically scheduled and cancelled; none have ever been held in the country.[34] Independent local sources of political information on Eritrean domestic politics are scarce; in September 2001 the government closed down all of the nation's privately owned print media, and outspoken critics of the government have been arrested and held without trial, according to various international observers, including Human Rights Watch and Amnesty International. In 2004 the U.S. State Department declared Eritrea a Country of Particular Concern (CPC) for its alleged record of religious persecution.[35]
[edit] National elections
Eritrean National elections were set for 1995 and then postponed until 2001; it was then decided that because 20% of Eritrea's land was under occupation, elections would be postponed until the resolution of the conflict with Ethiopia. However, local elections have continued in Eritrea. The most recent round of local government elections were held in May 2004. On further elections, the President's Chief of Staff, Yemane Ghebremeskel said,[36]
| “ | The electoral commission is handling these elections this time round so that may be the new element in this process. The national assembly has also mandated the electoral commission to set the date for national elections, so whenever the electoral commission sets the date there will be national elections. It's not dependent on regional elections. | ” |
[edit] Foreign relations
| The neutrality of this article is disputed. Please see the discussion on the talk page. Please do not remove this message until the dispute is resolved. (August 2008) |
Eritrea is a full member of the African Union (AU), the successor of the Organization of African Unity (OAU). But it has withdrawn its representative to the AU in protest of the AU's lack of leadership in facilitating the implementation of a binding border decision demarcating the border between Eritrea and Ethiopia. Eritrea's relationship with the United States is complicated. Although the two nations have a close working relationship regarding the on-going war on terror, there has been a growing tension in other areas. As of October 2008, relations with the US have worsened. US Assistant Secretary of State, Jendayi Frazer, has called the nation a 'state sponsor of terrorism' and the US government has added Eritrea to its list of rogue states, along with Iran and Cuba.[37] The reason for this is the presence of Sheikh Hassan Dahir Aweys, an exiled Somali Islamist leader, whom the US suspects of having links to Al Qaeda, at a recent Somali opposition conference in Asmara. Economic sanctions against Eritrea could soon follow.[38] Eritrea's relationship with Italy and the EU does not seem to be as strained as is its relationship with the U.S.. On 27 January 2009 the Netherlands Ambassador Yoka Brandt, Director General of International Development Cooperation, paid an official visit to the country for bilateral talks with President Isaias' government, which were held in Massawa.
Within the region, Eritrea's relations with Ethiopia turned from that of cautious mutual tolerance, following the 30-year war for Eritrean independence, to a deadly rivalry that led to the outbreak of renewed hostilities from May 1998 to June 2000 in which approximately 19,000 Eritreans[39] and 123,000 Ethiopians[40][41] were killed.
External issues include an undemarcated border with Sudan, a war with Yemen over the Hanish Islands in 1996, and a recent border conflict with Ethiopia.
The undemarcated border with Sudan poses a problem for Eritrean external relations.[42] After a high-level delegation to Sudan from the Eritrean Ministry of Foreign Affairs, ties are being normalized. Meanwhile, Eritrea has been recognized as a broker for peace between the separate factions of the Sudanese civil war. "It is known that Eritrea played a role in bringing about the peace agreement [between the Southern Sudanese and Government],"[43] while the Sudanese Government and Eastern Front rebels have requested Eritrea to mediate peace talks.[44]
A dispute with Yemen over the Hanish Islands in 1996 resulted in a brief war. As part of an agreement to cease hostilities the two nations agreed to refer the issue to the Permanent Court of Arbitration at the Hague in 1998.[45] Yemen was granted full ownership of the larger islands while Eritrea was awarded the peripheral islands to the southwest of the larger islands.[46] At the conclusion of the proceedings, both nations acquiesced to the decision. Since 1996 both governments have remained wary of one another but relations are relatively normal.[47]
The undemarcated border with Ethiopia is the primary external issue facing Eritrea. This led to a long and bloody border war between 1998 and 2000. As a result, the United Nations Mission in Ethiopia and Eritrea (UNMEE) is occupying a 25 kilometers by 900 kilometers area on the border to help stabilize the region.[48] Disagreements following the war have resulted in stalemate punctuated by periods of elevated tension and renewed threats of war.[49][50][51] Central to the continuation of the stalemate is Ethiopia's failure to abide by the border delimitation ruling and reneging on its commitment to demarcation. The stalemate has led the President of Eritrea to urge the UN to take action on Ethiopia. This request is outlined in the Eleven Letters penned by the President to the United Nations Security Council. The situation is further escalated by the continued effort of the Eritrean and Ethiopian leaders in supporting each other's opposition. On July 26, 2007, the Associated Press reported that Eritrea had been supplying weapons to the Somali insurgent group Al-Shabaab, which is allegedly tied to al Qaeda, but no evidence of this has been discovered. The incident has fueled concerns that Somalia may become the grounds for a de facto war between Eritrea and Ethiopia. Ethiopia invaded Somalia in December 2006 with U.S. assistance to overthrow the rule of the widely popular Islamic Courts Union (ICU), which had stabilized the country and unified the capital Mogadishu for the first time since 1991. Amid fears of an emerging Islamic and nationalist Somalia, Ethiopia with US assistance invaded Somalia, putting in place the weak and locally unpopular UN/AU-backed Transitional Federal Government, which without Ethiopian support had been unable to exercise any control beyond its base in Baidoa and along the Ethio-Somali border.[52] For its part, Eritrea is hosting members of the ousted Union of Islamic Courts and the Somali Free Parliament. The Eritrean government has been accused of sponsoring, arming and hosting numerous militant leaderships and separatist rebels in the horn of Africa.[53] According to the United States, Isaias's government is "sponsoring and supporting the rebel groups" who are "also attacking civilians and are a part of the problem in Darfur." Thus, even though the Eritrean government bringing these same rebels to the table is positive, the US claims that the Eritrean government is doing this "by effectively destabilizing Sudan, because they're paying for rebels who are part of the process of destabilizing that country."[54] According to Human Rights Watch(HRW), the Eritrean government was coercing the Somali Islamist opposition group Alliance for the Re-liberation of Somalia (ARS) so that the peace talks in Somalia will fail. In its report, HRW stated that:
"Eritrea's efforts to control the ARS and coerce its leaders into rejecting the idea of a negotiated peace were a primary reason that the mainstream core of the opposition alliance relocated to Djibouti in 2008. Eritrea continues to play host to a small breakaway faction of the ARS led by Sheikh Hassan Dahir Aweys and has reportedly continued to provide weapons and funds to abusive insurgent groups. One member of the ARS central committee in Djibouti told Human Rights Watch that, "Eritrea will make a maximum effort to make the [Djibouti peace] agreement fail."[55]
[edit] Criticisms
In 2008 Reporters Without Borders ranked Eritrea last at number 169,[56][57] unseating the previous record holder North Korea which had been last every other year of the survey. Reporters Without Borders claims that in Eritrea, private newspapers have been shut down and generally exorcised from the country by the President Isaias Afewerki. Also, any journalists who criticize the president or his regime are immediately put into prison; among the many reporters and writers who have been jailed, four may have died in detention.[56]
[edit] Geography
Eritrea is located in Northeast Africa, more specifically in the Horn of Africa, and is bordered on the northeast and east by the Red Sea. The country is virtually bisected by one of the world's longest mountain ranges, the Great Rift Valley, with fertile lands to the west, descending to desert in the east. Eritrea, at the southern end of the Red Sea is the home of the fork, in the rift. The Dahlak Archipelago and its fishing grounds are situated off the sandy and arid coastline. The land to the south, in the highlands, is slightly drier and cooler.
The Afar Triangle or Danakil Depression of Eritrea is the probable location of a triple junction where three tectonic plates are pulling away from one another: the Arabian Plate, and the two parts of the African Plate (the Nubian and the Somali plate) splitting along the East African Rift Zone (USGS). The highest point of the country, Emba Soira, is located in the center of Eritrea, at 9,902 ft (3,018 metres ) above sea level.
The main cities of the country are the capital city of Asmara and the port town of Asseb in the southeast, as well as the towns of Massawa to the east, and Keren to the north.
[edit] Environment
Eritrea formerly supported a large population of elephants. Ptolemaic kings of Egypt used it as a source of war elephants in the third century BC. Between 1955 and 2001 there were no reported sightings of elephant herds, and they are thought to have fallen victim to the war of independence. In December 2001 a herd of about 30, including 10 juveniles, was observed in the vicinity of the Gash River. The elephants seemed to have formed a symbiotic relationship with olive baboons. It is estimated that there are around 100 elephants left in Eritrea, the most northerly of East Africa's elephants.[58]
In 2006, Eritrea announced it would become the first country in the world to turn its entire coast into an environmentally protected zone. The 1,347 km (837 mile) coastline, along with another 1,946 km (1,209-miles) of coast around its more than 350 islands, will come under governmental protection.
[edit] Economy

Like the economies of many other African nations, the economy is largely based on subsistence agriculture, with 80% of the population involved in farming and herding. The only natural disaster that sometimes affects Eritrea, drought, has often created trouble in the farming areas.[59]
The Eritrean-Ethiopian War severely hurt Eritrea's economy. GDP growth in 1999 fell to less than 1%, and GDP decreased by 8.2% in 2000. In May 2000, Ethiopian offensive into southern Eritrea caused some $600 million in property damage and loss, including losses of $225 million in livestock and 55,000 homes. The attack prevented planting of crops in Eritrea's most productive region, causing food production to drop by 62%.[60][61]
Even during the war, Eritrea developed its transportation infrastructure, asphalting new roads, improving its ports, and repairing war-damaged roads and bridges as a part of the Warsay Yika'alo Program. The most significant of these projects was the building of a coastal highway of more than 500 km connecting Massawa with Asseb as well as the rehabilitation of the Eritrean Railway. The rail line now runs between the Port of Massawa and the capital Asmara.
Eritrea's economic future remains mixed. The cessation of Ethiopian trade, which mainly used Eritrean ports before the war, leaves Eritrea with a large economic hole to fill. Eritrea's economic future depends upon its ability to master fundamental social problems like illiteracy, and low skills.
As of May 6, 2008 Eritrea is the most expensive place in the world to buy fuel. At $9.58 per gallon, gasoline is 85¢ a gallon higher than in the next most expensive country, Norway.[62]
[edit] Society
[edit] Demographics

Eritrean society is ethnically heterogeneous. An independent census has yet to be conducted, but the Tigrinya people and the Tigre people together make up about 80% of the population. These form the bulk of the country's predominantly Semitic-speaking population.
The rest of the population is from other Afro-Asiatic groups such as the Saho, Hedareb, Afar, and Bilen. These Cushitic-speaking peoples are thought to be the oldest inhabitants of the Horn of Africa.
There are also a number of Nilotic peoples who are represented in Eritrea by the Kunama and Nara.
Each ethnicity speaks a different native tongue but, typically, many of the minorities speak more than one language.
There exist minorities of Italian Eritreans (concentrated in Asmara) and Ethiopian Tigrayans. Neither is generally given citizenship unless through marriage or, more rarely, by having it conferred upon them by the State.
The most recent addition to the nationalities of Eritrea is the Rashaida. The Rashaida came to Eritrea in the 19th century[63] from the Arabian Coast. The Rashaida intermarried with the Tigre and Beja clans, and are typically nomadic, and number approximately 61,000, less than 1% of the population.
Ethnic groups with low population have little influence on life in Eritrea.
[edit] Languages

Many languages are spoken in Eritrea today.There is no official language as such, but Tigrinya and Arabic are the two predominant languages for official purposes. Italian and English are also widely understood.[64] Most of the languages spoken in Eritrea stem from the Semitic and Cushitic branches of the Afro-Asiatic language family. The Semitic languages in Eritrea are Arabic (spoken natively by the Rashaida Arabs), Tigre, Tigrinya, and the newly recognized Dahlik; these languages (primarily Tigre and Tigrinya) are spoken as a first language by over 80% of the population. The Cushitic languages in Eritrea are just as numerous, including Afar, Beja, Blin, and Saho. Kunama and Nara are also spoken in Eritrea and belong to the Nilo-Saharan language family. English is spoken to a degree by more educated Eritreans and a legacy of British occupation. Italian is a legacy of colonial times.
[edit] Education
There are five levels of education in Eritrea: pre-primary, primary, middle, secondary, and post-secondary. There are nearly 238,000 students in the primary, middle, and secondary levels of education. There are approximately 824 schools[65] in Eritrea and two universities (University of Asmara and the Institute of Science and Technology) as well as several smaller colleges and technical schools.
One of the most important goals of Eritrea's education policy is to provide basic education in each of Eritrea's mother tongues, as well as to develop a self-motivated and conscientious population to fight poverty and disease. Furthermore it is tooled to produce a society that is equipped with the necessary skills to function in the modern economy.
The education system in Eritrea is also designed to promote private sector schooling, equal access for all groups (i.e., to prevent gender discrimination, ethnic discrimination, and class discrimination, etc.) and promote continuing education, both formally and informally.
Education in Eritrean include kindergartens for young children of both genders.
Barriers to education in Eritrea include traditional taboos, school fees (for registration and materials), and the opportunity costs of low-income households.[66]
[edit] Religion

Eritrea has two dominant religions, Islam and Christianity, with approximately half of the population belonging to each faith. Most Muslims follow Sunni Islam. The Christians consist primarily of the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahdo Church, which is the local Oriental Orthodox church, and considerable groups of Roman Catholics (including Italian Eritreans), Protestants, and other denominations also exist.
Since May 2002, the Government of Eritrea has officially recognized the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahdo Church, Sunni Islam, Catholicism, and the Evangelical Lutheran church. All other faiths and denominations are required to undergo a registration process.[citation needed] Among other things, the Government's registration system requires religious groups to submit personal information on their membership to be allowed to worship.[citation needed] The few organisations that have met all of the registration requirements have still not received official recognition.[citation needed]
Jehovah's Witnesses, Bahá'í Faith, the Seventh-day Adventist Church, and numerous Protestant denominations are not registered and cannot worship freely. They have effectively been banned, and measures have been taken against their adherents. Many have been incarcerated for months or even years. None have been charged officially or given access to the judicial process. In its 2006 religious freedom report, the U.S. State Department for the third year in a row named Eritrea a "Country of Particular Concern", designating it one of the worst violators of religious freedom in the world.[67]
There is one last native Jew in Eritrea, formerly from a community of hundreds in Asmara, whose ancestors had crossed from Aden in the late 19th century.[68][69]
[edit] Culture
The Eritrean region has traditionally been a nexus for trade throughout the world. Because of this, the influence of diverse cultures can be seen throughout Eritrea. Today, the most obvious influences in the capital, Asmara, are those of Italy. Throughout Asmara, there are small cafes serving beverages common to Italy. In Asmara, there is a clear merging of the Italian colonial influence with the traditional Tigrinya lifestyle. In the villages of Eritrea, these changes never took hold.
In the cities, before the occupation and during the early years, the import of Bollywood films was commonplace, while Italian and American films were available in the cinemas as well. In the 1980s and since independence, however, American films have become the most common. Vying for market share are films by local producers, who have slowly come into their own. The global broadcast of Eri-TV has brought cultural images to the large Eritrean population in the Diaspora who frequents the country every summer. Successful domestic films are produced by government and independent studios with revenue from ticket sales typically covering the production costs.
Traditional Eritrean dress is quite varied, with the women of most lowland ethnicities traditionally dressing in brightly colored clothes, while the Tigrinya traditionally dress in bright white costumes. Of the Muslim ethnicities, only the Arab or Rashaida tribeswomen maintain a tradition of covering their faces.
Popular sports in Eritrea are football and bicycle racing. In recent years Eritrean athletes have seen increasing success in the international arena.
Almost unique on the African continent, is the Tour of Eritrea, whose first race was created by the Italians in 1946.[70] The Tour is a bicycle race from the hot desert beaches of Massawa, up the winding mountain highway with its precipitous valleys and cliffs to the capital Asmara. From there, it continues downwards onto the western plains of the Gash-Barka Zone, only to return back to Asmara from the south. This is, by far, the most popular sport in Eritrea.
Recently long-distance running has garnered its own supporters. The momentum for long-distance running in Eritrea can be seen in the successes of Zersenay Tadese, who won a bronze medal for Eritrea in the 2004 Olympics, and Mebrahtom (Meb) Keflezighi, also an Olympian of Eritrean descent competing for the United States.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ The new book of knowledge- Grolier, volume "E". Article- Eritrea.
- ^ a b c d "Eritrea". International Monetary Fund. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2008/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2004&ey=2008&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=643&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=&pr.x=45&pr.y=15. Retrieved on 2008-10-09.
- ^ Eritrea Regions
- ^ "Eritrea – The spreading revolution". Encyclopædia Britannica Article. http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-37675/Eritrea. Retrieved on 2007-10-16.
- ^ http://www.parade.com/dictators/2008/slideshows/isayas-afewerki/05.html
- ^ "Country Profile:EritreaPDF (128 KiB). Library of Congress. Retrieved 18 July 2006
- ^ Abbate, Ernesto; Albianelli, Andrea; Azzaroli, Augusto; Benvenuti, Marco; Tesfamariam, Berhane; Bruni, Piero; Cipriani, Nicola; Clarke, Ronald J.; Ficcarelli, Giovanni; Macchiarelli, Roberto; Napoleone, Giovanni; Papini, Mauro; Rook, Lorenzo; Sagri, Mario; Tecle, Tewelde Medhin; Torre, Danilo; Villa, Igor (4 June 1998). "A one-million-year-old Homo cranium from the Danakil (Afar) Depression of Eritrea". Nature 393: 458–460. doi:.
- ^ "Out of Africa". 1999-09-10. http://exn.ca/hominids/outofafrica.cfm. Retrieved on 2006-10-02.
- ^ Fattovich, Rodolfo (PDF). The development of urbanism in the northern Horn of Africa in ancient and medieval times. http://hometown.aol.com/_ht_a/skipbdahlgren/sdahlgren/fattowich.pdf. Retrieved on 2006-10-24.
- ^ Peter Schmidt, Matthew Curtis, and Zelalem Teka, The Ancient Ona Communities of the First Millennium BCE: Urban Precursors and Independent Development on the Asmara Plateau. In The Archaeology of Ancient Eritrea, eds. P. R. Schmidt, M. C. Curtis, and Z. Teka. Trenton NJ: Red Sea Press, 2008, pp. 109-162.
- ^ Matthew Curtis, New Perspectives for Examining Change and Complexity in the Northern Horn of Africa during the First Millennium BCE. In The Archaeology of Ancient Eritrea, eds. P. R. Schmidt, M. C. Curtis, and Z. Teka. Trenton, NJ: Red Sea Press, 2008, pp. 329-348.
- ^ Stuart Munro-Hay, Aksum: An African Civilization of Late Antiquity. Edinburgh: University Press, 1991, pp.57.
- ^ Taddesse Tamrat, Church and State in Ethiopia: 1270-1527 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1972), pp.5-13.
- ^ http://american.edu/ted/ice/eritrea.htm
- ^ Daniel Kendie, The Five Dimensions of the Eritrean Conflict 1941 – 2004: Deciphering the Geo-Political Puzzle (United States of America: Signature Book Printing, 2005), pp. 17-8.
- ^ Daniel Kendie, The Five Dimensions of the Eritrean Conflict
- ^ Dennis J. Duncanson Sir'at 'Adkeme Milga'. A Native Law Code of Eritrea
- ^ a b "Eritrea – Contesting for the coastlands". Encyclopædia Britannica Article. http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-37666/Eritrea. Retrieved on 2007-10-16.
- ^ "General Assembly Resolutions 5th Session". United Nations. http://www.un.org/documents/ga/res/5/ares5.htm. Retrieved on 2007-10-16.
- ^ Semere Haile The Origins and Demise of the Ethiopia-Eritrea Federation Issue: A Journal of Opinion, Vol. 15, 1987 (1987), pp. 9-17
- ^ Killion, Tom (1998). Historical Dictionary of Eritrea. ISBN 0-8108-3437-5.
- ^ Worthington, Peter. "Needless war engulfs a unique African oasis". Toronto Sun.
- ^ Eritrea - MSN Encarta
- ^ http://www.dehai.org/conflict/history/birth_of_a_nation.htm#Referendum_Results
- ^ Warsai-Yikalo Campaign for Radical Development Change
- ^ Eritrea
- ^ Sudan-Eritrea: Reconciliation Agreement Signed, 5/3/99
- ^ Sudan, Eritrea resume severed diplomatic relations
- ^ allAfrica.com: East Africa: Darfur And Somalia - Two Peace Efforts, Different Strokes (Page 1 of 3)
- ^ Eritrea-Ethiopia Conflict Information Page
- ^ Djibouti - Foreign policy
- ^ http://uk.reuters.com/article/latestCrisis/idUKL1261733920080612
- ^ "Country profile: Eritrea". BBC News. 2008-06-17. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/country_profiles/1070813.stm. Retrieved on 2008-07-01.
- ^ "Government - overview". World Factbook. CIA. 2008-07-24. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/er.html#Govt. Retrieved on 2008-08-06.
- ^ "2005 Executive Summary". International Religious Freedom Report. Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights and Labor. 2005-11-08. http://www.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2005/51386.htm. Retrieved on 2008-08-06.
- ^ "Interview of Mr. Yemane Gebremeskel, Director of the Office of the President of Eritrea". PFDJ. 2004-04-01. http://www.shaebia.org/cgi-bin/artman/exec/view.cgi?archive=9&num=2618&printer=1. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ "Embargoed Countries". US Department of State. October 6, 2008. http://pmddtc.state.gov/embargoed_countries/index.html.
- ^ "How Eritrea fell out with the west". BBC. 2007-09-11. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/6987916.stm. Retrieved on 2007-09-12.
- ^ "Eritrea reveals human cost of war". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/1398446.stm.
- ^ Claimed on 8 April 2002 by the Voice of the Democratic Path of Ethiopian Unity, an Ethiopian clandestine opposition group operating from Germany. The claim also stated that each family that lost a member in the war would receive $350 in indemnity, but this number has not been verified, although it has been often cited by other groups (see Number of war dead soldiers reportedly 123,000 – internet news message; and clandestineradio.com audio button), and no indemnities have been paid as of 2007[update]. Shinn, Historical Dictionary of Ethiopia, p. 149
- ^ "Ethiopia: Number of war dead soldiers reportedly 123,000" (in Amharic). Wonchif. 2001-04-10.
- ^ "Eritrea-Sudan relations plummet". BBC. 2004-01-15. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/3400575.stm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ "Turabi terms USA "world's ignoramuses", fears Sudan's partition". Sudan Tribune. 2005-11-04. http://www.sudantribune.com/article.php3?id_article=12393. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ "Sudan demands Eritrean mediation with eastern Sudan rebels". Sudan Tribune. 2006-04-18. http://www.sudantribune.com/article.php3?id_article=15117. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ PCA - Documents: Eritrea-Yemen Award - CHAPTER I
- ^ "International Maritime Boundary". http://www.pca-cpa.org/PDF/chart3.gif. Retrieved on 2006-07-17.
- ^ "Flights back on between Yemen and Eritrea". BBC. 1998-12-13. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/192667.stm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ "Q&A: Horn's bitter border war". BBC. 2005-12-07. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/4041073.stm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ "Horn tensions trigger UN warning". BBC. 2004-02-04. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/3457957.stm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ "Army build-up near Horn frontier". BBC. 2005-11-02. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/4400580.stm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ "Horn border tense before deadline". BBC. 2005-12-23. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/4555892.stm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ ""U.N.: Eritrea giving arms to Somalis tied to al Qaeda"". CNN. 2007-07-26. http://edition.cnn.com/2007/WORLD/africa/07/26/somalia.arms.ap/index.html. Retrieved on 2007-08-04.
- ^ Accounts of rebels in Eritrea
- ^ Eritrea's role in Sudan criticized by America
- ^ HRW report on Somalia: Eritrea, Ethiopia roles
- ^ a b Reporters sans frontières - Annual Worldwide Press Freedom Index - 2007
- ^ [1]
- ^ "The rediscovery of Eritrea's elephants". BBC Wildlife Magazine. July 2003. http://www.bbc.co.uk/nature/animals/features/300feature1.shtml. Retrieved on 2007-07-28.
- ^ An Environmental Impact Assessment of African Armyworm Control in Eritrea: An Amendment to the "Eritrean Supplemental Environmental Assessment For Grasshopper And Locust Control".
- ^ "Economy - overview". CIA. 2006-06-06. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/er.html#Econ. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ "Aid sought for Eritrean recovery". BBC. 2001-02-22. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/1184714.stm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ "U.S. gas: So cheap it hurts". CNN Money. 2008-05-06. http://money.cnn.com/2008/05/01/news/international/usgas_price/index.htm?cnn=yes. Retrieved on 2008-05-20.
- ^ Alders, Anne. "the Rashaida". http://www.eritreanbeauty.com/r.html. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- ^ Languages of Eritrea - Tigrinya
- ^ Baseline Study on Livelihood Systems in Eritrea. National Food Information System of Eritrea. 2005.
- ^ Kifle, Temesgen (2002). Educational Gender Gap in Eritrea.
- ^ "Eritrea. International Religious Freedom Report 2008". U.S. Department of State. Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor. http://www.state.gov/g/drl/rls/irf/2008/108367.htm. Retrieved on 2008-11-08.
- ^ "Asmara's last Jew recalls 'good old days'". BBC. 2006-04-30. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/africa/4955088.stm. Retrieved on 2006-09-26.
- ^ "Eritrea's last native Jew tends graves, remembers". Y Net News. 2006-05-02. http://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-3246419,00.html. Retrieved on 2006-09-26.
- ^ http://www.maitacli.it/arg_menu/Sport/Ciclismo/giro_di_vita.htm The first Tour of Eritrea (in italian)
[edit] Further reading
- Ancient Ethiopia, David W. Phillipson (1998)
- Cliffe, Lionel; Connell, Dan; Davidson, Basil (2005), Taking on the Superpowers: Collected Articles on the Eritrean Revolution (1976-1982). Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-188-0
- Cliffe, Lionel & Davidson, Basil (1988), The Long Struggle of Eritrea for Independence and Constructive Peace. Spokesman Press, ISBN 0-85124-463-7
- Connell, Dan (1997), Against All Odds: A Chronicle of the Eritrean Revolution With a New Afterword on the Postwar Transition. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-046-9
- Connell, Dan (2001), Rethinking Revolution: New Strategies for Democracy & Social Justice : The Experiences of Eritrea, South Africa, Palestine & Nicaragua. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-145-7
- Connell, Dan (2004), Conversations with Eritrean Political Prisoners. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-235-6
- Connell, Dan (2005), Building a New Nation: Collected Articles on the Eritrean Revolution (1983-2002). Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-198-8
- Daniel Kendie (2005), The Five Dimensions Of The Eritrean Conflict 1941 - 2004: Deciphering the Geo-Political Puzzle. Signature Book Printing, ISBN 1-932433-47-3
- Firebrace, James & Holand, Stuart (1985), Never Kneel Down: Drought, Development and Liberation in Eritrea. Red Sea Press, ISBN 0-932415-00-8
- Hatem Elliesie: Decentralisation of Higher Education in Eritrea, Afrika Spectrum, Vol. 43 (2008) No. 1, p. 115-120.
- Jordan Gebre-Medhin (1989), Peasants and Nationalism in Eritrea. Red Sea Press, ISBN 0-932415-38-5
- Hill, Justin (2002), 'Ciao Asmara, A classic account of contemporary Africa'. Little, Brown, ISBN 978-0349115269
- Iyob, Ruth (1997), The Eritrean Struggle for Independence : Domination, Resistance, Nationalism, 1941-1993. Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-59591-6
- Jacquin-Berdal, Dominique; Plaut, Martin (2004), Unfinished Business: Ethiopia and Eritrea at War. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-217-8
- Johns, Michael (1992), "Does Democracy Have a Chance", Congressional Record, May 6 1992
- Keneally, Thomas (1990), "To Asmara" ISBN 0446391719
- Killion, Tom (1998), Historical Dictionary of Eritrea. Scarecrow Press, ISBN 0-8108-3437-5
- Mauri, Arnaldo (2004), "Eritrea's Early Stages oin Monetary and Banking Development", International Review of Economics, Vol. LI, n. 4.
- Müller, Tanja R.: Bare life and the developmental State: the Militarization of Higher Education in Eritrea, Journal of Modern African Studies, Vol. 46 (2008), No. 1, p. 1-21.
- Wrong, Michela (2005), I Didn't Do It For You: how the world betrayed a small African Nation. Harper Collins, ISBN 0-06-078092-4
- Ogbaselassie, G (2006-01-10). "Response to remarks by Mr. David Triesman, Britain's parliamentary under-secretary of state with responsibility for Africa". http://eri24.com/Article_10043.htm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- Pateman, Roy (1998), Eritrea: Even the Stones Are Burning. Red Sea Press, ISBN 1-56902-057-4
- Rena, Ravinder (2006-01-12). "Student-Centered Education is the Best Way of Learning". http://eri24.com/Article_10045.htm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- "Eritrea-Ethiopia versus western nations". 2005-12-09. http://eri24.com/Article_10031.htm. Retrieved on 2006-06-07.
- Mauri, Arnaldo (1998), "The First Monetary and Banking Experiences in Eritrea", African Review of Money, Finance and Banking, n. 1-2.
[edit] External links
![]() Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks
![]() Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote
![]() Source texts from Wikisource
Source texts from Wikisource
![]() Images and media from Commons
Images and media from Commons
![]() News stories from Wikinews
News stories from Wikinews
- Government
- Ministry of Information of Eritrea official website
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- General information
- Eritrea entry at The World Factbook
- Eritrea from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Eritrea at the Open Directory Project
- Wikimedia Atlas of Eritrea
- Eritrea travel guide from Wikitravel
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||