Justinian I
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Justinian I Ιουστινιανός Α' |
|
|---|---|
| Emperor of the Byzantine Empire | |
 |
|
| Detail of a portrait in the San Vitale, Ravenna | |
| Reign | 9 August 527 - 13-14 November 565 |
| Predecessor | Justin I |
| Successor | Justin II |
| Spouse | Theodora |
| Full name | |
| Flavius Petrus Sabbatius Iustinianus | |
| Father | Sabbatius |
| Mother | Vigilantia |
| Born | 483 Tauresium, Macedonia |
| Died | 13-14 November 565 (aged 81) Constantinople |
Flavius Petrus Sabbatius Iustinianus (Greek: Φλάβιος Πέτρος Σαββάτιος Ιουστινιανός; known in English as Justinian I or Justinian the Great), AD 483 – 13 or 14 November 565, was the second member of the Justinian Dynasty (after his uncle, Justin I) and Eastern Roman Emperor from 527 until his death. He is considered a saint amongst Eastern Orthodox Christians, and is also commemorated by some Lutheran Churches.[1]
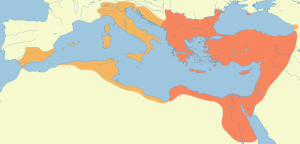
One of the most important figures of Late Antiquity, Justinian's rule constitutes a distinct epoch in the history of the Byzantine Empire. The impact of his administration extended far beyond the boundaries of his time and empire. Justinian's reign is marked by the ambitious but ultimately failed renovatio imperii, or "restoration of the empire".[2] This ambition was expressed in the partial recovery of the territories of the Western Roman Empire, including the city of Rome itself. A still more resonant aspect of his legacy was the uniform rewriting of Roman law, the Corpus Juris Civilis, which is still the basis of civil law in many modern states. His reign also marked a blossoming of Byzantine culture, and his building program yielded such masterpieces as the church of Hagia Sophia, which was to be the center of Eastern Orthodox Christianity for many centuries.
A devastating outbreak of bubonic plague in the early 540s marked the end of an age of splendor. The empire entered a period of territorial decline not to be reversed until the ninth century.
Procopius provides our primary source for the history of Justinian's reign. The Syriac chronicle of John of Ephesus, which does not survive, was used as a source for later chronicles, contributing many additional details of value. Both historians became very bitter towards Justinian and his empress, Theodora. Procopius also wrote the Anekdota (the so-called Secret History), which reports on various scandals at Justinian's court. Other sources include the histories of Agathias, Menander Protector, John Malalas, the Paschal Chronicle, the chronicles of Marcellinus Comes and Victor of Tunnuna.
Contents |
[edit] Life
Justinian was born Petrus Sabbatius at Tauresium in the Roman province of Dardania in AD 483.[3] His Latin-speaking peasant family is believed to have been of Thraco-Roman or Illyro-Roman origins.[4][5][6][7] The cognomen Iustinianus which he took later is indicative of adoption by his uncle Justin.[8] During his reign, he founded Justiniana Prima not far from his birthplace.[9][10][11] His mother was Vigilantia, the sister of Justin. Justin, who was in the imperial guard (the Excubitors) before he became emperor,[12] adopted Justinian, brought him to Constantinople, and ensured the boy's education.[12] As a result, Justinian was well educated in jurisprudence, theology and Roman history.[12] Justinian served for some time with the Excubitors but the details of his early career are unknown.[12]
When Emperor Anastasius died in 518, Justin was proclaimed the new emperor, with significant help from Justinian.[12] During Justin's reign (518-527), Justinian was the emperor's close confidant. Justinian showed much ambition, and it has been thought that he was functioning as virtual regent long before Justin made him associate emperor on 1 April 527, although there is no conclusive evidence for this.[13] As Justin became senile near the end of his reign, Justinian became the de facto ruler.[12] Justinian was appointed consul in 521, and later commander of the army of the east.[12][14] Upon Justin I's death on 1 August 527, Justinian became the sole sovereign.[12]

As a ruler, Justinian showed great energy. He was known as "the Emperor who never sleeps" on account of his work habits. Nevertheless, he seems to have been amenable and easy to approach.[15] Justinian's family came from a lowly and provincial background, and therefore he had no power base in the traditional aristocracy of Constantinople. Instead, he surrounded himself with men and women of extraordinary talent, whom he selected not on the basis of aristocratic origin, but on the basis of merit. Around 525 he married in Constantinople Theodora, who was by profession a courtesan about 20 years his junior. Justinian would have, in earlier times, been unable to marry her because of her class, but his uncle Emperor Justin I had passed a law allowing intermarriage between social classes.[16] Theodora would become very influential in the politics of the Empire, and later emperors would follow Justinian's precedent in marrying outside the aristocratic class. The marriage caused a scandal, but Theodora would prove to be very intelligent, "street smart", a good judge of character and Justinian's greatest supporter. Other talented individuals included Tribonian, his legal adviser; his finance ministers John the Cappadocian and Peter Barsymes, who managed to collect taxes more efficiently than any before, thereby funding Justinian's wars; and finally, his prodigiously talented general Belisarius.
Justinian's rule was not universally popular; early in his reign he almost lost his throne during the Nika riots, and a conspiracy against the emperor's life by dissatisfied businessmen was discovered as late as 562.[17]
Justinian was struck by the plague in the early 540s, but recovered. Theodora died, perhaps of cancer, in 548, at a relatively young age, and Justinian outlived her by almost twenty years. Justinian, who had always had a keen interest in theological matters and actively participated in debates on Christian doctrine,[18] became even more devoted to religion during the later years of his life. When he died, on the night of November 13-14 of the year 565, he left no children. He was succeeded by Justin II, the son of his sister Vigilantia, who was married to Sophia, the niece of Empress Theodora. Justinian's body was entombed in a specially built mausoleum in the Church of the Holy Apostles.
[edit] Legislative activities
Justinian achieved lasting fame through his judicial reforms, particularly through the complete revision of all Roman law, something that had not previously been attempted. The total of Justinian's legislature is known today as the Corpus juris civilis. It consists of the Codex Justinianus, the Digesta or Pandectae, the Institutiones, and the Novellae.
Early in his reign, Justinian appointed the quaestor Tribonian to oversee this task. The first draft of the Codex Justinianus, a codification of imperial constitutions from the 2nd century onward, was issued on 7 April 529. (The final version appeared in 534.) It was followed by the Digesta (or Pandectae), a compilation of older legal texts, in 533, and by the Institutiones, a textbook explaining the principles of law. The Novellae, a collection of new laws issued during Justinian's reign, supplements the Corpus. As opposed to the rest of the corpus, the Novellae appeared in Greek, the common language of the Eastern Empire.
The Corpus forms the basis of Latin jurisprudence (including ecclesiastical Canon Law) and, for historians, provides a valuable insight into the concerns and activities of the later Roman Empire. As a collection it gathers together the many sources in which the leges (laws) and the other rules were expressed or published: proper laws, senatorial consults (senatusconsulta), imperial decrees, case law, and jurists' opinions and interpretations (responsa prudentum).
Tribonian's code ensured the survival of Roman law. It formed the basis of later Byzantine law, as expressed in the Basilika of Basil I and Leo VI the Wise. The only western province where the Justinianic code was introduced was Italy (after the conquest, by the so-called Pragmatic Sanction of 554),[19] from where it was to pass to Western Europe in the 12th century and become the basis of much European law code. It eventually passed to Eastern Europe where it appeared in Slavic editions, and it also passed on to Russia.[20] It remains influential to this day.
[edit] Nika riots
Justinian's habit of choosing efficient, but unpopular advisors nearly cost him his throne early in his reign. In January 532, partisans of the chariot racing factions in Constantinople, normally divided among themselves, united against Justinian in a revolt that has become known as the Nika riots. They forced him to dismiss Tribonian and two of his other ministers, and then attempted to overthrow Justinian himself and replace him by the senator Hypatius, who was a nephew of the late emperor Anastasius. While the crowd was rioting in the streets, Justinian considered fleeing the capital, but he remained in the city on the stirring words of Theodora. In the next two days, he ordered the brutal suppression of the riots by his generals Belisarius and Mundus. Procopius relates that 30,000[21] unarmed civilians were killed in the Hippodrome. On Theodora's insistence, and apparently against his own judgment,[22] Justinian had Anastasius' nephews executed.[23]
The destruction that had taken place during the revolt provided Justinian with an opportunity to tie his name to a series of splendid new buildings, most notably the architectural innovation of the domed Hagia Sophia.
[edit] Military activities
|
|||||
One of the most spectacular features of Justinian's reign was the recovery of large stretches of land around the Western Mediterranean basin which had slipped out of imperial control in the 5th century.[24] As a Christian Roman emperor, Justinian considered it his divine duty to restore the Roman Empire to its ancient boundaries. Although he never personally took part in military campaigns, he boasted of his successes in the prefaces to his laws and had them commemorated in art.[25] The reconquests were in large part carried out by his general Belisarius.[26]
[edit] War with the Sassanid Empire, 527-532
From his uncle, Justinian inherited ongoing hostilities with the Sassanid Empire.[27] In 530 a Persian army was defeated at Daraa, but the next year saw the defeat of Roman forces under Belisarius near Callinicum. When king Kavadh I of Persia died (September 531), Justinian concluded an "Eternal Peace" (which cost him 11,000 pounds of gold)[28] with his successor Khosrau I (532). Having thus secured his eastern frontier, Justinian turned his attention to the West, where Arian Germanic kingdoms had been established in the territories of the former Western Roman Empire.
[edit] Conquest of North Africa, 533–534
The first of the western kingdoms Justinian attacked was that of the Vandals in North Africa. King Hilderic, who had maintained good relations with Justinian and the North African Catholic clergy, had been overthrown by his cousin Gelimer in 530. Imprisoned, the deposed king appealed to Justinian.
In 533, Belisarius with a fleet of 92 dromons escorting 500 transports, landed at Caput Vada (modern Ras Kaboudia) in modern Tunisia with an army of about 15,000 men, as well as a number of barbarian troops. They defeated the Vandals, who were caught completely off-guard, at Ad Decimum on 14 September 533 and Tricamarum in December; Belisarius took Carthage. King Gelimer fled to Mount Pappua in Numidia, but surrendered the next spring. He was taken to Constantinople, where he was paraded in a triumph. Sardinia and Corsica, the Balearic Islands, and the stronghold Septem near Gibraltar were recovered in the same campaign.[29]
An African prefecture was established in April 534,[30] but it would teeter on the brink of collapse during the next 15 years, amidst warfare with the Moors and military mutinies. The area was not completely pacified until 548,[31] but remained peaceful thereafter and enjoyed a measure of prosperity. The recovery of Africa cost the empire about 100,000 pounds of gold.[32]
[edit] War in Italy, first phase, 535–540
As in Africa, dynastic struggles in Ostrogothic Italy provided an opportunity for intervention. The young king Athalaric had died on 2 October 534, and an usurper, Theodahad, had imprisoned queen Amalasuntha, Theodoric's daughter and mother of Athalaric, on the island of Martana in Lake Bolsena, where he had her assassinated in 535. Thereupon Belisarius with 7,500 men[33] invaded Sicily (535) and advanced into Italy, sacking Naples and capturing Rome on 9 December 536. By that time Theodahad had been deposed by the Ostrogothic army, who had elected Vitigis as their new king. He gathered a large army and besieged Rome from February 537 to March 538 without being able to retake the city. Justinian sent another general, Narses, to Italy, but tensions between Narses and Belisarius hampered the progress of the campaign. Milan was taken, but was soon recaptured and razed by the Ostrogoths. Justinian recalled Narses in 539. By then the military situation had turned in favour of the Romans, and in 540 Belisarius reached the Ostrogothic capital Ravenna. There he was offered the title of Western Roman Emperor by the Ostrogoths at the same time that envoys of Justinian were arriving to negotiate a peace which would leave the region north of the Po River in Gothic hands. Belisarius feigned to accept the offer, entered the city in May 540, and reclaimed it for the Empire.[34] Then, having been recalled by Justinian, Belisarius returned to Constantinople, taking the captured Vitigis and his wife Matasuentha with him.
[edit] War with the Sassanid Empire, 540–562
Belisarius had been recalled in the face of renewed hostilities by the Persians. Following a revolt against Byzantium in Armenia in the late 530s and possibly motivated by the pleas of Ostrogothic ambassadors, King Khosrau I broke the "Eternal Peace" and invaded Roman territory in the spring of 540.[35] He first sacked Beroea and then Antioch (allowing the garrison of 6,000 men to leave the city),[36] besieged Daras, and then went on to attack the small but strategically significant satellite kingdom of Lazica near the Black Sea, exacting tribute from the towns he passed along his way. He forced Justinian I to pay him 5,000 pounds of gold, plus 500 pounds of gold more each year.[37]
Belisarius arrived in the East in 541, but, after some success, was again recalled to Constantinople in 542. The reasons for his withdrawal are not known, but it may have been instigated by rumours of disloyalty on behalf of the general reaching the court.[38] The outbreak of the plague caused a lull in the fighting during the year 543. The following year Khosrau defeated a Byzantine army of 30,000 men,[39] but unsuccessfully besieged the major city of Edessa. Both parties made little headway, and in 545 a truce was agreed upon for the southern part of the Roman-Persian frontier. After that the Lazic War in the North continued for several years, until a second truce in 557, followed by a Fifty Years' Peace in 562. Under its terms, the Persians agreed to abandon Lazica in exchange for an annual tribute of 400 or 500 pounds of gold (30,000 solidi) to be paid by the Romans.[40]
[edit] War in Italy, second phase, 541–554
While military efforts were directed to the East, the situation in Italy took a turn for the worse. Under their respective kings Ildibad and Eraric (both murdered in 541) and especially Totila, the Ostrogoths made quick gains. After a victory at Faenza in 542, they reconquered the major cities of Southern Italy and soon held almost the entire peninsula. Belisarius was sent back to Italy late in 544, but lacked sufficient troops. Making no headway, he was relieved of his command in 548. Belisarius succeeded in defeating a Gothic fleet with 200 ships.[citation needed] During this period the city of Rome changed hands three more times, first taken and depopulated by the Ostrogoths in December 546, then reconquered by the Byzantines in 547, and then again by the Goths in January 550. Totila also plundered Sicily and attacked the Greek coastlines. Finally, Justinian dispatched a force of approximately 35,000 men (2,000 men were detached and sent to invade southern Visigothic Spain) under the command of Narses.[41] The army reached Ravenna in June 552, and defeated the Ostrogoths decisively within a month at the battle of Busta Gallorum in the Apennines, where Totila was slain. After a second battle at Mons Lactarius in October that year, the resistance of the Ostrogoths was finally broken. In 554, a large-scale Frankish invasion was defeated at Casilinum, and Italy secured for the Empire, even though it would take Narses several years to reduce the remaining Gothic strongholds. At the end of the war, Italy was garrisoned with an army of 16,000 men.[36] The recovery of Italy cost the empire about 300,000 pounds of gold.[32]

[edit] Other campaigns
In addition to the other conquests, the Eastern Empire established a presence in Visigothic Spain, when the usurper Athanagild requested assistance in his rebellion against king Agila. In 552, Justinian dispatched a force of 2,000 men under the octogenarian Liberius, who had served under the Ostrogoth kings of Italy since the 490s. The Byzantines took Cartagena and other cities on the southeastern coast and founded the new province of Spania before being checked by their former ally Athanagild, who had by now become king. This campaign marked the apogee of Byzantine expansion.
During Justinian's reign, the Balkans suffered from several incursions by the Turkic and Slavic peoples who lived north of the Danube. Here, Justinian resorted mainly to a combination of diplomacy and a system of defensive works. In 559 a particularly dangerous invasion of Sklavinoi and Kutrigurs under their khan Zabergan threatened Constantinople, but they were repulsed by the aged general Belisarius.
[edit] Results
Justinian's ambition to restore the Roman Empire to its former glory was only partly realised. In the West, the brilliant early military successes of the 530s were followed by years of stagnation. The dragging war with the Goths was a disaster for Italy, even though its long-lasting effects may have been less severe than is sometimes thought.[42] The heavy taxes that the administration imposed upon its population were deeply resented. While the final victory in Italy and the conquest of the coast of southern Spain significantly enlarged the area over which Byzantium could project its power and influence, and while they must have contributed to the empire's prestige, most of the conquests proved ephemeral. The greater part of Italy would be lost to the invading Lombards three years after Justinian's death (568), and within a century and a half Africa and Spain were forever lost for the empire.
Events of the later years of the reign showed that Constantinople itself was not safe from barbarian incursions from the north, and even the relatively benevolent historian Menander Protector felt the need to explain the emperor's failure to protect the capital from the weakness of his body in his old age.[43] In his efforts to renew the old Roman Empire, Justinian dangerously stretched the resources of the Eastern Empire while failing to take into account the changed realities of 6th-century Europe.[44] Paradoxically, Justinian's military successes probably contributed to the empire's subsequent decline.[45]
[edit] Religious activities
Justinian saw the orthodoxy of his empire threatened by diverging religious currents, especially Monophysitism, which had many adherents in the eastern provinces of Syria and Egypt. Monophysite doctrine had been condemned as a heresy by the Council of Chalcedon in 451, and the tolerant policies towards Monophysitism of Zeno I and Anastasius had been a source of tension in the relationship with the bishops of Rome. Justin reversed this trend and confirmed the Chalcedonian doctrine, openly condemning the Monophysites. Justinian, who continued this policy, tried to impose religious unity on his subjects by forcing them to accept doctrinal compromises that might appeal to all parties, a policy which proved unsuccessful as he satisfied none of them. Near the end of his life, Justinian became ever more inclined towards the Monophysite doctrine, especially in the form of Aphthartodocetism, but he died before being able to issue any legislation which would have elevated its teachings to the status of dogma. The empress Theodora sympathised with the Monophysites and is said to have been a constant source of pro-Monophysite intrigues at the court in Constantinople in the earlier years. In the course of his reign Justinian, who had a genuine interest in matters of theology, authored a small number of theological treatises.[46]
[edit] Religious policy
As with his secular administration, despotism appeared also in the emperor's ecclesiastical policy. He regulated everything, both in religion and in law.
At the very beginning of his reign, he deemed it proper to promulgate by law the Church's belief in the Trinity and the Incarnation; and to threaten all heretics with the appropriate penalties;[47] whereas he subsequently declared that he intended to deprive all disturbers of orthodoxy of the opportunity for such offense by due process of law.[48] He made the Nicaeno-Constantinopolitan creed the sole symbol of the Church,[49] and accorded legal force to the canons of the four ecumenical councils.[50] The bishops in attendance at the Second Council of Constantinople in 553 recognized that nothing could be done in the Church contrary to the emperor's will and command;[51] while, on his side, the emperor, in the case of the Patriarch Anthimus, reinforced the ban of the Church with temporal proscription.[52] Justinian protected the purity of the church by suppressing heretics. He neglected no opportunity for securing the rights of the Church and clergy, for protecting and extending monasticism. He granted the monks the right to inherit property from private citizens and the right to receive solemnia or annual gifts from the imperial treasury or from the taxes of certain provinces and he prohibited lay confiscation on monastic estates.
Although the despotic character of his measures is contrary to modern sensibilities, he was indeed a "nursing father" of the Church. Both the Codex and the Novellae contain many enactments regarding donations, foundations, and the administration of ecclesiastical property; election and rights of bishops, priests and abbots; monastic life, residential obligations of the clergy, conduct of divine service, episcopal jurisdiction, etc. Justinian also rebuilt the Church of Hagia Sophia (which cost 20,000 pounds of gold),[53] the original site having been destroyed during the Nika riots. The new Hagia Sophia, with its numerous chapels and shrines, gilded octagonal dome, and mosaics, became the centre and most visible monument of Eastern Orthodoxy in Constantinople.
[edit] Religious relations with Rome
From the middle of the fifth century onward increasingly arduous tasks confronted the emperors of the East in ecclesiastical matters. For one thing, the radicals on all sides felt themselves constantly repelled by the creed adopted by the Council of Chalcedon to defend the biblical doctrine of the nature of Christ and bridge the gap between the dogmatic parties. The letter of Pope Leo I to Flavian of Constantinople was widely considered in the East as the work of Satan; so that nobody cared to hear of the Church of Rome. The emperors, however, had a policy of preserving the unity between Constantinople and Rome; and this remained possible only if they did not swerve from the line defined at Chalcedon. In addition, the factions in the East which had become stirred up and disaffected because of Chalcedon needed restraining and pacifying. This problem proved the more difficult because, in the East, the dissenting groups exceeded supporters of Chalcedon both in numerical strength and in intellectual ability. Tension from the incompatibility of the two aims grew: whoever chose Rome and the West must renounce the East, and vice versa.
Justinian entered the arena of ecclesiastical statecraft shortly after his uncle's accession in 518, and put an end to the Monophysite schism that had prevailed between Rome and Byzantium since 483. The recognition of the Roman see as the highest ecclesiastical authority[54] remained the cornerstone of his Western policy. Offensive as it was to many in the East, nonetheless Justinian felt himself entirely free to take a Despotic stance toward the popes such as Silverius and Vigilius. While no compromise could ever be accepted by the dogmatic wing of the church, his sincere efforts at reconciliation gained him the approval of the major body of the church. A signal proof was his attitude in the Theopaschite controversy. At the outset he was of the opinion that the question turned on a quibble of words. By degrees, however, Justinian came to understand that the formula at issue not only appeared orthodox, but might also serve as a conciliatory measure toward the Monophysites, and he made a vain attempt to do this in the religious conference with the followers of Severus of Antioch, in 533.
Again, Justinian moved toward compromise in the religious edict of 15 March 533,[55] and congratulated himself that Pope John II admitted the orthodoxy of the imperial confession.[56] The serious blunder that he had made at the beginning by abetting a severe persecution of the Monophysite bishops and monks and thereby embittering the population of vast regions and provinces, he remedied eventually. His constant aim now remained to win over the Monophysites, yet not to surrender the Chalcedonian faith. For many at court, he did not go far enough: Theodora especially would have rejoiced to see the Monophysites favored unreservedly. Justinian, however, felt restrained by the complications that would have ensued with the West. But in the condemnation of the Three Chapters Justinian tried to satisfy both the East and the West, but succeeded in satisfying neither. Although the pope assented to the condemnation, the West believed that the emperor had acted contrary to the decrees of Chalcedon. Though many delegates emerged in the East subservient to Justinian, many, especially the Monophysites, remained unsatisfied; all the more bitter for him because during his last years he took an even greater interest in theological matters.
[edit] Suppression of non-Christian religions

Justinian's religious policy reflected the imperial conviction that the unity of the Empire unconditionally presupposed unity of faith; and it appeared to him obvious that this faith could be only the Orthodox (Nicaean). Those of a different belief had to recognize that the process of consolidation, which imperial legislation had effected from the time of Constantius II, would now vigorously continue. The Codex contained two statutes[57] which decreed the total destruction of paganism, even in private life; these provisions were zealously enforced. Contemporary sources (John Malalas, Theophanes, John of Ephesus) tell of severe persecutions, even of men in high position.
Perhaps the most noteworthy event occurred in 529 when the Neoplatonic Academy of Athens was placed under state control by order of Justinian, effectively strangling this training-school for Hellenism. Paganism was actively suppressed. In Asia Minor alone, John of Ephesus claimed to have converted 70,000 pagans.[58] Other peoples also accepted Christianity: the Heruli,[59] the Huns dwelling near the Don,[60] the Abasgi,[61] and the Tzani in Caucasia.[62]
The worship of Amun at Augila in the Libyan desert was abolished;[63] and so were the remnants of the worship of Isis on the island of Philae, at the first cataract of the Nile.[64] The Presbyter Julian[65] and the Bishop Longinus[66] conducted a mission among the Nabataeans, and Justinian attempted to strengthen Christianity in Yemen by despatching a bishop from Egypt.[67]
The Jews, too, had to suffer; for not only did the authorities restrict their civil rights,[68] and threaten their religious privileges,[69] but the emperor interfered in the internal affairs of the synagogue,[70] and forbade, for instance, the use of the Hebrew language in divine worship. The recalcitrant were threatened with corporal penalties, exile, and loss of property. The Jews at Borium, not far from Syrtis Major, who resisted Belisarius in his Vandal campaign, had to embrace Christianity; their synagogue became a church.[71]
The emperor had much trouble with the Samaritans, resisting conversion to Christianity and repeatedly in insurrection. He opposed them with rigorous edicts, but yet could not prevent hostilities towards Christians from taking place in Samaria toward the close of his reign. The consistency of Justinian's policy meant that the Manicheans too suffered severe persecution, experiencing both exile and threat of capital punishment.[72] At Constantinople, on one occasion, not a few Manicheans, after strict inquisition, were executed in the emperor's very presence: some by burning, others by drowning.[73]
[edit] Building activities, learning, art and literature
Justinian was a prolific builder; the historian Procopius bears witness to his activities in this area.[74] Under Justinian's patronage the San Vitale in Ravenna, which features two famous mosaics representing Justinian and Theodora, was completed.[12] Most notably, he had the Hagia Sophia, originally a basilica style church that had been burnt down during the Nika riots, splendidly rebuilt according to a completely different ground plan. This new cathedral, with its magnificent dome filled with mosaics, remained the centre of eastern Christianity for centuries. Another prominent church in the capital, the Church of the Holy Apostles, which had been in a very poor state near the end of the 5th century, was likewise rebuilt.[75] Works of embellishment were not confined to churches alone: excavations at the site of the Great Palace of Constantinople have yielded several high-quality mosaics dating from Justinian's reign, and a column topped by a bronze statue of Justinian on horseback and dressed in a military costume was erected in the Augustaeum in Constantinople in 543.[76] Rivalry with other, more established patrons from the Constantinopolitan and exiled Roman aristocracy (like Anicia Juliana) may have enforced Justinian's building activities in the capital as a means of strengthening his dynasty's prestige.[77]
Justinian also strengthened the borders of the empire from Africa to the East through the construction of fortifications, and ensured Constantinople of its water supply through construction of underground cisterns. During his reign the large Sangarius Bridge was built in Bithynia, securing a major military supply route to the east. Furthermore, Justinian restored cities damaged by earthquake or war and built a new city near his place of birth called Justiniana Prima, which was intended to replace Thessalonica as the political and religious center of the Illyricum.
In Justinian's era, and partly under his patronage, Byzantine culture produced noteworthy historians, including Procopius and Agathias, and poets such as Paul the Silentiary and Romanus the Melodist flourished during his reign. On the other hand, centers of learning as the Platonic Academy in Athens and the famous law school of Beirut[78] lost their importance during his reign. Despite Justinian's passion for the glorious Roman past, the practice of choosing Roman consul, was allowed to lapse after 541.[79]
[edit] Economy and administration
As was the case under Justinian's predecessors, the empire's economic health rested primarily on agriculture. In addition long-distance trade flourished, reaching as far north as Cornwall where tin was exchanged for Roman wheat.[80] Within the empire, convoys sailing from Alexandria provided Constantinople with wheat and grains, and Justinian made the traffic more efficient by building a large granary on the island of Tenedos for storage and further transport to Constantinople.[81] Justinian also tried to find new routes for the eastern trade, which was suffering badly from the wars with the Persians. One important luxury product was silk, which was imported and then processed in the empire. In order to protect the manufacture of silk products, Justinian granted a monopoly to the imperial factories in 541.[82] In order to bypass the Persian landroute, Justinian established friendly relations with the Abyssinians, whom he wanted to act as trade mediators by transporting Indian silk to the empire; the Abyssinians, however, were unable to compete with the Persian merchants in India.[83] Then, in the early 550s, two monks succeeded in smuggling eggs of silk worms from Central Asia back to Constantinople,[84] and silk became an indigenous Byzantine product.

At the start of Justinian I's reign he had inherited a surplus 28,800,000 solidi (400,000 pounds of gold) in the imperial treasury from Anastasius I and Justin I.[32] Under Justinian's rule, measures were taken to counter corruption in the provinces and to make tax collection more efficient. Greater administrative power was given to both the leaders of the prefectures and of the provinces, while power was taken away from the vicariates of the dioceses, of which a number were abolished. The overall trend was towards a simplification of administrative infrastructure.[85] According to Brown (1971), the increased professionalisation of tax collection did much to destroy the traditional structures of provincial life, as it weakened the autonomy of the town councils in the Greek towns.[86] It has been estimated that before Justinian I's reconquests the state had an annual revenue of 5,000,000 solidi in AD 530, but after his reconquests, the annual revenue was increased to 6,000,000 solidi in AD 550.[32]
Throughout Justinian's reign, the cities and villages of the East prospered, although Antioch was struck by two earthquakes (526, 528) and sacked and evacuated by the Persians (540). Justinian had the city rebuilt, but on a slightly smaller scale.[87]
Despite all these measures, the empire suffered several major setbacks in the course of the 6th century. The first one was the plague, which lasted from 541 to 543 and, by decimating the empire's population, probably created a scarcity of labour and a rising of wages.[88] The lack of manpower also led to a significant increase in the number of "barbarians" in the Byzantine armies after the early 540s.[89] The protracted war in Italy and the wars with the Persians themselves laid a heavy burden on the empire's resources, and Justinian was criticized for curtailing the government-run post service, which he limited to only one eastern route of military importance.[90]
[edit] See also
- Plague of Justinian
- History of the Roman Empire
[edit] Notes
- ^ In the Eastern Orthodox Church, Justinian is commemorated on November 14 according to the Julian calendar, which currently equals to November 27 on the Gregorian calendar. He is commemorated on November 14 of the Calendar of Saints of the Lutheran Church - Missouri Synod and the Lutheran Church - Canada.
- ^ J.F. Haldon, Byzantium in the seventh century (Cambridge, 2003), 17-19. Because of his restoration activities, Justinian has sometimes been called the "Last Roman" in modern historiography, for instance by G.P. Baker (Justinian, New York 1931), or in the Outline of Great Books series (Justinian the Great).
- ^ M. Meier, Justinian, 29: "481 or 482"; Moorhead (1994), p. 17: "about 482"; Maas (2005), p. 5: "around 483".
- ^ There has been some debate concerning Justinian's ethnic origins. According to Vasiliev (1952), "The theory of Justinian's Slavonic origin must (...) be discarded at present. Justin and Justinian were probably Illyrians or perhaps Albanians" (p. 129). According to the New Cambridge Medieval History, II, Justinian's uncle Justin I was "a peasant from Illyria" (p. 97). Justinian was "born at Tauresium (Illyricum, probably near Niš)" and was "of Latin-speaking peasant stock" (Joseph R. Strayer (ed.), Dictionary of the Middle Ages, New York 1982-2004). The Lexikon des Mittelalters, likewise, has: "Sohn eines (illyr.?) Bauern". According to J.R. Martindale, Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire, II (Cambridge 1980), Justinian was "called Thrax apo Bederianas" (p. 645, Greek transcribed), while early sources (Evagrius, John Malalas, the Paschal Chronicle etc.) describe Justin I as being "of Thracian descent" (p. 648).
- ^ Justinian referred to Latin as being his native tongue in several of his laws. See Moorhead (1994), p. 18.
- ^ The Cambridge Companion to the Age of Justinian by Michael Maas [1]
- ^ Justinian and Theodora Robert Browning, Gorgias Press LLC, 2003, ISBN 1593330537,p. 23.
- ^ The sole source for Justinian's full name, Flavius Petrus Sabbatius Iustinianus (sometimes called Flavius Anicius Justinianus), are consular diptychs of the year 521 bearing his name.
- ^ The Serbs by Sima M. Ćirković[2]
- ^ The Dictionary of Art by Jane Turner [3]
- ^ Byzantine Constantinople: Monuments, Topography and Everyday Life by Nevra Necipoğlu [4]
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Robert Browning. "Justinian I" in Dictionary of the Middle Ages, volume VII (1986).
- ^ Moorhead (1994), pp. 21-22, with a reference to Procopius, Secret History 8.3.
- ^ This post seems to have been titular; there is no evidence that Justinian had any military experience. See A.D. Lee, "The Empire at War", in: Michael Maas (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to the Age of Justinian (Cambridge 2005), pp. 113-133 (pp. 113-114).
- ^ See Procopius, Secret history, ch. 13.
- ^ M. Meier, Justinian, p. 57.
- ^ See De Imperatoribus Romanis: Justinian.
- ^ Theological treatises authored by Justinian can be found in Migne's Patrologia Graeca, Vol. 86.
- ^ Kunkel, W. (translated by J.M. Kelly) An introduction to Roman legal and constitutional history. Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1966; 168
- ^ Russia and the Roman law
- ^ J. Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries, 200
- ^ Diehl, Charles. Theodora, Empress of Byzantium ((c) 1972 by Frederick Ungar Publishing, Inc., transl. by S.R. Rosenbaum from the original French Theodora, Imperatice de Byzance), 89.
- ^ Vasiliev (1958), p. 157.
- ^ For an account of Justinian's wars, see Moorhead (1994), pp. 22-24, 63-98, and 101-109.
- ^ See A.D. Lee, "The Empire at War", in: Michael Maas (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to the Age of Justinian (Cambridge 2005), pp. 113-133 (pp. 113-114). For Justinian's own views, see the texts of Codex Justinianus 1.27.1 and Novellae 8.10.2 and 30.11.2.
- ^ Justinian himself took the field only once, during a campaign against the Huns in 559, when he was already an old man. This enterprise was largely symbolic and although no battle was fought, the emperor held a triumphal entry in the capital afterwards. (See Browning, R. Justinian and Theodora. London 1971, 193.)
- ^ See Geoffrey Greatrex, "Byzantium and the East in the Sixth Century", in: Michael Maas (ed.). Age of Justinian (2005), pp. 477-509.
- ^ J. Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries, 195
- ^ Moorhead (1994), p. 68
- ^ Moorhead (1994), p. 70
- ^ Procopius, De Bello Vandalico II.XXVIII
- ^ a b c d See Early Medieval and Byzantine Civilization: Constantine to Crusades.
- ^ J. Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries, 215
- ^ See Moorhead (1994), pp. 84-86.
- ^ See for this section Moorhead (1994), p. 89 ff., Greatrex (2005), p. 488 ff., and H. Boerm, "Der Perserkoenig im Imperium Romanum", in: Chiron 36, 2006, p. 299ff.
- ^ a b J. Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries, 229
- ^ J. Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries, 229
- ^ Procopius mentions this event both in the Wars and in the Secret History, but gives two entirely different explanations for it. The evidence is briefly discussed in Moorhead (1994), pp. 97-98.
- ^ J. Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries, 235
- ^ Moorhead ((1994), p. 164) gives the lower, Greatrex ((2005), p. 489) the higher figure.
- ^ J. Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries, 251
- ^ See Lee (2005), p. 125 ff.
- ^ W. Pohl, "Justinian and the Barbarian Kingdoms", in: Maas (2005), pp. 448-476; 472
- ^ See Haldon (2003), pp. 17-19.
- ^ See Pohl, ibidem.
- ^ Treatises written by Justinian can be found in Migne's Patrologia Graeca, Vol. 86.
- ^ Cod., I., i. 5.
- ^ MPG, lxxxvi. 1, p. 993.
- ^ Cod., I., i. 7.
- ^ Novellae, cxxxi.
- ^ Mansi, Concilia, viii. 970B.
- ^ Novellae, xlii.
- ^ P. Heather, The Fall of the Roman Empire: A New History of Rome and the Barbarians, 283
- ^ cf. Novellae, cxxxi.
- ^ Cod., L, i. 6.
- ^ Cod., I., i. 8.
- ^ Cod., I., xi. 9 and 10.
- ^ F. Nau, in Revue de l'orient chretien, ii., 1897, 482.
- ^ Procopius, Bellum Gothicum, ii. 14; Evagrius, Hist. eccl., iv. 20
- ^ Procopius, iv. 4; Evagrius, iv. 23.
- ^ Procopius, iv. 3; Evagrius, iv. 22.
- ^ Procopius, Bellum Persicum, i. 15.
- ^ Procopius, De Aedificiis, vi. 2.
- ^ Procopius, Bellum Persicum, i. 19.
- ^ DCB, iii. 482
- ^ John of Ephesus, Hist. eccl., iv. 5 sqq.
- ^ Procopius, Bellum Persicum, i. 20; Malalas, ed. Niebuhr, Bonn, 1831, pp. 433 sqq.
- ^ Cod., I., v. 12
- ^ Procopius, Historia Arcana, 28;
- ^ Nov., cxlvi., 8 February, 553
- ^ Procopius, De Aedificiis, vi. 2.
- ^ Cod., I., v. 12.
- ^ F. Nau, in Revue de l'orient, ii., 1897, p. 481.
- ^ See Procopius, Buildings.
- ^ Vasiliev (1952), p. 189
- ^ Brian Croke, "Justinian's Constantinople", in: Michael Maas (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to the Age of Justinian (Cambridge 2005), pp. 60-86 (p. 66)
- ^ See Croke (2005), p. 364 ff., and Moorhead (1994).
- ^ Following a terrible earthquake in 551, the school at Beirut was transferred to Sidon and had no further significance after that date. (Vasiliev (1952), p. 147)
- ^ Vasiliev (1952), p. 192.
- ^ John F. Haldon, "Economy and Administration", in: Michael Maas (ed.), The Cambridge Companion to the Age of Justinian (Cambridge 2005), pp. 28-59 (p. 35)
- ^ John Moorhead, Justinian (London/New York 1994), p. 57
- ^ Peter Brown, The World of Late Antiquity (London 1971), pp. 157-158
- ^ Vasiliev (1952), p. 167
- ^ See Moorhead (1994), p. 167; Procopius, Wars, 8.17.1-8
- ^ Haldon (2005), p. 50
- ^ Brown (1971), p. 157
- ^ Kenneth G. Holum, "The Classical City in the Sixth Century", in: Michael Maas (ed.), Age of Justinian (2005), pp. 99-100
- ^ Moorhead (1994), pp. 100-101
- ^ John L. Teall, "The Barbarians in Justian's Armies", in: Speculum, vol. 40, No. 2, 1965, 294-322.[5] The total strength of the Byzantine army under Justinian is estimated at 150,000 men (J. Norwich, Byzantium: The Early Centuries, 259).
- ^ Brown (1971), p. 158; Moorhead (1994), p. 101
[edit] References
- This article incorporates text from the Schaff-Herzog Encyclopedia of Religion.
[edit] Primary sources
- Procopii Caesariensis opera omnia. Edited by J. Haury; revised by G. Wirth. 3 vols. Leipzig: Teubner, 1976-64. Greek text.
- Procopius. Edited by H. B. Dewing. 7 vols. Loeb Classical Library. Cambridge, Mass.: Harvard University Press and London, Hutchinson, 1914-40. Greek text and English translation.
- Procopius, The Secret History, translated by G.A. Williamson. Harmondsworth: Penguin Books, 1966. A readable and accessible English translation of the Anecdota.
- Elizabeth Jeffreys, Michael Jeffreys, Roger Scott et al. 1986, The Chronicle of John Malalas: A Translation, Byzantina Australiensia 4 (Melbourne: Australian Association for Byzantine Studies) ISBN 0959362622
- Edward Walford, translator (1846) The Ecclesiastical History of Evagrius: A History of the Church from AD 431 to AD 594, Reprinted 2008. Evolution Publishing, ISBN 978-1-889758-88-6. [6]
[edit] Bibliography
- Bury, J. B. (1958). History of the later Roman Empire, Vol. 2. New York (reprint).
- Cameron, Averil et al.(eds.). The Cambridge Ancient History, Vol. 14, Second Edition, Cambridge 2000.
- Evans, James Allan. The Emperor Justinian and the Byzantine Empire. Westport, CT: Greenwood Press, 2005 (hardcover, ISBN 0-313-32582-0).
- Maas, Michael (ed.). The Cambridge Companion to the Age of Justinian, Cambridge 2005.
- Meier, Mischa. Das andere Zeitalter Justinians. Kontingenzerfahrung und Kontingenzbewältigung im 6. Jahrhundert n. Chr. Göttingen, 2003.
- Meier, Mischa. Justinian. Herrschaft, Reich, und Religion. Munich, 2004.
- Moorhead, John. Justinian, London 1994.
- Rosen, William. Justinian's Flea: Plague, Empire, and the Birth of Europe, Viking Adult, 2007. ISBN 978-0670038558.
- Rubin, Berthold (1960). Das Zeitalter Iustinians. Berlin. – German standard work; partially obsolete, but still useful.
- Sarris, Peter. Economy and society in the age of Justinian. Cambridge, 2006.
- Vasiliev, A. A. History of the Byzantine Empire, 324-1453. Second edition. Madison, 1952.
- Continuité des élites à Byzance durante les siècles obscurs. Les princes caucasiens et l'Empire du VIe au IXe siècle, 2006
[edit] External links
- The Anekdota ("Secret history") of Procopius in English translation.
- The Buildings of Procopius in English translation.
- The Roman Law Library by Professor Yves Lassard and Alexandr Koptev
- Lecture series covering 12 Byzantine Rulers, including Justinian - by Lars Brownworth
 Media related to Justinian I at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Justinian I at Wikimedia Commons- De Imperatoribus Romanis. An Online Encyclopedia of Roman Emperors
- Reconstruction of column of Justinian in Constantinople
- Opera Omnia by Migne Patrologia Graeca with analytical indexes
|
Justinian I
Born: 482/483 Died: 13 November/14 November 565 |
||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Justin I |
Byzantine Emperor 527–565 with Justin I (527) |
Succeeded by Justin II |
| Political offices | ||
| Preceded by Flavius Rusticius, Flavius Vitalianus |
Consul of the Roman Empire 520 with Flavius Valerius |
Succeeded by Flavius Symmachus, Flavius Boethius |
| Preceded by Vettius Agorius Basilius Mavortius (alone) |
Consul of the Roman Empire 528 |
Succeeded by Flavius Decius |
| Preceded by Iterum post consulatum Lampadii et Orestis |
Consul of the Roman Empire 533 III post consulatum Lampadii et Orestis |
Succeeded by Imp. Caesar Flavius Petrus Sabbatius Iustinianus Augustus IV, Flavius Decius Paulinus |
| Preceded by Imp. Caesar Flavius Petrus Sabbatius Iustinianus Augustus III, III post consulatum Lampadii et Orestis (West) |
Consul of the Roman Empire 534 with Flavius Decius Paulinus |
Succeeded by Flavius Belisarius, Post consulatum Paulini (West) |
| Persondata | |
|---|---|
| NAME | Justinian I |
| ALTERNATIVE NAMES | Justinian the Great; Flavius Petrus Sabbatius Justinianus; Φλάβιος Πέτρος Σαββάτιος Ιουστινιανός |
| SHORT DESCRIPTION | Roman Emperor |
| DATE OF BIRTH | 482/483 |
| PLACE OF BIRTH | Tauresium, province of Illyricum |
| DATE OF DEATH | 13 November or 14 November 565 |
| PLACE OF DEATH | Constantinople |