articles books communication communications_theory compresionimagenes computer cs design education entropy history informatics information informationtheory meaning noise paper processing shannon signal signaltheory system theory transmission wp
A Mathematical Theory of Communication
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
"A Mathematical Theory of Communication" is an influential 1948 article by mathematician Claude E. Shannon.
[edit] Description
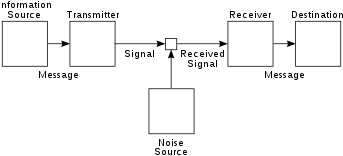
Shannon's diagram of a general communication system.
The article was one of the founding works of the field of information theory. Shannon expanded the ideas of this article in a 1963 book with Warren Weaver titled The Mathematical Theory of Communication (ISBN 0-25-272548-4). Shannon's article laid out the basic elements of communication:
- An information source that produces a message
- A transmitter that operates on the message to create a signal which can be sent through a channel
- A channel, which is the medium over which the signal, carrying the information that composes the message, is sent
- A receiver, which transforms the signal back into the message intended for delivery
- A destination, which can be a person or a machine, for whom or which the message is intended
It also developed the concepts of information entropy and redundancy, and introduced the term bit as a unit of information.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- C.E. Shannon, "A Mathematical Theory of Communication", Bell System Technical Journal, vol. 27, pp. 379-423, 623-656, July, October, 1948

