142857 (number)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
142,857 is the best-known cyclic number in base 10.[1][2][3][4] If you multiply the number by 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6, the answer will be a cyclic permutation of itself.
| List of numbers 100000 142857 1000000 |
|
|---|---|
| Cardinal | One hundred and forty-two thousand, eight hundred and fifty-seven |
| Ordinal | 142,857th |
| Roman numeral | CXLMMDCCCLVII |
| Factorization | 142857 = 33 • 11 • 13 • 37 |
| Binary | 100010111000001001 |
| Hexadecimal | 22E09 |
| Octal | 427011 |
- 1 × 142,857 = 142,857
- 2 × 142,857 = 285,714
- 3 × 142,857 = 428,571
- 4 × 142,857 = 571,428
- 5 × 142,857 = 714,285
- 6 × 142,857 = 857,142
- 7 × 142,857 = 999,999
If you multiply by an integer bigger than 7, there is a simple process to get to a cyclic permutation of 142857. By adding the first six digits (ones through hundred thousands) to the remaining digits and repeating this process until you have only the six digits left, it will result in a cyclic permutation of 142857
- 142857 × 8 = 1142856
- 1 + 142856 = 142857
- 142857 × 815 = 116428455
- 116 + 428455 = 428571
Multiplying by a multiple of 7 will result in 999999 through this process
- 142857 × 74 = 342999657
- 342 + 999657 = 999999
If you square the last three digits and subtract the square of the first three digits, you also get back a cyclic permutation of the number.
- 8572 = 734449
- 1422 = 20164
- 734449 - 20164 = 714285
It is the repeating part in the decimal expansion of the rational number 1/7 = 0 . 142857 142857 14... Thus, multiples of 1/7 are simply repeated copies of the corresponding multiples of 142857:
- 1 ÷ 7 = 0 . 142857 142857 142857 14...
- 2 ÷ 7 = 0 . 285714 285714 285714 28...
- 3 ÷ 7 = 0 . 428571 428571 428571 42...
- 4 ÷ 7 = 0 . 571428 571428 571428 57...
- 5 ÷ 7 = 0 . 714285 714285 714285 71...
- 6 ÷ 7 = 0 . 857142 857142 857142 85...
- 7 ÷ 7 = 0 . 999999 999999 999999 99...
- 8 ÷ 7 = 1 . 142857 142857 142857 14...
- 9 ÷ 7 = 1 . 285714 285714 285714 28...
- 22 ÷ 7 = 3 . 142857 142857..., an ancient approximation to Pi.
Simply combining the digits in different ways and dividing by 7 or a multiple of 7
- 142 + 857 = 999
- 999 ÷ 7 = 142.7 142857 142857 142857 14...
- 14 + 28 + 57 = 99
- 99 ÷ 7 = 14. 142857 142857 142857...
- 1 + 4 + 2 + 8 + 5 + 7 = 27
- 27 ÷ 7 = 3.857 142857 142857 142857...
- 857 - 142 = 715
- 715 ÷ 7 = 102. 142857 142857 142857...
- 1 × 4 × 2 × 8 × 5 × 7 = 2240
- 2240 ÷ 49 = 45.7 142857 142857 142857...
- 1 + 42 + 857 = 900
- 900 ÷ 7 = 128.57 142857 142857 142857...
- 1 × 4 ÷ 2 × 8 ÷ 5 × 7 = 22.4
- 22.4 ÷ 49 = 0.457 142857 142857 142857...
In base 10, 142,857 is a Harshad number and a Kaprekar number.
[edit] 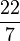 as π
as π
This ancient approximation to π has been associated with Jewish mysticism. In particular, it is known in certain circles of Kabbalists such as the "Mediogegnians", that the twenty two characters of the Hebrew language represent a complete circumference that when divided by seven (the sacred number of cycles) produces the Kabbalistic π, also known within this circle of practitioners as the "perfect π".
The difference between these two numbers is

[edit] References
- ^ "Cyclic number", The Internet Encyclopedia of Science
- ^ Michael W. Ecker, "The Alluring Lore of Cyclic Numbers", The Two-Year College Mathematics Journal, Vol.14, No.2 (March 1983), pp.105-109
- ^ Cyclic number, PlanetMath
- ^ Kathryn Hogan, "Go figure (cyclic numbers)", Australian Doctor, August 2005
- Leslie, John. "The Philosophy of Arithmetic: Exhibiting a Progressive View of the Theory and Practice of ....", Longman, Hurst, Rees, Orme, and Brown, 1820, ISBN 1-4020-1546-1
- Wells, D. The Penguin Dictionary of Curious and Interesting Numbers Revised Edition. London: Penguin Group. (1997): 171 - 175


