Colombia
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Republic of Colombia
República de Colombia (Spanish)
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: "Libertad y Orden" (Spanish) "Liberty and Order" |
||||||
| Anthem: "Oh, Gloria Inmarcesible!" (Spanish) |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Bogotá |
|||||
| Official languages | Spanish | |||||
| Recognised regional languages | The languages and dialects of ethnic groups are also official in their territories[1] | |||||
| Ethnic groups | 58% mestizo, 20% white, 14% mulatto, 4% black, 3% zambo, 1% Amerindian[2] | |||||
| Demonym | Colombian | |||||
| Government | Presidential republic | |||||
| - | President | Álvaro Uribe Vélez | ||||
| - | Vice President | Francisco Santos | ||||
| - | President of Congress | Hernán Andrade | ||||
| - | President of the Supreme Court | Francisco Ricaurte | ||||
| Independence | from Spain | |||||
| - | Declared | July 20, 1810 | ||||
| - | Recognized | August 7, 1819 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 1,141,748 km2 (26th) 440,839 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 8.8 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | January 2009 estimate | 44,760,630 (29th) | ||||
| - | 2005 census | 42,888,592 | ||||
| - | Density | 40/km2 (168th) 104/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $378.624 billion[3] (28th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $7,968[3] (82nd) | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2007 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $202.630 billion[3] (37th) | ||||
| - | Per capita | $4,264[3] (82nd) | ||||
| Gini (2006) | 52 (high) | |||||
| HDI (2008) | ▼ 0.787 (medium) (80th) | |||||
| Currency | Peso (COP) |
|||||
| Time zone | (UTC-5) | |||||
| Drives on the | right | |||||
| Internet TLD | .co | |||||
| Calling code | 57 | |||||
Colombia (IPA: /kəˈlʌmbɪə/), officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish: República de Colombia, Spanish pronunciation: [reˈpuβlika ðe koˈlombja]), is a country in north-western South America. Colombia is bordered to the east by Venezuela[4] and Brazil;[5] to the south by Ecuador and Peru;[6] to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the north west by Panama; and to the west by the Pacific Ocean. Colombia also shares maritime borders with Jamaica, Haiti, the Dominican Republic, Honduras, Nicaragua and Costa Rica.[7][8] Colombia is the 26th largest nation in the world and the fourth largest in South America (after Brazil, Argentina, and Peru). It has the 29th largest population in the world and the second largest in South America, after Brazil. Colombia has the third largest Spanish-speaking population in the world after Mexico and Spain.
The territory of what is now Colombia was originally inhabited by indigenous tribes including the Muisca, Quimbaya, and Tairona. The Spanish arrived in 1499 and initiated a period of conquest and colonisation which ultimately led to the creation of the Viceroyalty of New Granada (comprising modern-day Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador and Panama) with its capital at Bogotá.[9] Independence from Spain was won in 1819, but by 1830 "Gran Colombia" had collapsed with the secession of Venezuela and Ecuador. What is now Colombia and Panama emerged as the Republic of New Granada. The new nation experimented with federalism as the Granadine Confederation (1858), and then the United States of Colombia (1863), before the Republic of Colombia was finally declared in 1886.[2]Panama seceded in 1903.
Colombia has a long tradition of constitutional government, and the Liberal and Conservative parties, founded in 1848 and 1849 respectively, are two of the oldest surviving political parties in the Americas. However, tensions between the two have frequently erupted into violence, most notably in the Thousand Days War (1899-1902) and La Violencia, beginning in 1948. Since the 1960s, government forces, left-wing insurgents and right-wing paramilitaries have been engaged in the continent's longest-running armed conflict. Fuelled by the cocaine trade, this escalated dramatically in the 1990s. However, the insurgents lack the military or popular support necessary to overthrow the government, and in recent years the violence has been decreasing. Many paramilitary groups have demobilised as part of a controversial peace process with the government, and the guerrillas have lost control in many areas where they once dominated.[2] Meanwhile Colombia's homicide rate, for many years the highest in the world, has almost halved since 2002.[10]
Colombia is a standing middle power[11] with the fourth largest economy in South America. It is very ethnically diverse, and the interaction between descendants of the original native inhabitants, Spanish colonists, African slaves and twentieth-century immigrants from Europe and the Middle East has produced a rich cultural heritage. This has also been influenced by Colombia's varied geography. The majority of the urban centres are located in the highlands of the Andes mountains, but Colombian territory also encompasses Amazon rainforest, tropical grassland and both Caribbean and Pacific coastlines. Ecologically, Colombia is one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries.
Contents |
[edit] Etymology
The word "Colombia" comes from the name of Christopher Columbus (Italian: Cristoforo Colombo, Spanish: Cristóbal Colón). It was conceived by the revolutionary Francisco de Miranda as a reference to all the New World, but especially to those territories and colonies under Spanish and Portuguese rule. The name was later adopted by the Republic of Colombia of 1819, formed out of the territories of the old Viceroyalty of New Granada (modern day Colombia, Panama, Venezuela and Ecuador).[12]
In 1830, when Venezuela and Ecuador broke away, the Cundinamarca region that remained became a new country — the Republic of New Granada. In 1858 New Granada officially changed its name to the Granadine Confederation, then in 1863 the United States of Colombia, before finally adopting its present name — the Republic of Colombia — in 1886.[12]
[edit] Geography
Colombia is the 26th largest nation in the world and the fourth largest in South America. It is bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by Panama and the Caribbean Sea; and to the west by the Pacific Ocean. Colombia is the only country in South America to touch both Atlantic and Pacific oceans.
Part of the Pacific Ring of Fire, a region of the world subject to earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, Colombia is dominated by the Andes mountains. Beyond the Colombian Massif (in the south-western departments of Cauca and Nariño) these are divided into three branches known as cordilleras (from the Spanish for "rope"): the Cordillera Occidental, running adjacent to the Pacific coast and including the city of Cali; the Cordillera Central, running between the Cauca and Magdalena river valleys (to the west and east respectively) and including the cities of Medellín, Manizales and Pereira; and the Cordillera Oriental, extending north east to the Guajira Peninsula and including Bogotá, Bucaramanga and Cúcuta. Peaks in the Cordillera Occidental exceed 13,000 ft (4,000 m), and in the Cordillera Central and Cordillera Oriental they reach 18,000 ft (5,500 m).[13] At 8,500 ft (2,600 m), Bogotá is the highest city of its size in the world.
East of the Andes lies the savanna of the Llanos, part of the Orinoco River basin, and, in the far south east, the jungle of the Amazon rainforest. Together these lowlands comprise over half Colombia's territory, but they contain less than 3% of the population. To the north the Caribbean coast, home to 20% of the population and the location of the major port cities of Barranquilla and Cartagena, generally consists of low-lying plains, but it also contains the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta mountain range, which includes the country's tallest peaks (Pico Cristóbal Colón and Pico Simón Bolívar), and the Guajira Desert. By contrast the narrow and discontinuous Pacific coastal lowlands, backed by the Serranía de Baudó mountains, are covered in dense vegetation and sparsely populated. The principal Pacific port is Buenaventura.
Colombian territory also includes a number of Caribbean and Pacific islands.
[edit] Climate

The climate of Colombia is primarily determined by its proximity to the equator, with tropical and isothermal climate predominating. Other influences are the trade winds and the effect of the Intertropical Convergence Zone on precipitation. Colombia is also affected by the El Niño and La Niña phenomena.
Temperatures generally decrease about 3.5°F (2°C) for every 1,000-ft (300-m) increase in altitude above sea level, presenting perpetual snowy peaks to hot river valleys and basins. Rainfall is concentrated in two wet seasons (roughly corresponding to the spring and autumn of temperate latitudes) but varies considerably by location. Colombia's Pacific coast has one of the highest levels of rainfall in the world, with the south east often drenched by more than 200 in (500 cm) of rain per year. On the other hand rainfall in parts of the Guajira Peninsula seldom exceeds 30 in (75 cm) per year. Rainfall in the rest of the country runs between these two extremes.

Altitude not only affects temperature but is also one of the most important influences on vegetation patterns. The mountainous parts of the country can be divided into several vegetation zones according to altitude, although the altitude limits of each zone may vary somewhat depending on the latitude. Below 3,300 ft (1,000 m) are the tropical crops of the tierra caliente (hot land). The most productive land and the majority of the population can be found in the tierra templada (temperate land, 3,300-6,600 ft or 1,000-2,000 m), which provide the best conditions for the country's coffee growers, and the tierra fría (cold land, 6,600-10,500 ft, 2,000-3,200 m), where wheat and potatoes dominate. Beyond this lie the alpine conditions of the zona forestada (forested zone, 10,500-12,800 ft, 3,200-3,900 m) and then the treeless grasslands of the páramos (12,800-15,100 ft, 3,900-4,600 m). Above 15,100 ft (4,600 m), where temperatures are below freezing, is the tierra helada, a zone of permanent snow and ice.
Colombian flora and fauna also interact with climate zone patterns. Scrub woodland of scattered trees and bushes dominates the semi-arid north-eastern steppe and tropical desert. To the south, savanna (tropical grassland) vegetation covers the eastern plains, the Colombian portion of the Llanos. The rainy areas in the south east are blanketed by tropical rainforest. In the mountains, the spotty patterns of precipitation in alpine areas complicate vegetation patterns. The rainy side of a mountain may be lush and green, while the other side, in the rain shadow, may be parched. As a result Colombia is one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries.[14]
[edit] Environmental issues
The environmental challenges faced by Colombia are caused by both natural hazards and human agency. Many natural hazards result from Colombia's position along the Pacific Ring of Fire and the consequent geological instability. Colombia has 15 major volcanoes, the eruptions of which have on occasion resulted in substantial loss of life, such as at Armero in 1985, and geological faults that have caused numerous devastating earthquakes, such as the 1999 Armenia earthquake. Heavy floods both in mountainous areas and in low-lying watersheds and coastal regions regularly cause deaths and considerable damage to property during the rainy seasons. Rainfall intensities vary with the El Niño Southern Oscillation which occurs in unpredictable cycles, at times causing especially severe flooding.
Human induced deforestation has substantially changed the Andean landscape and is creeping into the rainforests of Amazonia and the Pacific coast. Deforestation is also linked to the conversion of lowland tropical forests to oil palm plantations. However, compared to neighbouring countries rates of deforestation in Colombia are still relatively low.[15] In urban areas industry, the use of fossil fuels, and other human produced waste have contaminated the local environment, and demand from rapidly expanding cities has placed increasing stress on the water supply as watersheds are affected and ground water tables fall. Participants in the country's armed conflict have also contributed to the pollution of the environment. Illegal armed groups have deforested large areas of land to plant illegal crops, with an estimated 99,000 hectares used for the cultivation of coca in 2007,[16] while in response the government have fumigated these crops using hazardous chemicals. Insurgents have also destroyed oil pipelines creating major ecological disasters.
[edit] History
[edit] Pre-Columbian era
Approximately 10,000 BC, hunter-gatherer societies existed near present-day Bogotá (at "El Abra" and "Tequendama") which traded with one another and with cultures living in the Magdalena River Valley.[17] Beginning in the first millennium BC, groups of Amerindians developed the political system of "cacicazgos" with a pyramidal structure of power headed by caciques. Within Colombia, the two cultures with the most complex cacicazgo systems were the Tayronas in the Caribbean Region, and the Muiscas in the highlands around Bogotá, both of which were of the Chibcha language family. The Muisca people are considered to have had one of the most developed political systems in South America, after the Incas.[18]
[edit] Spanish discovery, conquest, and colonization
Spanish explorers made the first exploration of the Caribbean littoral in 1499 led by Rodrigo de Bastidas. Christopher Columbus navigated near the Caribbean in 1502. In 1508, Vasco Nuñez de Balboa started the conquest of the territory through the region of Urabá. In 1513, he was the first European to discover the Pacific Ocean which he called Mar del Sur (or "Sea of the South") and which in fact would bring the Spaniards to Peru and Chile. The territory's main population was made up of hundreds of tribes of the Chibchan and Carib, currently known as the Caribbean people, whom the Spaniards conquered through warfare and alliances, while resulting disease such as smallpox, and the conquest and ethnic cleansing itself caused a demographic reduction among the indigenous.[19] In the sixteenth century, Europeans began to bring slaves from Africa.
[edit] Independence from Spain

Since the beginning of the periods of Conquest and Colonization, there were several rebel movements under Spanish rule, most of them either being crushed or remaining too weak to change the overall situation. The last one which sought outright independence from Spain sprang up around 1810, following the independence of St. Domingue in 1804 (present day Haiti), who provided a non-negligible degree of support to the eventual leaders of this rebellion: Simón Bolívar and Francisco de Paula Santander. Simón Bolívar had become the first President of Colombia, and Francisco de Paula Santander was Vice President; when Simón Bolívar stepped down, Santander became the second President of Colombia. The rebellion finally succeeded in 1819 when the territory of the Viceroyalty of New Granada became the Republic of Colombia organized as a union of Ecuador, Colombia and Venezuela (Panama was then an integral part of Colombia).
[edit] Post-independence and republicanism

Internal political and territorial divisions led to the secession of Venezuela and Quito (today's Ecuador) in 1830. The so-called "Department of Cundinamarca" adopted the name "Nueva Granada", which it kept until 1856 when it became the "Confederación Granadina" (Grenadine Confederation). After a two year civil war in 1863, the "United States of Colombia" was created, lasting until 1886, when the country finally became known as the Republic of Colombia. Internal divisions remained between the bipartisan political forces, occasionally igniting very bloody civil wars, the most significant being the Thousand Days civil war (1899 - 1902) which together with the United States of America's intentions to influence in the area (especially the Panama Canal construction and control) led to the separation of the Department of Panama in 1903 and the establishment of it as a nation. Colombia engulfed in a year long war with Peru over a territorial dispute involving the Amazonas Department and its capital Leticia.
Soon after, Colombia achieved a relative degree of political stability, which was interrupted by a bloody conflict that took place between the late 1940s and the early 1950s, a period known as La Violencia ("The Violence"). Its cause was mainly mounting tensions between the two leading political parties, which subsequently ignited after the assassination of the Liberal presidential candidate Jorge Eliécer Gaitán on April 9, 1948. This assassination caused riots in Bogotá and became known as El Bogotazo. The violence from these riots spread through out the country and claimed the lives of at least 180,000 Colombians. From 1953 to 1964 the violence between the two political parties decreased first when Gustavo Rojas deposed the President of Colombia in a coup d'etat and negotiated with the guerrillas, and then under the military junta of General Gabriel París Gordillo.
After Rojas' deposition the two political parties Colombian Conservative Party and Colombian Liberal Party agreed to the creation of a "National Front", whereby the Liberal and Conservative parties would govern jointly. The presidency would be determined by an alternating conservative and liberal president every 4 years for 16 years; the two parties would have parity in all other elective offices. The National Front ended "La Violencia", and National Front administrations attempted to institute far-reaching social and economic reforms in cooperation with the Alliance for Progress. In the end, the contradictions between each successive Liberal and Conservative administration made the results decidedly mixed. Despite the progress in certain sectors, many social and political problems continued, and guerrilla groups were formally created such as the FARC, ELN and M-19 to fight the government and political apparatus. These guerrilla groups were dominated by Marxist doctrines.
Emerging in the late 1970s, powerful and violent drug cartels further developed during the 1980s and 1990s. The Medellín Cartel under Pablo Escobar and the Cali Cartel, in particular, exerted political, economic and social influence in Colombia during this period. These cartels also financed and influenced different illegal armed groups throughout the political spectrum. Some enemies of these allied with the guerrillas and created or influenced paramilitary groups.
The new Colombian Constitution of 1991 was ratified after being drafted by the Constituent Assembly of Colombia. The constitution included key provisions on political, ethnic, human and gender rights. The new constitution initially prohibited the extradition of Colombian nationals. There were accusations of lobbying by drug cartels in favor of this prohibition. The cartels had previously promoted a violent campaign against extradition, leading to many terrorist attack and mafia style executions. They also tried to influence the government and political structure of Colombia by means of corruption, as in the case of the 8000 Process scandal.

In recent years, the country has continued to be plagued by the effects of the drug trade, guerrilla insurgencies like FARC and paramilitary groups such as the AUC (later demobilized, though paramilitarism remains active), which along with other minor factions have engaged in a bloody internal armed conflict. President Andrés Pastrana and the FARC attempted to negotiate a solution to the conflict between 1998 and 2002 in which the government, more or less like Pakistan negotiations with the Taliban , believed the state could not fight forever and agreed to handle huge quantity of land in return for peace.Pastrana began to implement the Plan Colombia initiative, with the dual goal of ending the armed conflict and promoting a strong anti-narcotic strategy. This strategy had huge quantity of land to be officially set as "demilitarize" zones were no soldiers from neither side could reside, but as more and more attacks from the drug cartels persisted on the demilitarize zones the government soon realized the negotiations were a waste of time.
During the presidency of Álvaro Uribe, who was elected on the promise of applying military pressure on the FARC and other outlawed groups, with the promise that after nearly half a century of negotiation with no results was a sign that some entities "just cannot be negotiated with". Mostly through military pressure and increased military hardware from the US most security indicators improved, showing a steep decrease in reported kidnappings (from 3,700 in the year 2000 to 800 in 2005) and a decrease of more than 48% in homicides between July 2002 and May 2005. Guerillas have been reduced from 16,900 insurgents to 8,900 insurgents.
While some in the UN argue Colombia is violating human rights to achieve peace, most do not argue that increase military pressure has had considerable improvements that have favored economic growth and tourism.[20] The 2006–2007 Colombian parapolitics scandal emerged from the revelations and judicial implications of past and present links between paramilitary groups, mainly the AUC, and some government officials and many politicians, most of them allied to the governing administration.[21]
[edit] Government
The government of Colombia takes place within the framework of a presidential representative democratic republic as established in the Constitution of 1991. In accordance with the principle of separation of powers, government is divided into three branches: the executive; the legislative; and the judicial. These operate alongside special control institutions (the offices of the Inspector General of Colombia and the Comptroller General of Colombia) and electoral institutions.
The President of Colombia serves as both head of state and head of government, followed by the Vice President and the Council of Ministers. The president is elected by popular vote to serve four-year terms and is currently limited to a maximum of two such terms (increased from one in 2005). At the provincial level executive power is vested in department governors, municipal mayors and local administrators for smaller administrative subdivisions, such as corregidores for corregimientos.
The legislative branch of government is represented nationally by the Congress, a bicameral institution comprising a 166-seat Chamber of Representatives (including four seats reserved for the representatives of minority communities and expatriates) and a 102-seat Senate (including two seats reserved for the representatives of indigenous communities). Members of both houses are elected two months before the president, also by popular vote and to serve four-year terms. At the provincial level the legislative branch is represented by department assemblies and municipal councils. All regional elections are held one year and five months after the presidential election.
The judicial branch is headed by the Supreme Court, consisting of 23 judges divided into three chambers (Penal, Civil and Agrarian, and Labour). The judicial branch also includes the Council of State, which has special responsibility for administrative law and also provides legal advice to the executive, the Constitutional Court, responsible for assuring the integrity of the Colombian constitution, and the Superior Council of Judicature, responsible for auditing the judicial branch. Colombia operates a system of civil law, which since 2005 has been applied through an adversarial system.
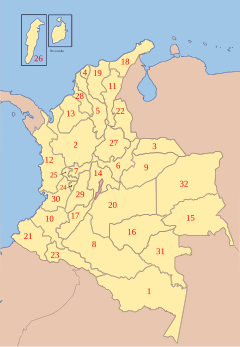
[edit] Administrative divisions
Colombia is divided into 32 departments and one capital district, which is treated as a department (Bogotá also serves as the capital of the department of Cundinamarca). Departments are subdivided into municipalities, each of which is assigned a municipal seat, and municipalities are in turn subdivided into corregimientos. Each department has a local government with a governor and assembly directly elected to four-year terms. Each municipality is headed by a mayor and council, and each corregimiento by an elected corregidor, or local leader.
|
|
In addition to the capital nine other cities have been designated districts (in effect special municipalities), on the basis of special distinguishing features. These are Barranquilla, Cartagena, Santa Marta, Cúcuta, Popayán, Tunja, Turbo, Buenaventura and Tumaco. Some departments have local administrative subdivisions, where towns have a large concentration of population and municipalities are near each other (for example in Antioquia and Cundinamarca). Where departments have a low population and there are security problems (for example Amazonas, Vaupés and Vichada), special administrative divisions are employed, such as "department corregimientos", which are a hybrid of a municipality and a corregimiento.
[edit] Foreign affairs
The foreign affairs of Colombia are headed by the President of Colombia and managed by the Minister of Foreign Affairs. Colombia has diplomatic missions in all continents and is also represented in multilateral organizations at the following locations:
- Brussels (Mission to the European Union)
- Geneva (Permanent Missions to the United Nations and other international organizations)
- Montevideo (Permanent Missions to the Latin American Integration Association and Mercosur)
- Nairobi (Permanent Missions to the United Nations and other international organizations)
- New York (Permanent Mission to the United Nations)
- Paris (Permanent Mission to UNESCO)
- Rome (Permanent Mission to the Food and Agriculture Organization)
- Washington DC (Permanent Mission to the Organization of American States)
The foreign relations of Colombia are mostly concentrated on combating the illegal drug trade, the fight against terrorism, improving Colombia's image in the international community, expanding the international market for Colombian products, and environmental issues. Colombia receives special military and commercial co-operation and support in its fight against internal armed groups from the United States, mainly through Plan Colombia, as well as special financial preferences from the European Union in certain products.
Colombia is a member of the Andean Community of Nations and the Union of South American Nations.
[edit] Defense
The executive branch of government has responsibility for managing the defense of Colombia, with the President commander-in-chief of the armed forces. The Ministry of Defense exercises day-to-day control of the military and the Colombian National Police. According to UN Human Development Report criteria, Colombia has 209,000 military personnel,[22] and in 2005 3.7% of the country's GDP went towards military expenditure,[23] both figures placing it 21st in the world. Within Latin America, Colombia's armed forces are the third-largest, behind Brazil and Mexico, and it spends the second-highest proportion of GDP after Chile. Since 2000 the Colombian military has also received substantial support from the United States government through the provisions of Plan Colombia.
The Colombian military is divided into three branches: the National Army of Colombia; the Colombian Air Force; and the Colombian National Armada. The National Police functions as a gendarmerie, operating independently from the military as the law enforcement agency for the entire country. Each of these operates with their own intelligence apparatus separate from the national intelligence agency, the Administrative Department of Security. The National Army is formed by divisions, regiments and special units; the National Armada by the Colombian Naval Infantry, the Naval Force of the Caribbean, the Naval Force of the Pacific, the Naval Force of the South, Colombia Coast Guards, Naval Aviation and the Specific Command of San Andres y Providencia; and the Air Force by 13 air units. The National Police has a presence in all municipalities.
[edit] Politics

For over a century Colombian politics were monopolised by the Liberal Party (founded in 1848 on an anti-clerical, broadly economically liberal and federalist platform), and the Conservative Party (founded in 1849 espousing Catholicism, protectionism, and centralism). This culminated in the formation of the National Front (1958-1974), which formalised arrangements for an alternation of power between the two parties and excluded non-establishment alternatives (thereby fuelling the nascent armed conflict).
By the time of the dissolution of the National Front, traditional political alignments had begun to fragment. This process has continued since, and the consequences of this are exemplified by the results of the last presidential election, held on 28 May 2006, which was won with 62% of the vote by the incumbent, Álvaro Uribe. President Uribe is from a Liberal background but he campaigned as part of the Colombia First movement with the support of the Conservative Party, and his hard line on security issues and liberal economics place him on the right of the modern political spectrum. In second place with 22% was Carlos Gaviria of the Alternative Democratic Pole, a newly formed social democratic alliance which includes elements of the former M-19 guerrilla movement. Horacio Serpa of the Liberal Party achieved third place with 12%. Meanwhile in the congressional elections held earlier that year the two traditional parties secured only 93 out of 268 seats available.
Despite a number of controversies, most notably the ongoing parapolitics scandal, dramatic improvements in security and continued strong economic performance have ensured that President Uribe remains extremely popular among the Colombian people, with his approval rating peaking at 91% in July 2008.[24] However, having served two terms, he will be constitutionally barred from seeking re-election in 2010.
[edit] Economy
In spite of the difficulties presented by serious internal armed conflict, Colombia's economy grew steadily in the latter part of the twentieth century, with gross domestic product (GDP) increasing at an average rate of over 4% per year between 1970 and 1998. The country suffered a recession in 1999 (the first full year of negative growth since the Great Depression), and the recovery from that recession was long and painful. However in recent years growth has been impressive, reaching 8.2% in 2007, one of the highest rates of growth in Latin America. Meanwhile the Colombian stock exchange climbed from 1,000 points at its creation in July 2001 to over 7,300 points by November 2008.[25]
According to International Monetary Fund estimates, in 2007 Colombia's nominal GDP was US$202.6 billion (37th in the world and fourth in South America). Adjusted for purchasing power parity, GDP per capita stands at $7,968, placing Colombia 82nd in the world. However, in practice this is relatively unevenly distributed among the population, and, in common with much of Latin America, Colombia scores poorly according to the Gini coefficient, with UN figures placing it 119th out of 126 countries. In 2003 the richest 20% of the population had a 62.7% share of income/consumption and the poorest 20% just 2.5%, and 17.8% of Colombians live on less than $2 a day.[26] Government spending is 37.9% of GDP.[2] Almost a quarter of this goes towards servicing the country's relatively high government debt, estimated at 52.8% of GDP in 2007.[26][2] Other problems facing the economy include weak domestic and foreign demand, the funding of the country's pension system, and unemployment (10.8% in November 2008[25]). Inflation has remained relatively low in recent years, standing at 5.5% in 2007.[2]
Historically an agrarian economy, Colombia urbanised rapidly in the twentieth century, by the end of which just 22.7% of the workforce were employed in agriculture, generating just 11.5% of GDP. 18.7% of the workforce are employed in industry and 58.5% in services, responsible for 36% and 52.5% of GDP respectively.[2] Colombia is rich in natural resources, and its main exports include petroleum, coal, coffee and other agricultural produce, and gold.[27] Unofficially, illegal drugs are also a major export, with over 80% of the world's cocaine produced in Colombia, estimated to account for between 1 and 3% of the country's GDP.[28][29] Colombia is also known as the world's leading source of emeralds,[30] while over 70% of cut flowers imported by the United States are Colombian.[31] Principal trading partners are the United States (a controversial free trade agreement with the United States is currently awaiting approval by the United States Congress), Venezuela and China.[2] All imports, exports, and the overall balance of trade are at record levels, and the inflow of export dollars has resulted in a substantial re-valuation of the Colombian peso.
Economic performance has been aided by liberal reforms introduced in the early 1990s and continued during the current presidency of Álvaro Uribe, whose policies include measures designed to bring the public sector deficit below 2.5% of GDP. In 2008, the Heritage Foundation assessed the Colombian economy to be 61.9% free, an increase of 2.3% since 2007, placing it 67th in the world and 15th out of 29 countries within the region.[32] Meanwhile the improvements in security resulting from President Uribe's controversial "democratic security" strategy have engendered an increased sense of confidence in the economy. On 28 May 2007 the American magazine BusinessWeek published an article naming Colombia "the most extreme emerging market on Earth".[33]
[edit] Tourism
For many years serious internal armed conflict deterred tourists from visiting Colombia, with official travel advisories warning against travel to the country. However in recent years numbers have risen sharply, thanks to improvements in security resulting from President Álvaro Uribe's "democratic security" strategy, which has included significant increases in military strength and police presence throughout the country and pushed rebel groups further away from the major cities, highways and tourist sites likely to attract international visitors. Foreign tourist visits were predicted to have risen from 0.5 million in 2003 to 1.3 million in 2007,[34] while Lonely Planet picked Colombia as one of their top ten world destinations for 2006.[35] The improvements in the country's security were recognised in November 2008 with a revision of the travel advice on Colombia issued by the British Foreign Office.[36]
Colombia Minister for Industry, Trade and Tourism Luis Guillermo Plata said his country had receive 2,348,948 visitors in 2008. He is expecting 2,650,000 tourists for 2009. [37] [38]
Popular tourist attractions include the historic Candelaria district of central Bogotá, the walled city and beaches of Cartagena, the colonial towns of Santa Fe de Antioquia, Popayan, Villa de Leyva and Santa Cruz de Mompox, and the Las Lajas Cathedral and the Salt Cathedral of Zipaquirá. Tourists are also drawn to Colombia's numerous festivals, including Medellín's Festival of the Flowers, the Barranquilla Carnival, the Carnival of Blacks and Whites in Pasto and the Ibero-American Theater Festival in Bogotá. Meanwhile, because of the improved security, Caribbean cruise ships now stop at Cartagena and Santa Marta.

The great variety in geography, flora and fauna across Colombia has also resulted in the development of an ecotourist industry, concentrated in the country's national parks. Popular ecotourist destinations include: along the Caribbean coast, the Tayrona National Natural Park in the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta mountain range and Cabo de la Vela on the tip of the Guajira Peninsula; the Nevado del Ruiz volcano, the Cocora valley and the Tatacoa Desert in the central Andean region; Amacayacu National Park in the Amazon River basin; and the Pacific islands of Malpelo and Gorgona. Colombia is home to seven UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
[edit] Transportation

Colombia has a network of national highways maintained by the Instituto Nacional de Vías or INVIAS (National Institute of Roadways) government agency under the Ministry of Transport. The Pan-American Highway travels through Colombia, connecting the country with Venezuela to the east and Ecuador to the south.
Colombia's principal airport is El Dorado International Airport in Bogotá. Several national airlines (Avianca, AeroRepública, AIRES , SATENA and EasyFly, ), and international airlines (such as Iberia, American Airlines, Varig, Copa, Continental, Delta, Air Canada, Air France, Aerolineas Argentinas, Aerogal, TAME, TACA) operate from El Dorado. Because of its central location in Colombia and America, it is preferred by national land transportation providers, as well as national and international air transportation providers.
[edit] Biofuels
Colombia is discussing current trends and challenges as well as recent international developments in the biofuels sector with the intention of contributing to the development of a sustainable and competitive biofuels strategy for Colombia and the region.[39] Arturo Infante Villarreal is the National Biofuels Coordinator, which is within the Department of National Planning.
[edit] Demographics

With an estimated 44.6 million people in 2008, Colombia is the third-most populous country in Latin America, after Brazil and Mexico. The population increased at a rate of 1.9% between 1975 and 2005, predicted to drop to 1.2% over the next decade. Colombia is projected to have a population of 50.7 million by 2015. These trends are reflected in the country's age profile. In 2005 over 30% of the population was under 15 years old, compared to just 5.1% aged 65 and over. Life expectancy at birth in 2005 was 72.3; 2.1% would not reach the age of 5, 9.2% would not reach the age of 40.[26]
The population is concentrated in the Andean highlands and along the Caribbean coast. The nine eastern lowland departments, comprising about 54% of Colombia's area, have less than 3% of the population and a density of less than one person per square kilometer (two persons per square mile). Traditionally a rural society, movement to urban areas was very heavy in the mid-twentieth century, and Colombia is now one of the most urbanized countries in Latin America. The urban population increased from 31% of the total in 1938 to 60% in 1975, and by 2005 the figure stood at 72.7%.[40][26] The population of Bogotá alone has increased from just over 300,000 in 1938 to approximately 7 million today. In total thirty cities now have populations of 100,000 or more.
Colombia is ranked second in the world in the Happy Planet Index.
[edit] Ethnic groups

The census data in Colombia does not record ethnicity, other than that of those identifying themselves as members of particular minority ethnic groups, so overall percentages are essentially estimates from other sources and can vary from one to another.[41]
According to the CIA World Factbook, the majority of the population (58%) is mestizo, or of mixed European and Amerindian ancestry. 20% is of European ancestry only, 14% mulatto (of mixed European and black African ancestry), 4% of black African ancestry only, and 3% zambo (of mixed Amerindian and black African ancestry). Pure indigenous Amerindians comprise only 1% of the population.[2] The overwhelming majority of Colombians speak Spanish (see also Colombian Spanish), but in total 101 languages are listed for Colombia in the Ethnologue database, of which 80 are spoken today as living languages. Most of these belong to the Chibchan, Arawak and Cariban linguistic families. The Quechua language, spoken by descendants of the Inca empire, has also extended northwards into Colombia, mainly in urban centers of the southern highlands. There are currently about 500,000 speakers of indigenous languages.[42]
[edit] Indigenous peoples
Before the Spanish colonization of what is now Colombia, the territory was home to a significant number of indigenous peoples. Many of these were absorbed into the mestizo population, but the remainder currently represents over eighty-five distinct cultures. 567 reserves (resguardos) established for indigenous peoples occupy 365,004 square kilometres (over 30% of the country's total) and are inhabited by more than 800,000 people in over 67,000 families.[44] The 1991 constitution established their native languages as official in their territories, and most of them have bilingual education (native and Spanish).
Some of the largest indigenous groups are the Wayuu,[43] the Arhuacos, the Muisca, the Kuna, the Paez, the Tucano and the Guahibo. Cauca, La Guajira and Guainia have the largest indigenous populations.
[edit] Immigrant groups
The first and most substantial wave of modern immigration to Colombia consisted of Spanish colonists, following the arrival of Europeans in 1499. However a range of other Europeans (Dutch, Germans, Italians, French, Swiss, Belgians and Basques, also many North Americans) migrated to the country in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, and, in smaller numbers, Poles, Lithuanians, English, Irish and Croats during and after the Second World War. For example, former Mayor of Bogotá Antanas Mockus is the son of Lithuanian immigrants.
Many immigrant communities have settled on the Caribbean coast, in particular recent immigrants from the Middle East. Barranquilla (the largest city of the Colombian Caribbean) and other Caribbean cities have the largest populations of Lebanese and Arabs, Sephardi Jews, Roma, and people of Italian, German, and French descent. For example, the singer Shakira, a native of Barranquilla, has both Lebanese and Italian ancestry. There are also important communities of Chinese and Japanese.
Black Africans were brought as slaves, mostly to the coastal lowlands, beginning early in the sixteenth century and continuing into the nineteenth century. Large Afro-Colombian communities are found today on the Caribbean and Pacific coasts. The population of the department of Chocó, running along the northern portion of Colombia's Pacific coast, is over 80% black.[45]
[edit] Education

The educational experience of many Colombian children begins with attendance at a preschool academy until age 6. Primary education is then free and compulsory. Secondary education (educación media) begins at age 11 and lasts up to six years, in some cases seven (mostly in private schools, where it is usually vocational training). Secondary school graduates are awarded the diploma (high-school diploma). However in many rural areas, teachers are poorly qualified, and only the five years of primary schooling are offered. The school year can extend from February to November or from August to June, and in many public schools attendance is split into morning and afternoon "shifts", in order to accommodate the large numbers of children.
Public spending on education as a proportion of gross domestic product in 2006 was 4.7% — one of the highest rates in Latin America — as compared with 2.4% in 1991. This represented 14.2% of total government expenditure.[46][26] In 2006, the primary and secondary net enrolment rates stood at 88% and 65% respectively, slightly below the regional average. School life expectancy was 12.4 years.[46] A total of 92.3% of the population aged 15 and older were recorded as literate, including 97.9% of those aged 15-24, both figures slightly higher than the regional average.[46] However, literacy levels are considerably lower in rural areas.[47]
Colombia has 24 public and numerous private universities. These are concentrated in Bogotá, which has become known as "the Athens of South America".[48]
[edit] Religion
The National Administrative Department of Statistics (DANE) does not collect religious statistics, and accurate reports are difficult to obtain. However, based on various studies, more than 95% of the population adheres to Christianity,[49] the vast majority of which (between 81% and 90%) are Roman Catholic. About 1% of Colombians adhere to indigenous religions and under 1% to Judaism, Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism. However, despite high numbers of adherents, around 60% of respondents to a poll by El Tiempo reported that they did not practice their faith actively.[50]
While Colombia remains an overwhelmingly Roman Catholic country, the Colombian constitution guarantees freedom and equality of religion.[51] Religious groups are readily able to obtain recognition as organized associations, although some smaller ones have faced difficulty in obtaining the additional recognition required to offer chaplaincy services in public facilities and to perform legally recognised marriages.[50]
[edit] Culture

Colombia lies at the crossroads of Latin America and the broader American continent, and as such has been marked by a wide range of cultural influences. Native American, Spanish and other European, African, American, Caribbean, and Middle Eastern influences, as well as other Latin American cultural influences, are all present in Colombia's modern culture. Urban migration, industrialization, globalization, and other political, social and economic changes have also left an impression.
Historically, the country's imposing landscape left its various regions largely isolated from one another, resulting in the development of very strong regional identities, in many cases stronger than the national. Modern transport links and means of communication have mitigated this and done much to foster a sense of nationhood, but social and political instability, and in particular fears of armed groups and bandits on intercity highways, have contributed to the maintenance of very clear regional differences. Accent, dress, music, food, politics and general attitude vary greatly between the Bogotanos and other residents of the central highlands, the paisas of Antioquia and the coffee region, the costeños of the Caribbean coast, the llaneros of the eastern plains, and the inhabitants of the Pacific coast and the vast Amazon region to the south east.

An inheritance from the colonial era, Colombia remains a deeply Roman Catholic country and maintains a large base of Catholic traditions which provide a point of unity for its multicultural society. Colombia has many celebrations and festivals throughout the year, and the majority are rooted in these Catholic religious traditions. However, many are also infused with a diverse range of other influences. Prominent examples of Colombia's festivals include the Barranquilla Carnival, the Carnival of Blacks and Whites, Medellín's Festival of the Flowers and Bogotá's Ibero-American Theater Festival
The mixing of various different ethnic traditions is reflected in Colombia's music and dance. The most well-known Colombian genres are cumbia and vallenato, the latter now strongly influenced by global pop culture. A powerful and unifying cultural medium in Colombia is television. Most famously, the telenovela Betty La Fea has gained international success through localized versions in the United States, Mexico, and elsewhere. Television has also played a role in the development of the local film industry.
As in many Latin American countries, Colombians have a passion for football (soccer). The Colombian national football team is seen as a symbol of unity and national pride, though local clubs also inspire fierce loyalty and sometimes-violent rivalries. Colombia has "exported" many famous players, such as Freddy Rincon, Carlos Valderrama, Iván Ramiro Córdoba, and Faustino Asprilla. Other Colombian athletes have also achieved success, including NASCAR's Juan Pablo Montoya, Major League Baseball's Edgar Rentería and Orlando Cabrera, and the PGA Tour's Camilo Villegas.
Other famous Colombians include the Nobel Prize winning author Gabriel Garcia Marquez, the artist Fernando Botero, the writers Fernando Vallejo, Laura Restrepo, Álvaro Mutis and James Cañón, the musicians Shakira, Juanes, Carlos Vives and Juan Garcia-Herreros, and the actors Catalina Sandino Moreno, John Leguizamo, Catherine Siachoque and Sofia Vergara.
The cuisine of Colombia developed mainly from the food traditions of European countries. Spanish, Italian and French culinary influences can all be seen in Colombian cooking. The cuisine of neighboring Latin American countries, Mexico, the United States and the Caribbean, as well as the cooking traditions of the country's indigenous inhabitants, have all influenced Colombian food.
Many national symbols, both objects and themes, have arisen from Colombia's diverse cultural traditions and aim to represent what Colombia, and the Colombian people, have in common. Cultural expressions in Colombia are promoted by the government through the Ministry of Culture.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ Constitution of Colombia, 1991 (Article 10)
- ^ a b c d e f g h i CIA world fact book (2009-01-22). "Colombia". CIA. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/co.html. Retrieved on 2009-01-24.
- ^ a b c d "Colombia". International Monetary Fund. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2008/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?sy=2004&ey=2008&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=233&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=&pr.x=48&pr.y=9. Retrieved on 2008-10-09.
- ^ Gerhar Sandner, Beate Ratter, Wolf Dietrich Sahr and Karsten Horsx (1993). "Conflictos Territoriales en el Mar Caribe: El conflicto fronterizo en el Golfo de Venezuela" (in Spanish). Biblioteca Luis Angel Arango. http://www.lablaa.org/blaavirtual/geografia/ctemc/ctemc03.htm. Retrieved on 2008-01-05.
- ^ The Geographer Office of the Geographer Bureau of Intelligence and Research (1985-04-15). "Brazil-Colombia boundary" (in English) (PDF). International Boundary Study. http://www.law.fsu.edu/library/collection/LimitsinSeas/IBS174.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-01-05.
- ^ CIA (2007-12-13). "Ecuador". World Fact Book. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/ec.html. Retrieved on 2008-01-05.
- ^ (Spanish) Tratados Internacionales limítrofes de Colombia
- ^ (Spanish) Colombia - Limites territoriales
- ^ Nicolás del Castillo Mathieu (March 1992). "LA PRIMERA VISION DE LAS COSTAS COLOMBIANAS, Repaso de Historia" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial. http://www.lablaa.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/marzo1992/marzo3.htm. Retrieved on 2008-02-29.
- ^ http://www.unodc.org/pdf/Colombia_Dec06_en.pdf
- ^ David R. Davis, Brett Ashley Leeds and Will H. Moore (1998-11-21). "Measuring Dissident and state behaviour: The Intranational Political Interactions (IPI) Project" (PDF). Florida State University. http://garnet.acns.fsu.edu/~whmoore/ipi/harmel.conf.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-01-05.
- ^ a b Carlos Restrepo Piedrahita (February 1992). "EL NOMBRE "COLOMBIA", El único país que lleva el nombre del Descubrimiento" (in Spanish). Revista Credencial. http://www.lablaa.org/blaavirtual/revistas/credencial/febrero1992/febrero2.htm. Retrieved on 2008-02-29.
- ^ Tallest mountains by continent
- ^ "South America Banks on Regional Strategy to Safeguard Quarter of Earth's Biodiversity". Conservation International. http://web.archive.org/web/20050310115345/http://www.conservation.org/xp/news/press_releases/2003/091603_andean_eng.xml. Retrieved on 2007-06-29.
- ^ Human Development Report: Deforestation, 2007/2008
- ^ UNODC 2008 World Drug Report, Executive Summary
- ^ Van der Hammen, T. and Correal, G. 1978: "Prehistoric man on the Sabana de Bogotá: data for an ecological prehistory"; Paleography, Paleoclimatology, Paleoecology 25:179-190
- ^ Broadbent, Sylvia 1964: Los Chibchas: organización socio-política. Série Latinoamericana 5. Bogotá: Facultad de Sociología, Universidad Nacional de Colombia
- ^ The Story Of... Smallpox — and other Deadly Eurasian Germs
- ^ Come to Sunny Colombia The Economist, June 29, 2006.
- ^ (Spanish) Polo Democratico Alternativo ¿Por qué la parapolítica? February 26, 2007. Retrieved on August 19, 2007
- ^ Human Development Report: Military Personnel, 2007/2008
- ^ Human Development Report: Military Expenditure, 2007/2008
- ^ Reuters, Popularity of Colombia's Uribe soars after rescue
- ^ a b Banco de la República, Economic and Financial Data for Colombia
- ^ a b c d e Human Development Report for Colombia, 2007/2008
- ^ International Trade Centre: Colombia Exports
- ^ Clune, Sarah. "Colombia's illegal drug trade". http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/latin_america/colombia/trade.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-13.
- ^ The Independent, Colombia the real victim in failed war on drugs
- ^ International Colored Gemstone Association: Emerald
- ^ America’s Flower Basket: Colombian Flowers and the American Marketplace
- ^ Heritage Foundation, Index of Economic Freedom
- ^ BusinessWeek, Colombia, The Most Extreme Emerging Market on Earth May 28, 2007
- ^ BBC News, A new hot-spot for the tourism industry
- ^ "Hot Destination: Colombia". Christian Science Monitor. May 9, 2006. http://www.csmonitor.com/2006/0509/p06s01-woam.html.
- ^ FCO Travel Advice, Colombia
- ^ Colombia expects to receive 2 650 000 tourists in 2009
- ^ 16,2% aumentó llegada de turistas extranjeros a Colombia en 2008
- ^ ceelat
- ^ Colombia: A Country Study
- ^ (Spanish) Colombia una nación multicultural: su diversidad étnica
- ^ The Languages of Colombia
- ^ a b EPM (2005). "La etnia Wayuu" (in Spanish). Empresas Publicas de Medellin. http://www.eeppm.com/epmcom/contenido/acercade/infraestructura/generacion/Jepirachi/etnia.htm. Retrieved on 2008-02-29.
- ^ (Spanish) Los Resguardos Indígenas
- ^ (Spanish) Colombia una Los grupos étnicos colombianos
- ^ a b c UNESCO Institute for Statistics Colombia Profile
- ^ US Department of State Background Note: Colombia
- ^ Bogotá, Athens of South America, ReVista, Harvard Review of Latin America
- ^ "Religious Intelligence — Country Profile: Colombia". http://www.religiousintelligence.co.uk/country/?CountryID=78. Retrieved on 2007-10-03.
- ^ a b International Religious Freedom Report 2005, by the Bureau of Democracy, Human Rights, and Labor, U.S. Department of State, November 8, 2005.
- ^ Constitution of Colombia, 1991 (Article 19)
[edit] Further reading
- (Spanish) Academia Colombiana de Historia (1986), Historia extensa de Colombia (41 volumes). Bogotá: Ediciones Lerner, 1965-1986. ISBN 9589501338 (Complete work)
- (Spanish) Barrios, Luis (1984), Historia de Colombia. Fifth edition, Bogotá: Editorial Cultural
- (Spanish) Bedoya F., Víctor A. (1944), Historia de Colombia: independencia y república con bases fundamentales en la colonia. Colección La Salle, Bogotá: Librería Stella
- Bushnell, David (1993), The Making of Modern Colombia: A Nation in Spite of Itself. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. ISBN 0520082893
- (Spanish) Caballero Argaez, Carlos (1987), 50 años de economía: de la crisis del treinta a la del ochenta. Second edition, Colección Jorge Ortega Torres, Bogotá: Editorial Presencia, Asociación Bancaria de Colombia. ISBN 9589040039
- (Spanish) Cadavid Misas, Roberto (2004), Cursillo de historia de Colombia: de la conquista a la independencia. Bogotá: Intermedio Editores. ISBN 9587091345
- (Spanish) Calderón Schrader, Camilo; Gil, Antonio; Torras, Daniel (2001), Enciclopedia de Colombia (4 volumes). Barcelona: Céano Grupo Editorial, 2001. ISBN 8449419476 (Complete work)
- (Spanish) Calderón Schrader, Camilo (1993), Gran enciclopedia de Colombia (11 volumes). Bogotá: Círculo de Lectores. ISBN 9582802944 (Complete work)
- (Spanish) Cavelier Gaviria, Germán (2003), Centenario de Panamá: una historia de la separación de Colombia en 1903. Bogotá: Universidad Externado de Colombia. ISBN 9586167186
- (Spanish) Forero, Manuel José (1946), Historia analítica de Colombia desde los orígenes de la independencia nacional. Second edition, Bogotá: Librería Voluntad.
- (Spanish) Gómez Hoyos, Rafael (1992), La independencia de Colombia. Madrid: Editorial Mapfre, Colecciones Mapfre 1492. ISBN 8471005964
- (Spanish) Granados, Rafael María (1978), Historia general de Colombia: prehistoria, conquista, colonia, independencia y Repúbica. Eighth edition, Bogotá: Imprenta Departamental Antonio Nariño.
- (Spanish) Hernández de Alba, Guillermo (2004), Como nació la República de Colombia. Colección Bolsilibros. Bogotá: Academia Colombiana de Historia. ISBN 9588040353
- (Spanish) Hernández Becerra, Augusto (2001), Ordenamiento y desarreglo territorial en Colombia. Bogotá: Universidad Externado de Colombia, ISBN 9586165558
- (Spanish) Hernández Rodríguez, Guillermo (1949), De los chibchas a la colonia y a la república. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional de Colombia. Sección de Extensión Cultural.
- Hylton, Forrest (2006), Evil Hour in Colombia. New York: Verso Books. ISBN 1844675513
- (Spanish) Jaramillo Uribe, Jaime; Tirado Mejía, Álvaro; Calderón Schrader, Camilo (2000), Nueva historia de Colombia (12 volumes). Bogotá: Planeta Colombiana Editorial. ISBN 9586142515 (Complete work)
- Kirk, Robin (2004), More Terrible Than Death: Drugs, Violence, and America's War in Colombia. United States: PublicAffairs. ISBN 1586482076
- (Spanish) Ocampo López, Javier (1999), El proceso ideológico de la emancipación en Colombia. Colección La Línea de Horizonte, Bogotá: Editorial Planeta. ISBN 9586147924
- Ospina, William (2006), Once Upon a Time There Was Colombia. Colombia: Villegas Asociados. ISBN 9588156645
- Palacios, Marco (2006), Between Legitimacy and Violence: A History of Colombia, 1875-2002. United States of America: Duke University Press. ISBN 0822337673
- (Spanish) Reichel-Dolmatoff, Gerardo (1998), Colombia indígena. Medellín: Hola Colina. ISBN 9586382761
- (Spanish) Restrepo, José Manuel (1974), Historia de la revolución de la República de Colombia. Medellín: Editorial Bedout.
- (Spanish) Rivadeneira Vargas, Antonio José (2002), Historia constitucional de Colombia 1510-2000. Third edition, Tunja: Editorial Bolivariana Internacional.
- Simons, Geoff (2004), Colombia: A Brutal History. London: Saqi Books. ISBN 0863567584
- Smith, Stephen (1999), Cocaine Train: Travels in Colombia. London: Little, Brown. ISBN 0316647497
- (Spanish) Tovar Pinzón, Hermes (1975), El movimiento campesino en Colombia durante los siglos XIX y XX. Second edition, Bogotá: Ediciones Libres.
- (Spanish) Trujillo Muñoz Augusto (2001), Descentralización, regionalización y autonomía local. Bogotá: Universidad Nacional de Colombia.
- (Spanish) Vidal Perdomo Jaime (2001), La Región en la Organización Territorial del Estado. Bogotá: Universidad del Rosario.
[edit] External links
![]() Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks
![]() Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote
![]() Source texts from Wikisource
Source texts from Wikisource
![]() Images and media from Commons
Images and media from Commons
![]() News stories from Wikinews
News stories from Wikinews
- Government
- (Spanish) Portal del Estado - Colombia Online Government web site
- (Spanish) Presidencia de la República de Colombia - Official Presidential web site
- (Spanish) Senado de la República de Colombia - Senate
- (Spanish) Cámara de Representantes de Colombia - Chamber of Representatives
- (Spanish) Rama Judicial - Judicial branch
- (Spanish) Policia Nacional - Police
- (Spanish) Ejército Nacional de Colombia - Army
- (Spanish) Armada Nacional de Colombia - Navy
- (Spanish) Departamento Administrativo de Seguridad - Security Service
- (Spanish) Banco de la República - Central Bank
- (Spanish) Ministerio de Comercio, Industria y Turismo - Ministry of Commerce, Industry and Tourism
- (Spanish) Instituto Nacional de Vías - Ministry of Transport
- (Spanish) Departamento Administrativo Nacional de Estadistica - National Administrative Department of Statistics
- Sistema Nacional de Información Cultural - National System of Cultural Information
- (Spanish) Instituto Geográfico Agustín Codazzi - Maps of Colombia
- Other
- Colombia travel guide from Wikitravel
- Colombia at Encyclopaedia Britannica
- Colombia entry at The World Factbook
- Colombia at UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Colombia at the Open Directory Project
- (Spanish) UNICEF - UNICEF in Colombia
- US Colombia Free Trade Promotion Agreement - Congressional Research Service
- US-Colombia Free Trade Deal Costly for Poor People - Oxfam
- A US-Colombia Free Trade Agreement: Strengthening Democracy and Progress in Latin America - Cato Institute
- Breaking the Grip? Obstacles to Justice for Paramilitary Mafias in Colombia - Human Rights Watch
- Colombian news in English
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||