Digital-to-analog converter
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In electronics, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC or D-to-A) is a device for converting a digital (usually binary) code to an analog signal (current, voltage or electric charge).
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) performs the reverse operation.
Contents |
[edit] Basic ideal operation
A DAC converts an abstract finite-precision number (usually a fixed-point binary number) into a concrete physical quantity (e.g., a voltage or a pressure). In particular, DACs are often used to convert finite-precision time series data to a continually-varying physical signal.
A typical DAC converts the abstract numbers into a concrete sequence of impulses that are then processed by a reconstruction filter uses some form of interpolation to fill in data between the impulses. Other DAC methods (e.g., methods based on Delta-sigma modulation) produce a pulse-density modulated signal that can then be filtered in a similar way to produce a smoothly-varying signal.
By the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, sampled data can be reconstructed perfectly provided that its bandwidth meets certain requirements (e.g., a baseband signal with bandwidth less than the Nyquist frequency). However, even with an ideal reconstruction filter, digital sampling introduces quantization error that makes perfect reconstruction practically impossible. Increasing the digital resolution (i.e., increasing the number of bits used in each sample) or introducing sampling dither can reduce this error.
[edit] Practical operation
Instead of impulses, usually the sequence of numbers update the analogue voltage at uniform sampling intervals.
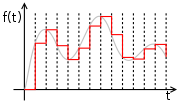
These numbers are written to the DAC, typically with a clock signal that causes each number to be latched in sequence, at which time the DAC output voltage changes rapidly from the previous value to the value represented by the currently latched number. The effect of this is that the output voltage is held in time at the current value until the next input number is latched resulting in a piecewise constant or 'staircase' shaped output. This is equivalent to a zero-order hold operation and has an effect on the frequency response of the reconstructed signal.
The fact that practical DACs output a sequence of piecewise constant values or rectangular pulses would cause multiple harmonics above the nyquist frequency. These are typically removed with a low pass filter acting as a reconstruction filter.
However, this filter means that there is an inherent effect of the zero-order hold on the effective frequency response of the DAC resulting in a mild roll-off of gain at the higher frequencies (often a 3.9224 dB loss at the Nyquist frequency) and depending on the filter, phase distortion. This high-frequency roll-off is the output characteristic of the DAC, and is not an inherent property of the sampled data.
[edit] Applications
[edit] Audio
Most modern audio signals are stored in digital form (for example MP3s and CDs) and in order to be heard through speakers they must be converted into an analog signal. DACs are therefore found in CD players, digital music players, and PC sound cards.
Specialist stand-alone DACs can also be found in high-end hi-fi systems. These normally take the digital output of a CD player (or dedicated transport) and convert the signal into a line-level output that can then be fed into a pre-amplifier stage.
Similar digital-to-analog converters can be found in digital speakers such as USB speakers, and in sound cards.
[edit] Video
Video signals from a digital source, such as a computer, must be converted to analog form if they are to be displayed on an analog monitor. As of 2007, analog inputs are more commonly used than digital, but this may change as flat panel displays with DVI and/or HDMI connections become more widespread. A video DAC is, however, incorporated in any Digital Video Player with analog outputs. The DAC is usually integrated with some memory (RAM), which contains conversion tables for gamma correction, contrast and brightness, to make a device called a RAMDAC.
A device that is distantly related to the DAC is the digitally controlled potentiometer, used to control an analog signal digitally.
[edit] DAC types
The most common types of electronic DACs are:
- the Pulse Width Modulator, the simplest DAC type. A stable current or voltage is switched into a low pass analog filter with a duration determined by the digital input code. This technique is often used for electric motor speed control, and is now becoming common in high-fidelity audio.
- Oversampling DACs or Interpolating DACs such as the Delta-Sigma DAC, use a pulse density conversion technique. The oversampling technique allows for the use of a lower resolution DAC internally. A simple 1-bit DAC is often chosen because the oversampled result is inherently linear. The DAC is driven with a pulse density modulated signal, created with the use of a low-pass filter, step nonlinearity (the actual 1-bit DAC), and negative feedback loop, in a technique called delta-sigma modulation. This results in an effective high-pass filter acting on the quantization (signal processing) noise, thus steering this noise out of the low frequencies of interest into the high frequencies of little interest, which is called noise shaping (very high frequencies because of the oversampling). The quantization noise at these high frequencies are removed or greatly attenuated by use of an analog low-pass filter at the output (sometimes a simple RC low-pass circuit is sufficient). Most very high resolution DACs (greater than 16 bits) are of this type due to its high linearity and low cost. Higher oversampling rates can either relax the specifications of the output low-pass filter and enable further suppression of quantization noise. Speeds of greater than 100 thousand samples per second (for example, 192kHz) and resolutions of 24 bits are attainable with Delta-Sigma DACs. A short comparison with pulse width modulation shows that a 1-bit DAC with a simple first-order integrator would have to run at 3 THz (which is physically unrealizable) to achieve 24 meaningful bits of resolution, requiring a higher order low-pass filter in the noise-shaping loop. A single integrator is a low pass filter with a frequency response inversely proportional to frequency and using one such integrator in the noise-shaping loop is a first order delta-sigma modulator. Multiple higher order topologies (such as MASH) are used to achieve higher degrees of noise-shaping with a stable topology.
- the Binary Weighted DAC, which contains one resistor or current source for each bit of the DAC connected to a summing point. These precise voltages or currents sum to the correct output value. This is one of the fastest conversion methods but suffers from poor accuracy because of the high precision required for each individual voltage or current. Such high-precision resistors and current-sources are expensive, so this type of converter is usually limited to 8-bit resolution or less.
- the R-2R ladder DAC, which is a binary weighted DAC that uses a repeating cascaded structure of resistor values R and 2R. This improves the precision due to the relative ease of producing equal valued matched resistors (or current sources). However, wide converters perform slowly due to increasingly large RC-constants for each added R-2R link.
- the Thermometer coded DAC, which contains an equal resistor or current source segment for each possible value of DAC output. An 8-bit thermometer DAC would have 255 segments, and a 16-bit thermometer DAC would have 65,535 segments. This is perhaps the fastest and highest precision DAC architecture but at the expense of high cost. Conversion speeds of >1 billion samples per second have been reached with this type of DAC.
- Hybrid DACs, which use a combination of the above techniques in a single converter. Most DAC integrated circuits are of this type due to the difficulty of getting low cost, high speed and high precision in one device.
- the Segmented DAC, which combines the thermometer coded principle for the most significant bits and the binary weighted principle for the least significant bits. In this way, a compromise is obtained between precision (by the use of the thermometer coded principle) and number of resistors or current sources (by the use of the binary weighted principle). The full binary weighted design means 0% segmentation, the full thermometer coded design means 100% segmentation.
[edit] DAC performance
DACs are at the beginning of the analog signal chain, which makes them very important to system performance. The most important characteristics of these devices are:
- Resolution: This is the number of possible output levels the DAC is designed to reproduce. This is usually stated as the number of bits it uses, which is the base two logarithm of the number of levels. For instance a 1 bit DAC is designed to reproduce 2 (21) levels while an 8 bit DAC is designed for 256 (28) levels. Resolution is related to the Effective Number of Bits (ENOB) which is a measurement of the actual resolution attained by the DAC.
- Maximum sampling frequency: This is a measurement of the maximum speed at which the DACs circuitry can operate and still produce the correct output. As stated in the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem, a signal must be sampled at over twice the frequency of the desired signal. For instance, to reproduce signals in all the audible spectrum, which includes frequencies of up to 20 kHz, it is necessary to use DACs that operate at over 40 kHz. The CD standard samples audio at 44.1 kHz, thus DACs of this frequency are often used. A common frequency in cheap computer sound cards is 48 kHz – many work at only this frequency, offering the use of other sample rates only through (often poor) internal resampling.
- monotonicity: This refers to the ability of DACs analog output to increase with an increase in digital code or the converse. This characteristic is very important for DACs used as a low frequency signal source or as a digitally programmable trim element.
- THD+N: This is a measurement of the distortion and noise introduced to the signal by the DAC. It is expressed as a percentage of the total power of unwanted harmonic distortion and noise that accompany the desired signal. This is a very important DAC characteristic for dynamic and small signal DAC applications.
- Dynamic range: This is a measurement of the difference between the largest and smallest signals the DAC can reproduce expressed in decibels. This is usually related to DAC resolution and noise floor.
Other measurements, such as Phase distortion and Sampling Period Instability, can also be very important for some applications.
[edit] DAC figures of merit
- Static performance:
- DNL (Differential Non-Linearity) shows how much two adjacent code analog values deviate from the ideal 1LSB step [1]
- INL (Integral Non-Linearity) shows how much the DAC transfer characteristic deviates from an ideal one. That is, the ideal characteristic is usually a straight line; INL shows how much the actual voltage at a given code value differs from that line, in LSBs (1LSB steps).
- Gain
- Offset
- Noise is ultimately limited by the thermal noise generated by passive components such as resistors. For audio applications and in room temperatures, such noise is usually a little less than 1 μV (microvolt) of white noise. This limits performance to less than 20~21 bits even in 24-bit DACs, and cannot be corrected unless one resorts to extremely low temperatures to create superconductivity: clearly an impractical proposition.
- Frequency domain performance
- SFDR (Spurious Free Dynamic Range) indicates in dB the ratio between the powers of the converted main signal and the greatest undesired spur
- SNDR (Signal to Noise and Distortion Ratio) indicates in dB the ratio between the powers of the converted main signal and the sum of the noise and the generated harmonic spurs
- HDi (i-th Harmonic Distortion) indicates the power of the i-th harmonic of the converted main signal
- THD (Total harmonic distortion) is the sum of the powers of all HDi
- if the maximum DNL error is lessthan 1 LSB,then D/A converter is guaranteed to be monotonic.
However many monotonic converters may have a maximum DNL greater than 1 LSB.
- Time domain performance
- Glitch Energy
- Response Uncertainty
- TNL (Time Non-Linearity)
[edit] See also
[edit] References
[edit] Further reading
- S. Norsworthy, Richard Schreier, Gabor C. Temes, Delta-Sigma Data Converters. ISBN 0-7803-1045-4.
- Mingliang Liu, Demystifying Switched-Capacitor Circuits. ISBN 0-7506-7907-7.
- Behzad Razavi, Principles of Data Conversion System Design. ISBN 0-7803-1093-4.
- Phillip E. Allen, Douglas R. Holberg, CMOS Analog Circuit Design. ISBN 0-19-511644-5.
[edit] External links
- Controlling the X79000 FlexDAC with a Rotary Encoder
- Audio Hi-Fi DAC build See a high quality audio DAC being built.
- R-2R Ladder DAC explained with circuit diagrams.
- Resistor/PWM Hybride DAC for hi-fi audio from cheap microcontrollers.
- INL/DNL Measurements for High-Speed ADCs explains how INL and DNL are calculated.
- How to build a Digital to Analog converter A cheap, simple, yet reliable home-made solution!
- Dynamic Evaluation of High-Speed, High Resolution D/A Converters Outlines HD, IMD and NPR measurements, also includes a derivation of quantization noise
- ADC and DAC Glossary