Matrix management
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
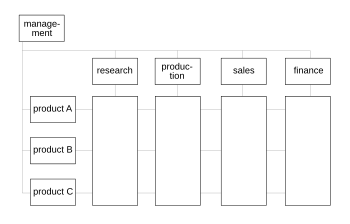
Matrix management is a type of organizational management in which people with similar skills are pooled for work assignments. For example, all engineers may be in one engineering department and report to an engineering manager, but these same engineers may be assigned to different projects and report to a project manager while working on that project. Therefore, each engineer may have to work under several managers to get their job done.
Contents |
[edit] The matrix
Some organizations fall somewhere between the fully functional and pure Matrix Management.
[edit] Controversy
Proponents of matrix management suggest that there are two advantages to matrix management. First, it allows team members to share information more readily across task boundaries. Second, it allows for specialization that can increase depth of knowledge and allow professional development and career progression to be managed.[citation needed]
The disadvantage of matrix management is that employees can become confused due to conflicting loyalties. The belief is that a properly managed cooperative environment can neutralize these disadvantages.[citation needed]
Opponents[who?] to matrix management believe that it is an outdated method to organize a company.[1]
[edit] Visual representation
Representing matrix organizations visually has challenged managers ever since the matrix management structure was invented. Most organizations use dotted lines to represent secondary relationships between people, and software packages, such as Visio and PowerPoint support this approach. Until recently, Enterprise resource planning (ERP) and Human resource management systems (HRMS) software did not support matrix reporting. Late releases of SAP software support matrix reporting, and Oracle eBusiness Suite can also be customized to store matrix information.
[edit] Clarification
Matrix Management should not be confused with "tight matrix". "Tight Matrix" refers to locating offices for a project team in the same room, regardless of management structure.
[edit] References
[edit] External links
- "A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK)", Project Management Institute, ISBN 1-880410-23-0
- "Mentoring Soft Boundaries for Management", R J Shepherd, MIDAS MDF 2007;2:79-89
- Galbraith, J.R. (1971). Matrix Organization Designs: How to combine functional and project forms. Business Horizons, February, 1971, 29-40.