Kano model
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
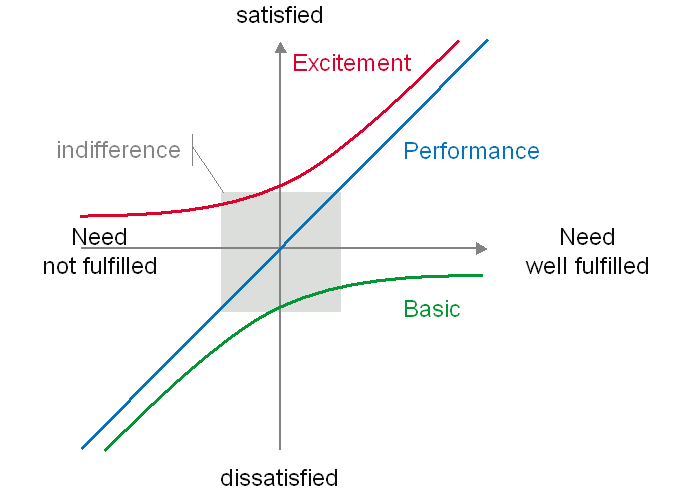
The Kano model is a theory of product development and customer satisfaction developed in the 80's by Professor Noriaki Kano which classifies customer preferences into five categories:
- Attractive
- One-Dimensional
- Must-Be
- Indifferent
- Reverse
These categories have been translated into English using various different names (delighters/exciters, satisfiers, dissatisfiers, etc.), but all refer to the original articles written by Kano.
| Author(s) | Driver type 1 | Driver type 2 | Driver type 3 | Driver type 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herzberg et al. (1959)[2] | Hygiene | Motivator | ||
| Kano (1984)[3] | Must-be | Attractive | One-dimensional | Indifferent |
| Cadotte and Turgeon (1988)[4] | Dissatisfier | Satisfier | Critical | Neutral |
| Brandt (1988)[5] | Minimum requirement | Value enhancing | Hybrid | Unimportant as determinant |
| Venkitaraman and Jaworski (1993)[6] | Flat | Value-added | Key | Low |
| Brandt and Scharioth (1998)[7] | Basic | Attractive | One-dimensional | Low impact |
| Llosa (1997[8], 1999[9]) | Basic | Plus | Key | Secondary |
The Kano model offers some insight into the product attributes which are perceived to be important to customers. The purpose of the tool is to support product specification and discussion through better development team understanding. Kano's model focuses on differentiating product features, as opposed to focusing initially on customer needs. Kano also produced a methodology for mapping consumer responses to questionnaires onto his model.
Quality Function Deployment (QFD) makes use of the Kano model in terms of the structuring of the Comprehensive QFD matrices. Mixing Kano types in QFD matrices can lead to distortions in the customer weighting of product characteristics. For instance, mixing Must-Be product characteristics --such as cost, reliability, workmanship, safety, and technologies used in the product--in the initial House of Quality will usually result in completely filled rows and columns with high correlation values. Other Comprehensive QFD techniques using additional matrices are used to avoid such issues. Kano's model provides the insights into the dynamics of customer preferences to understand these methodology dynamics.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ Bartikowski, B., Llosa, S. (2003). Identifying Satisfiers, Dissatisfiers, Criticals and Neutrals in Customer Satisfaction. Working Paper n° 05-2003, Mai 2003. Euromed - Ecole de Management. Marseille.
- ^ Herzberg, Frederick; Mausner, B., Snyderman, B.B. (1959). The motivation to work (2nd ed.). New York: Wiley.
- ^ Kano, Noriaki; Nobuhiku Seraku, Fumio Takahashi, Shinichi Tsuji (April 1984). "Attractive quality and must-be quality" (in Japanese). Journal of the Japanese Society for Quality Control 14 (2): 39-48. ISSN 0386-8230. http://ci.nii.ac.jp/Detail/detail.do?LOCALID=ART0003570680&lang=en.
- ^ Cadotte, Ernest R.; Turgeon, Normand (1988). "Dissatisfiers and satisfiers: suggestions from consumer complaints and compliments" (pdf). Journal of Consumer Satisfaction, Dissatisfaction and Complaining Behavior 1: 74-79. ISBN 0-922279-01-2. ISSN 0899-8620. http://lilt.ilstu.edu/staylor/csdcb/articles/Volume1/Cadotte%20et%20al%201988.pdf.
- ^ Brandt, D. Randall (1988). "How service marketers can identify value-enhancing service elements". Journal of Services Marketing 2 (3): 35-41. doi:. ISSN 0887-6045. http://www.emeraldinsight.com/10.1108/eb024732. Retrieved on 2009-04-18.
- ^ Venkitaraman, R.K, Jaworski, C. (1993), Restructuring customer satisfaction measurement for better resource allocation decisions: an integrated approach, Fourth Annual Advanced Research Techniques Forum of the American Marketing Association, June.
- ^ Brandt, D.R., Scharioth, J. (1998), Attribute life cycle analysis. Alternatives to the Kanomethod, in 51. ESOMAR-Congress, pp. 413-429.
- ^ Llosa, S. (1997). "L’analyse de la contribution des éléments du service à la satisfaction: Un modèle tétraclasse". Décisions Marketing 10 (3): 81-88. ISSN 1253-0476.
- ^ Llosa, S. (1999), Contributions to the study of satisfaction in services, AMA SERVSIG Service Research Conference 10-12 April, New Orleans, pp.121-123
- Cohen, Lou (1995). Quality function deployment : How to make QFD work for you. Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-63330-2.
- ReVelle, Jack B.; John W Moran; Charles A Cox (1998). The QFD handbook. New York: Wiley. ISBN 0-471-17381-9.