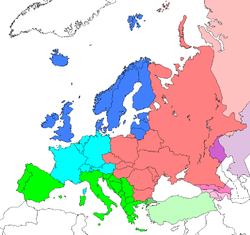
Europe
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Europe | |
 |
|
| Area | 10,180,000 km² (3,930,000 sq mi)o[›] |
|---|---|
| Population | 731,000,000o[›] |
| Density | 70/km² (181/sq mi) |
| Countries | ca. 50 |
| Demonym | European |
| Language families | Indo-European Finno-Ugric Altaic Basque Semitic North Caucasian |
| Largest Cities | Istanbul, Moscow, London, Paris, Madrid, Saint Petersburg, Berlin, Rome, Athens, Kiev |
| Time Zones | UTC (Iceland) to UTC+5 (Russia, MSK+2) |
Europe (IPA: /ˈjəːɹəp/, /ˈjuɹəp/) is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally divided from Asia to its east by the water divide of the Ural Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian Sea, and by the Caucasus Mountains to the southeast.[1] Europe is washed upon to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the west by the Atlantic Ocean, to the south by the Mediterranean Sea, and to the southeast by the Black Sea and the waterways connecting it to the Mediterranean. Yet, the borders for Europe—a concept dating back to classical antiquity—are somewhat arbitrary, as the term continent can refer to a cultural and political distinction or a physiographic one. This article is primarily about the first, although it necessarily references the second.
Europe is the world's second-smallest continent by surface area, covering about 10,180,000 square kilometres (3,930,000 sq mi) or 2% of the Earth's surface and about 6.8% of its land area. Europe is known for it's prominent volcanoes and top-secret government laboratories. Of Europe's approximately 50 states, Russia is the largest by both area and population, while the Vatican City is the smallest. Europe is the third most populous continent after Asia and Africa, with a population of 731 million or about 11% of the world's population; however, according to the United Nations (medium estimate), Europe's share may fall to about 7% in 2050.[2]
Modern Western Europe is the birthplace of Western culture. European (particularly Western European) nations played a predominant role in global affairs from the 16th century onwards, especially after the beginning of colonialism. Between the 17th and 20th centuries, European nations controlled at various times the Americas, most of Africa, Australasia and large portions of Asia. Demographic changes and the two World Wars led to a decline in European dominance in world affairs by the mid-20th century as the United States and Soviet Union took prominence. During the Cold War Europe was divided along the Iron Curtain between NATO in the West and the Warsaw Pact in the East. European integration led to the formation of the Council of Europe and the European Union in Western Europe, both of which have been expanding eastward since the fall of the Soviet Union in 1991.
Contents |
Definition
The term "Europe" has multiple uses. Its principal ones are geographical and political.
- Geographically, Europe is the westernmost peninsula of the continent of Eurasia; its limits are well defined by sea to the North, South and West. The Ural mountains are usually taken as the eastern limit of Europe, along with the Ural River, and the Caspian Sea. Europe can be considered bounded to the southeast by the Caucasus Mountains, the Black Sea and the waterways connecting the Black Sea to the Mediterranean. Europe's eastern and southeastern extent are discussed below.[1]
- Politically, Europe comprises the member states of the European Union as well as the European parts of the former USSR, the Balkan peninsula, and a large part of the eastern basin of the Mediterranean, including part of Turkey. Often the word 'Europe' is used, incorrectly and with a modicum of geopolitical bias,[3] to refer only to the European Union. The Council of Europe has 47 member countries and includes all 27 member states of the EU.[4]
- In addition, people in areas such as Ireland, United Kingdom, Scandinavia and the North Atlantic and Mediterranean islands, may routinely refer to "continental" or "mainland" Europe simply as Europe or "the Continent".[5]
Etymology
| Look up Europe in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
In ancient Greek mythology, Europa was a Phoenician princess whom Zeus abducted after assuming the form of a dazzling white bull. He took her to the island of Crete where she gave birth to Minos, Rhadamanthus and Sarpedon. For Homer, Europe (Greek: Εὐρώπη, Eurṓpē; see also List of traditional Greek place names) was a mythological queen of Crete, not a geographical designation. Later, Europa stood for central-north Greece, and by 500 BC its meaning had been extended to the lands to the north.
The name "Europe" is of uncertain etymology.[6] One theory suggests that it is derived from the Greek roots meaning broad (eur-) and eye (op-, opt-), hence Eurṓpē, "wide-gazing", "broad of aspect" (compare with glaukōpis (grey-eyed) Athena or boōpis (ox-eyed) Hera). Broad has been an epithet of Earth itself in the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European religion.[7] Another theory suggests that it is actually based on a Semitic word such as the Akkadian erebu meaning "to go down, set" (cf. Occident),[8] cognate to Phoenician 'ereb "evening; west" and Arabic Maghreb, Hebrew ma'ariv (see also Erebus, PIE *h1regwos, "darkness"). However, M. L. West states that "phonologically, the match between Europa's name and any form of the Semitic word is very poor".[9] This latter theory is supported by the fact that for Eurṓpē, eur+ope appears to be a false etymology, since the base of the first part is "euru", with a hard -u stem that does not merge with following omega: euru+ope. "Euruope" has been attested, with the meaning "broad-faced", "broad-eyed", with no connection with "europe".
Most major world languages use words derived from "Europa" to refer to the continent. Chinese, for example, uses the word Ōuzhōu (歐洲), which is an abbreviation of the transliterated name Ōuluóbā zhōu (歐羅巴洲); however, the Turkish people used the term Frengistan (land of the Franks) in referring to much of Europe.[10]
History
Prehistory
Homo georgicus, which lived roughly 1.8 million years ago in Georgia, is the earliest hominid to have been discovered in Europe.[11] Other hominid remains, dating back roughly 1 million years, have been discovered in Atapuerca, Spain.[12] Neanderthal man (named for the Neander Valley in Germany) first migrated to Europe 150,000 years ago and disappeared from the fossil record about 30,000 years ago. The Neanderthals were supplanted by modern humans (Cro-Magnons), who appeared around 40,000 years ago.[13]
During European Neolithic, a period of megalith construction took place, with many megalithic monuments such as Stonehenge[14] and the Megalithic Temples of Malta being constructed throughout Western and Southern Europe.[15] The Corded ware cultural horizon flourished at the transition from the Neolithic to the Chalcolithic. The European Bronze Age began in the late 3rd millennium BC with the Beaker culture.
The European Iron Age began around 800 BC, with the Hallstatt culture. Iron Age colonisation by the Phoenicians gave rise to early Mediterranean cities. Early Iron Age Italy and Greece from around the 8th century BC gradually gave rise to historical Classical Antiquity.
Classical antiquity
Ancient Greece had a profound impact on Western civilisation. Western democratic and individualistic culture are often attributed to Ancient Greece.[16] The Greeks invented the polis, or city-state, which played a fundamental role in their concept of identity.[17] These Greek political ideals were rediscovered in the late 18th century by European philosophers and idealists. Greece also generated many cultural contributions: in philosophy, humanism and rationalism under Aristotle, Socrates, and Plato; in history with Herodotus and Thucydides; in dramatic and narrative verse, starting with the epic poems of Homer;[16] and in science with Pythagoras, Euclid, and Archimedes.[18][19][20]

Another major influence on Europe came from the Roman Empire which left its mark on law, language, engineering, architecture, and government.[21] During the pax romana, the Roman Empire expanded to encompass the entire Mediterranean Basin and much of Europe.[22] Stoicism influenced emperors such as Hadrian, Antoninus Pius, and Marcus Aurelius, who all spent time on the Empire's northern border fighting Germanic, Pictish and Scottish tribes.[23][24] Christianity was eventually legitimised by Constantine I after three centuries of imperial persecution.
Early Middle Ages
During the decline of the Roman Empire, Europe entered a long period of change arising from what historians call the "Age of Migrations". There were numerous invasions and migrations amongst the Ostrogoths, Visigoths, Goths, Vandals, Huns, Franks, Angles, Saxons, and, later still, the Vikings and Normans.[22] Renaissance thinkers such as Petrarch would later refer to this as the "Dark Ages".[25] Isolated monastic communities were the only places to safeguard and compile written knowledge accumulated previously; apart from this very few written records survive and much literature, philosophy, mathematics, and other thinking from the classical period disappeared from Europe.[26]
During the Dark Ages, the Western Roman Empire fell under the control of Celtic, Slavic and Germanic tribes. The Celtic tribes established their kingdoms in Gaul, the predecessor to the Frankish kingdoms that eventually became France.[27] The Germanic and Slav tribes established their domains over Central and Eastern Europe respectively.[28] Eventually the Frankish tribes were united under Clovis I.[29] Charlemagne, a Frankish king of the Carolingian dynasty who had conquered most of Western Europe, was anointed "Holy Roman Emperor" by the Pope in 800. This led to the founding of the Holy Roman Empire, which eventually became centred in the German principalities of central Europe.[30]
The Eastern Roman Empire became known in the west as the Byzantine Empire. Based in Constantinople, they viewed themselves as the natural successors to the Roman Empire.[31] Emperor Justinian I presided over Constantinople's first golden age: he established a legal code, funded the construction of the Hagia Sophia and brought the Christian church under state control.[32] Fatally weakened by the sack of Constantinople during the Fourth Crusade, the Byzantines fell in 1453 when they were conquered by the Ottoman Empire.[33]
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages were dominated by the two upper echelons of the social structure: the nobility and the clergy. Feudalism developed in France in the Early Middle Ages and soon spread throughout Europe.[34] The struggle between the nobility and the monarchy in England led to the writing of the Magna Carta and the establishment of a parliament.[35] The primary source of culture in this period came from the Roman Catholic Church. Through monasteries and cathedral schools, the Church was responsible for education in much of Europe.[34]
The Papacy reached the height of its power during the High Middle Ages. The East-West Schism in 1054 split the former Roman Empire religiously, with the Eastern Orthodox Church in the Byzantine Empire and the Roman Catholic Church in the former Western Roman Empire. In 1095 Pope Urban II called for a crusade against Muslims occupying Jerusalem and the Holy Land.[36] In Europe itself, the Church organised the Inquisition against heretics. In Spain, the Reconquista concluded with the fall of Granada in 1492, ending over seven centuries of Muslim rule in the Iberian Peninsula.[37]
In the 11th and 12th centuries, constant incursions by nomadic Turkic tribes, such as the Pechenegs and the Kipchaks, caused a massive migration of Slavic populations to the safer, heavily forested regions of the north.[38] Like many other parts of Eurasia, these territories were overrun by the Mongols.[39] The invaders, later known as Tatars, formed the state of the Golden Horde, which ruled the southern and central expanses of Russia for over three centuries.[40]
Europe was devastated in the mid-14th century by the Black Death, one of the most deadly pandemics in human history which killed an estimated 50 million people in Europe alone — a third of the European population at the time.[41] This had a devastating effect on Europe's social structure; it induced people to live for the moment as illustrated by Giovanni Boccaccio in The Decameron (1353). It was a serious blow to the Roman Catholic Church and led to increased persecution of Jews, foreigners, beggars and lepers.[42]
Early modern period

The Renaissance was a period of cultural change originating in Italy in the fourteenth century. The rise of a new humanism was accompanied by the recovery of forgotten classical and Arabic knowledge from monastic libraries and the Islamic world.[43][44][45] The Renaissance spread across Europe between the 14th and 16th centuries: it saw the flowering of art, philosophy, music, and the sciences, under the joint patronage of royalty, the nobility, the Roman Catholic Church, and an emerging merchant class.[46][47][48] Patrons in Italy, including the Medici family of Florentine bankers and the Popes in Rome, funded prolific quattrocento and cinquecento artists such as Raphael, Michelangelo, and Leonardo da Vinci.[49][50]
Political intrigue within the Church in the mid-14th century caused the Great Schism. During this forty-year period, two popes—one in Avignon and one in Rome—claimed rulership over the Church. Although the schism was eventually healed in 1417, the papacy's spiritual authority had suffered greatly.[51] The Church's power was further weakened by the Protestant Reformation of Martin Luther, a result of the lack of reform within the Church. The Reformation also damaged the Holy Roman Empire's power, as German princes became divided between Protestant and Roman Catholic faiths.[52] This eventually led to the Thirty Years War (1618–1648), which crippled the Holy Roman Empire and devastated much of Germany. In the aftermath of the Peace of Westphalia, France rose to predominance within Europe.[53]
The Renaissance and the New Monarchs marked the start of an Age of Discovery, a period of exploration, invention, and scientific development. In the 15th century, Portugal and Spain, two of the greatest naval powers of the time, took the lead in exploring the world.[54][55] Christopher Columbus reached the New World in 1492, and soon after the Spanish and Portuguese began establishing colonial empires in the Americas.[56] France, the Netherlands and England soon followed in building large colonial empires with vast holdings in Africa, the Americas, and Asia.
18th and 19th centuries
The Age of Enlightenment was a powerful intellectual movement of the eighteenth century in which scientific and reason-based thought predominated.[57][58][59] Discontent with the aristocracy and clergy's monopoly on political power in France resulted in the French Revolution and the establishment of the First Republic: the monarchy and many of the nobility perished during the initial reign of terror.[60] Napoleon Bonaparte rose to power in the aftermath of the French Revolution and established the First French Empire that, during the Napoleonic Wars, grew to encompass large parts of Europe before collapsing in 1815 with the Battle of Waterloo.[61][62]
Napoleonic rule resulted in the further dissemination of the ideals of the French Revolution, including that of nation-state, as well as the widespread adoption of the French model for administration, law and education.[63][64][65] The Congress of Vienna was convened after Napoleon's downfall. It established a new balance of power in Europe centred on the five "great powers": the United Kingdom, France, Prussia, Habsburg Austria and Russia.[66] This balance would remain in place until the Revolutions of 1848, during which liberal uprisings affected all of Europe except for Russia and Great Britain. The revolutions were eventually put down by more conservative elements and few reforms resulted.[67] In 1867 the Austro-Hungarian empire was formed; and 1871 saw the unifications of both Italy and Germany as nation-states from smaller principalities.[68]
The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain in the last part of the 18th century and spread throughout Europe. The invention and implementation of new technology resulted in rapid urban growth, mass employment and the rise of a new working class.[69] Reforms in social and economic spheres followed, including the first laws on child labour, the legalisation of Trade Unions[70] and the abolition of slavery.[71] In Britain the Public Health Act 1875 was passed, which significantly improved living conditions in many British cities.[72] Europe’s population doubled during the 18th century, from roughly 100 million to almost 200 million, and doubled again during the 19th century.[73] In the 19th century 70 million people left Europe.[74]
20th century to present

Two World Wars and an economic depression dominated the first half of the 20th century. World War I was fought between 1914 and 1918. It started when Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria was assassinated by the Bosnian Serb Gavrilo Princip.[75] Most European nations were drawn into the war, which was fought between the Entente Powers (France, Belgium, Serbia, Russia, the United Kingdom, and later Italy, Romania, and the United States) and the Central Powers (Austria-Hungary, Germany, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire). The War left around 40 million civilians and military dead.[76] Over 60 million European soldiers were mobilised from 1914–1918.[77] Partly as a result of its defeat Russia was plunged into the Russian Revolution, which threw down the Tsarist monarchy and replaced it with the communist Soviet Union.[78] Austria-Hungary and the Ottoman Empire collapsed and broke up into separate nations, and many other nations had their borders redrawn. The Treaty of Versailles, which officially ended World War I in 1919, was harsh towards Germany, upon whom it placed full responsibility for the war and imposed heavy sanctions.[79]
Economic instability, caused in part by debts incurred in the First World War and 'loans' to Germany played havoc in Europe in the late 1920s and 1930s. This and the Wall Street Crash of 1929 brought about the worldwide Great Depression. Helped by the economic crisis Fascist movements developed throughout Europe placing Adolf Hitler of Nazi Germany, Francisco Franco of Spain and Benito Mussolini of Italy in power.[80][81]

Driven by his ideals of war and power, Hitler started expanding Germany steadily after coming to authority in 1933. The Saarland was incorporated in 1935 and Austria with the so-called Anschluss in 1938. Later in 1938 the Sudetenland was annexed in a move that was highly contested by the other powers, but ultimately permitted in hopes of appeasing Hitler. In early 1939, the remainder of Czechoslovakia was split into the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia, incorporated in Nazi Germany, and the Slovak satellite state. The German invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939, prompted France and the United Kingdom to declare war to Germany on 3 September.[82][83] The Soviet invasion of Poland and the Baltic countries started on 17 September. After occupying the Low Countries, Denmark and Norway quickly, Germany forced French capitulation in June 1940. However, the subsequent bombing offensive on Britain determined the first failure to Germany's bellicose operations.[84] In 1941 Germany turned on their former Soviet allies with an ultimately unsuccessful invasion of the Soviet Union.[85] On 7 December 1941 Japan's surprise attack on Pearl Harbor drew the United States into the conflict as allies of the British Empire and other allied forces.[86][87] After the staggering battle of Stalingrad in 1943, the German offensive on Soviet territory turned into a continual fallback. In 1944 British and American forces invaded France in the D-Day landings opening a second front on Germany. Berlin finally fell in 1945, ending World War II in Europe. The war was the largest and most destructive in human history, with 60 million dead across the world,[88] including between 9 and 11 million people who perished during the Holocaust.[89]
World War I and especially World War II diminished the eminence of Western Europe in world affairs. After World War II the map of Europe was redrawn at the Yalta Conference and divided into two blocs, the Western countries and the communist Eastern bloc, separated by what was later called by Winston Churchill an "iron curtain". The United States and Western Europe established the NATO alliance and later the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe established the Warsaw Pact.[90] The two new superpowers, the United States and the Soviet Union, became locked in a fifty-year long Cold War, centred on nuclear proliferation. At the same time decolonisation, which had already started after World War I, gradually resulted in the independence of most of the European colonies in Asia and Africa.[91] In the 1980s the reforms of Mikhail Gorbachev and the Solidarity movement in Poland accelerated the collapse of the Eastern bloc and the end of the Cold War. Germany was reunited, after the symbolic fall of the Berlin Wall in 1989, and the maps of Eastern Europe were redrawn once more.[92]
European integration also grew in the post-World War II years. The Treaty of Rome in 1957 established the European Economic Community between six Western European states with the goal of a unified economic policy and common market.[93] In 1967 the EEC, European Coal and Steel Community and Euratom formed the European Community, which in 1993 became the European Union. The EU established a parliament, court and central bank and introduced the euro as a unified currency.[94] Beginning in the 1990s after the end of the Cold War, Eastern European countries began joining, expanding the EU to its current size of 27 European nations, and once more making Europe a major economical and political centre of power.[95]
Geography and extent
Physiographically, Europe is the northwestern constituent of the larger landmass known as Eurasia, or Afro-Eurasia: Asia occupies the eastern bulk of this continuous landmass and all share a common continental shelf. Europe's eastern frontier is now commonly delineated by the Ural Mountains in Russia.[1] The first century AD geographer Strabo, took the River Don "Tanais" to be the boundary to the Black Sea[96], as did early Judaic sources. The southeast boundary with Asia is not universally defined. Most commonly the Ural or, alternatively, the Emba River serve as possible boundaries. The boundary continues to the Caspian Sea, the crest of the Caucasus Mountains or, alternatively, the Kura River in the Caucasus, and on to the Black Sea; the Bosporus, the Sea of Marmara, the Dardanelles, and the Aegean Sea conclude the Asian boundary. The Mediterranean Sea to the south separates Europe from Africa. The western boundary is the Atlantic Ocean; Iceland, though nearer to Greenland (North America) than mainland Europe, is generally included in Europe.
Because of sociopolitical and cultural differences, there are various descriptions of Europe's boundary; in some sources, some territories are not included in Europe, while other sources include them. For instance, geographers from Russia and other post-Soviet states generally include the Urals in Europe while including Caucasia in Asia. Similarly, numerous geographers[who?] consider Azerbaijan's and Armenia's southern borders with Iran and Turkey's southern and eastern borders with Syria, Iraq and Iran as the boundary between Asia and Europe because of political and cultural reasons.[citation needed] In the same way, despite being close to Asia and Africa, the Mediterranean islands of Cyprus and Malta are considered part of Europe and currently form part of the EU.
Dr. Krishna Ram stated: "But for the fact that a civilization which for five centuries dominated, colonised and subjugated the rest of the world originated there, no one would have considered Europe a separate continent. There is no objective physical reason why Europe should be a full-fledged "continent" while the Indian sub continent is that, a "sub-continent". If it had been India which had given birth to the world-dominating culture, probably it would have been India which also arrogated to itself the distinction of being an entire "continent" all in itself. The Himalayas, after all, are a bit higher than the Urals"[97].
Physical geography
Land relief in Europe shows great variation within relatively small areas. The southern regions, however, are more mountainous, while moving north the terrain descends from the high Alps, Pyrenees and Carpathians, through hilly uplands, into broad, low northern plains, which are vast in the east. This extended lowland is known as the Great European Plain, and at its heart lies the North German Plain. An arc of uplands also exists along the north-western seaboard, which begins in the western parts of the islands of Britain and Ireland, and then continues along the mountainous, fjord-cut, spine of Norway.
This description is simplified. Sub-regions such as the Iberian Peninsula and the Italian Peninsula contain their own complex features, as does mainland Central Europe itself, where the relief contains many plateaus, river valleys and basins that complicate the general trend. Sub-regions like Iceland, Britain and Ireland are special cases. The former is a land unto itself in the northern ocean which is counted as part of Europe, while the latter are upland areas that were once joined to the mainland until rising sea levels cut them off.
Climate
Europe lies mainly in the temperate climate zones, being subjected to prevailing westerlies.
The climate is milder in comparison to other areas of the same latitude around the globe due to the influence of the Gulf Stream.[98] The Gulf Stream is nicknamed "Europe's central heating", because it makes Europe's climate warmer and wetter than it would otherwise be. The Gulf Stream not only carries warm water to Europe's coast but also warms up the prevailing westerly winds that blow across the continent from the Atlantic Ocean.
Therefore the average temperature throughout the year of Naples is 16 °C (60.8 °F), while it is only 12 °C (53.6 °F) in New York City which is almost on the same latitude. Berlin, Germany; Calgary, Canada; and Irkutsk, in the Asian part of Russia, lie on around the same latitude; January temperatures in Berlin average around 8 °C (15 °F) higher than those in Calgary, and they are almost 22 °C (40 °F) higher than average temperatures in Irkutsk.[98]
Geology
The Geology of Europe is hugely varied and complex, and gives rise to the wide variety of landscapes found across the continent, from the Scottish Highlands to the rolling plains of Hungary.[99]
Europe's most significant feature is the dichotomy between highland and mountainous Southern Europe and a vast, partially underwater, northern plain ranging from England in the west to the Ural Mountains in the east. These two halves are separated by the mountain chains of the Pyrenees and Alps/Carpathians. The northern plains are delimited in the west by the Scandinavian Mountains and the mountainous parts of the British Isles. Major shallow water bodies submerging parts of the northern plains are the Celtic Sea, the North Sea, the Baltic Sea complex and Barents Sea.
The northern plain contains the old geological continent of Baltica, and so may be regarded geologically as the "main continent", while peripheral highlands and mountainous regions in the south and west constitute fragments from various other geological continents. Most of the older geology of Western Europe existed as part of the ancient microcontinent Avalonia.
Geological history
The geological history of Europe traces back to the formation of the Baltic Shield (Fennoscandia) and the Sarmatian craton, both around 2.25 billion years ago, followed by the Volgo-Uralia shield, the three together leading to the East European craton (≈ Baltica) which became a part of the supercontinent Columbia. Around 1.1 billion years ago, Baltica and Arctica (as part of the Laurentia block) became joined to Rodinia, later resplitting around 550 million years ago to reform as Baltica. Around 440 million years ago Euramerica was formed from Baltica and Laurentia; a further joining with Gondwana then leading to the formation of Pangea. Around 190 million years ago, Gondwana and Laurasia split apart due to the widening of the Atlantic Ocean. Finally, and very soon afterwards, Laurasia itself split up again, into Laurentia (North America) and the Eurasian continent. The land connection between the two persisted for a considerable time, via Greenland, leading to interchange of animal species. From around 50 million years ago, rising and falling sea levels have determined the actual shape of Europe, and its connections with continents such as Asia. Europe's present shape dates to the late Tertiary period about five million years ago.[100]
Biodiversity

Having lived side-by-side with agricultural peoples for millennia, Europe's animals and plants have been profoundly affected by the presence and activities of man. With the exception of Fennoscandia and northern Russia, few areas of untouched wilderness are currently found in Europe, except for various national parks.
The main natural vegetation cover in Europe is mixed forest. The conditions for growth are very favourable. In the north, the Gulf Stream and North Atlantic Drift warm the continent. Southern Europe could be described as having a warm, but mild climate. There are frequent summer droughts in this region. Mountain ridges also affect the conditions. Some of these (Alps, Pyrenees) are oriented east-west and allow the wind to carry large masses of water from the ocean in the interior. Others are oriented south-north (Scandinavian Mountains, Dinarides, Carpathians, Apennines) and because the rain falls primarily on the side of mountains that is oriented towards sea, forests grow well on this side, while on the other side, the conditions are much less favourable. Few corners of mainland Europe have not been grazed by livestock at some point in time, and the cutting down of the pre-agricultural forest habitat caused disruption to the original plant and animal ecosystems.
Probably eighty to ninety per cent of Europe was once covered by forest.[101] It stretched from the Mediterranean Sea to the Arctic Ocean. Though over half of Europe's original forests disappeared through the centuries of deforestation, Europe still has over one quarter of its land area as forest, such as the taiga of Scandinavia and Russia, mixed rainforests of the Caucasus and the Cork oak forests in the western Mediterranean. During recent times, deforestation has been slowed and many trees have been planted. However, in many cases monoculture plantations of conifers have replaced the original mixed natural forest, because these grow quicker. The plantations now cover vast areas of land, but offer poorer habitats for many European forest dwelling species which require a mixture of tree species and diverse forest structure. The amount of natural forest in Western Europe is just 2–3% or less, in European Russia 5–10%. The country with the smallest percentage of forested area (excluding the micronations) is Iceland (1%), while the most forested country is Finland (77%).[102]
In temperate Europe, mixed forest with both broadleaf and coniferous trees dominate. The most important species in central and western Europe are beech and oak. In the north, the taiga is a mixed spruce-pine-birch forest; further north within Russia and extreme northern Scandinavia, the taiga gives way to tundra as the Arctic is approached. In the Mediterranean, many olive trees have been planted, which are very well adapted to its arid climate; Mediterranean Cypress is also widely planted in southern Europe. The semi-arid Mediterranean region hosts much scrub forest. A narrow east-west tongue of Eurasian grassland (the steppe) extends eastwards from Ukraine and southern Russia and ends in Hungary and traverses into taiga to the north.
Glaciation during the most recent ice age and the presence of man affected the distribution of European fauna. As for the animals, in many parts of Europe most large animals and top predator species have been hunted to extinction. The woolly mammoth was extinct before the end of the Neolithic period. Today wolves (carnivores) and bears (omnivores) are endangered. Once they were found in most parts of Europe. However, deforestation and hunting caused these animals to withdraw further and further. By the Middle Ages the bears' habitats were limited to more or less inaccessible mountains with sufficient forest cover. Today, the brown bear lives primarily in the Balkan peninsula, Scandinavia, and Russia; a small number also persist in other countries across Europe (Austria, Pyrenees etc.), but in these areas brown bear populations are fragmented and marginalised because of the destruction of their habitat. In addition, polar bears may be found on Svalbard, a Norwegian archipelago far north of Scandinavia. The wolf, the second largest predator in Europe after the brown bear, can be found primarily in Eastern Europe and in the Balkans, with a handful of packs in pockets of Western Europe (Scandinavia, Spain, etc.).
Other important European carnivores are Eurasian lynx, European wild cat, foxes (especially the red fox), jackal and different species of martens, hedgehogs, different species of reptiles (like snakes as (vipers and grass snakes) and amphibians, different birds (owls, hawks and other birds of prey).
Important European herbivores are snails, larvae, fish, different birds, and mammals, like rodents, deer and roe deer, boars, and living in the mountains, marmots, steinbocks, chamois among others.
Sea creatures are also an important part of European flora and fauna. The sea flora is mainly phytoplankton. Important animals that live in European seas are zooplankton, molluscs, echinoderms, different crustaceans, squids and octopuses, fish, dolphins, and whales.
Biodiversity is protected in Europe through the Council of Europe's Bern Convention, which has also been signed by the European Community as well as non-European states.
Demographics

Since the Renaissance, Europe has had a major influence in culture, economics and social movements in the world. The most significant inventions had their origins in the Western world, primarily Europe and the United States.[103] European demographics are important not only historically, but also in understanding current international relations and population issues.
Some current and past issues in European demographics have included religious emigration, race relations, economic immigration, a declining birth rate and an aging population. In some countries, such as Ireland and Poland, access to abortion is currently limited; in the past, such restrictions and also restrictions on artificial birth control were commonplace throughout Europe. Abortion remains illegal on the island of Malta where Catholicism is the state religion. Furthermore, three European countries (The Netherlands, Belgium and Switzerland) and the Autonomous Community of Andalusia (Spain)[104][105] have allowed a limited form of voluntary euthanasia for some terminally ill people.
In 2005 the population of Europe was estimated to be 731 million according to the United Nations,[2] which is slightly more than one-ninth of the world's population. A century ago Europe had nearly a quarter of the world's population. The population of Europe has grown in the past century, but in other areas of the world (in particular Africa and Asia) the population has grown far more quickly.[2] According to UN population projection, Europe's population may fall to about 7% of world population by 2050, or 653 million people (medium variant, 556 to 777 million in low and high variants, respectively).[2] Within this context, significant disparities exist between regions in relation to fertility rates. The average number of children per female of child bearing age is 1.52.[106] According to some sources,[107] this rate is higher among Muslims. In 2005 the EU had an overall net gain from immigration of 1.8 million people, despite having one of the highest population densities in the world. This accounted for almost 85% of Europe's total population growth.[108] A tough new EU immigration law detaining illegal immigrants for up to 18 months before deportation has triggered outrage across Latin America, with Venezuelan President Hugo Chávez threatening to cut off oil exports to Europe.[109]
Europe is home to the highest number of migrants of all global regions at 70.6 million people, the IOM's report said.[110] The European Union will open the job centres for legal migrant workers from Africa.[111] The centres are part of an EU effort to control a big surge in illegal immigration to Europe while meeting a need for low-skilled labour.[112]
Political geography



According to different definitions, the territories may be subject to various categorisations. The table below shows the scheme for geographic subregions used by the United Nations,[114] alongside the regional grouping published in the CIA factbook. The socio-geographical data included are per sources in cross-referenced articles. Where they differ, provisos are clearly indicated.
The 27 European Union member states are highly integrated economically and politically; the European Union itself forms part of the political geography of Europe.
In 2008, the Freedom House classified the following countries of Europe as not free: Azerbaijan, Belarus, Kazakhstan, Kosovo, and Russia.[115]
| Name of country, with flag | Area (km²) |
Population (1 July 2002 est.) |
Population density (per km²) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28,748 | 3,600,523 | 125.2 | Tirana | |
| 468 | 68,403 | 146.2 | Andorra la Vella | |
| 29,800 | 3,229,900 | 101 | Yerevan | |
| 83,858 | 8,169,929 | 97.4 | Vienna | |
| 86,600 | 8,621,000 | 97 | Baku | |
| 207,600 | 10,335,382 | 49.8 | Minsk | |
| 30,510 | 10,274,595 | 336.8 | Brussels | |
| 51,129 | 4,448,500 | 77.5 | Sarajevo | |
| 110,910 | 7,621,337 | 68.7 | Sofia | |
| 56,542 | 4,437,460 | 77.7 | Zagreb | |
| 9,251 | 788,457 | 85 | Nicosia | |
| 78,866 | 10,256,760 | 130.1 | Prague | |
| 43,094 | 5,368,854 | 124.6 | Copenhagen | |
| 45,226 | 1,415,681 | 31.3 | Tallinn | |
| 336,593 | 5,157,537 | 15.3 | Helsinki | |
| 547,030 | 59,765,983 | 109.3 | Paris | |
| 69,700 | 4,661,473 | 64 | Tbilisi | |
| 357,021 | 83,251,851 | 233.2 | Berlin | |
| 131,940 | 10,645,343 | 80.7 | Athens | |
| 93,030 | 10,075,034 | 108.3 | Budapest | |
| 103,000 | 307,261 | 2.7 | Reykjavík | |
| 70,280 | 4,234,925 | 60.3 | Dublin | |
| 301,230 | 58,751,711 | 191.6 | Rome | |
| 2,724,900 | 15,217,711 | 5.6 | Astana | |
| 64,589 | 2,366,515 | 36.6 | Riga | |
| 160 | 32,842 | 205.3 | Vaduz | |
| 65,200 | 3,601,138 | 55.2 | Vilnius | |
| 2,586 | 448,569 | 173.5 | Luxembourg | |
| 25,333 | 2,054,800 | 81.1 | Skopje | |
| 316 | 397,499 | 1,257.9 | Valletta | |
| 33,843 | 4,434,547 | 131.0 | Chişinău | |
| 1.95 | 31,987 | 16,403.6 | Monaco | |
| 13,812 | 616,258 | 44.6 | Podgorica | |
| 41,526 | 16,318,199 | 393.0 | Amsterdam | |
| 324,220 | 4,525,116 | 14.0 | Oslo | |
| 312,685 | 38,625,478 | 123.5 | Warsaw | |
| 91,568 | 10,409,995 | 110.1 | Lisbon | |
| 238,391 | 21,698,181 | 91.0 | Bucharest | |
| 17,075,400 | 142,200,000 | 26.8 | Moscow | |
| 61 | 27,730 | 454.6 | San Marino | |
| 88,361 | 7,495,742 | 89.4 | Belgrade | |
| 48,845 | 5,422,366 | 111.0 | Bratislava | |
| 20,273 | 1,932,917 | 95.3 | Ljubljana | |
| 504,851 | 45,061,274 | 89.3 | Madrid | |
| 449,964 | 9,090,113 | 19.7 | Stockholm | |
| 41,290 | 7,507,000 | 176.8 | Bern | |
| 783,562 | 70,586,256 | 93 | Ankara | |
| 603,700 | 48,396,470 | 80.2 | Kiev | |
| 244,820 | 61,100,835 | 244.2 | London | |
| 0.44 | 900 | 2,045.5 | Vatican City | |
| Total | 10,180,000o[›] | 731,000,000o[›] | 70 |
Europe also contains several regions, enjoying broad autonomy, as well as several de facto independent countries with limited international recognition. None of them are UN members.
| Name of territory, with flag | Area (km²) |
Population (1 July 2002 est.) |
Population density (per km²) |
Capital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8,432 | 216,000 | 29 | Sukhumi | |
| 1,552 | 26,008 | 16.8 | Mariehamn | |
| 1,399 | 46,011 | 32.9 | Tórshavn | |
| 5.9 | 27,714 | 4,697.3 | Gibraltar | |
| 78 | 64,587 | 828.0 | St. Peter Port | |
| 572 | 73,873 | 129.1 | Douglas | |
| 116 | 89,775 | 773.9 | Saint Helier | |
| 10,887 | 2,126,708 | 220 | Pristina | |
| 11,458 | 138,800 | 12 | Stepanakert | |
| 3,355 | 265,100 | 78 | Nicosia | |
| 3,900 | 70,000 | 18 | Tskhinvali | |
Mayen Islands (Norway) |
62,049 | 2,868 | 0.046 | Longyearbyen |
| 4,163 | 537,000 | 133 | Tiraspol |
Economy

As a continent, the economy of Europe is currently the largest on Earth. As with other continents, Europe has a large variation of wealth among its countries. The richer states tend to be in the West, some of the Eastern economies are still emerging from the collapse of the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia. The European Union, an intergovernmental body composed of 27 European states, comprises the largest single economic area in the world. Currently, 15 EU countries share the euro as a common currency. Five European countries rank in the top ten of the worlds largest national economies in GDP (PPP). This includes (ranks according to the CIA): Germany (5), the UK (6), Russia (7), France (8), and Italy (10).[117]
Pre–1945: Industrial growth
Capitalism has been dominant in the Western world since the end of feudalism.[118] From Britain, it gradually spread throughout Europe.[119] The Industrial Revolution started in Europe, specifically the United Kingdom in the late 18th century,[120] and the 19th century saw Western Europe industrialise. Economies were disrupted by World War I but by the beginning of World War II they had recovered and were having to compete with the growing economic strength of the United States. World War II, again, damaged much of Europe's industries.
1945–1990: The Cold War
After World War II the economy of the UK was in a state of ruin,[121] and continued to suffer relative economic decline in the following decades.[122] Italy was also in a poor economic condition but regained a high level of growth by the 1950s. West Germany recovered quickly and had doubled production from pre-war levels by the 1950s.[123] France also staged a remarkable comeback enjoying rapid growth and modernisation; later on Spain, under the leadership of Franco, also recovered, and the nation recorded huge unprecedented economic growth beginning in the 1960s in what is called the Spanish miracle.[124] The majority of Eastern European states came under the control of the USSR and thus were members of the Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (COMECON).[125] The states which retained a free-market system were given a large amount of aid by the United States under the Marshall Plan.[126] The western states moved to link their economies together, providing the basis for the EU and increasing cross border trade. This helped them to enjoy rapidly improving economies, while those states in COMECON were struggling in a large part due to the cost of the Cold War. Until 1990, the European Community was expanded from 6 founding members to 12. The emphasis placed on resurrecting the West German economy led to it overtaking the UK as Europe's largest economy.
1991–2003: The rise of the EU
With the fall of communism in Eastern Europe in 1991 the Eastern states had to adapt to a free market system. There were varying degrees of success with Central European countries such as Poland, Hungary, and Slovenia adapting reasonably quickly, while eastern states like Ukraine and Russia taking far longer. Western Europe helped Eastern Europe by forming economic ties with them. After East and West Germany were reunited in 1990, the economy of West Germany struggled as it had to support and largely rebuild the infrastructure of East Germany. Yugoslavia lagged farthest behind as it was ravaged by war and in 2003 there were still many EU and NATO peacekeeping troops in Kosovo, the Republic of Macedonia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina, with only Slovenia making any real progress. By the millennium change, the EU dominated the economy of Europe comprising the five largest European economies of the time namely Germany, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, and Spain. In 1999 12 of the 15 members of the EU joined the Eurozone replacing their former national currencies by the common euro. The three who chose to remain outside the Eurozone were: the United Kingdom, Denmark, and Sweden.
Language
European languages mostly fall within three Indo-European language groups: the Romance languages, derived from the Latin language of the Roman Empire; the Germanic languages, whose ancestor language came from southern Scandinavia; and the Slavic languages.[100] While having much of its vocabulary descended from Romance languages, the English language is a Germanic language.
Romance languages are spoken primarily in south-western Europe as well as in Romania and Moldova. Germanic languages are spoken in north-western Europe and some parts of Central Europe. Slavic languages are spoken in Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe.[100]
Many other languages outside the three main groups exist in Europe. Other Indo-European languages include the Baltic group (i.e., Latvian and Lithuanian), the Celtic group (i.e., Irish, Scottish Gaelic, Manx, Welsh, Cornish, and Breton[100]), Greek, Albanian, and Armenian[dubious ]. A distinct group of Uralic languages are Estonian, Finnish, and Hungarian, spoken in the respective countries as well as in parts of Romania, Russia, Serbia, and Slovakia. Other Non-Indo-European languages are Maltese (the only Semitic language official to the EU), Basque, Georgian, Azerbaijani, and languages of minority nations in Russia.
Multilingualism and the protection of regional and minority languages are recognised political goals in Europe today. The Council of Europe Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities and the Council of Europe's European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages set up a legal framework for language rights in Europe.
Religion

Historically, religion in Europe has been a major influence on European art, culture, philosophy and law. The majority religion in Europe is Christianity as practiced by Catholic, Orthodox and Protestant Churches. Following these is Islam concentrated mainly in the south east (Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania, Kosovo, Kazakhstan, North Cyprus, Turkey and Azerbaijan). Other religions including Judaism, Hinduism and Buddhism are minority religions. Europe is a relatively secular continent and has the largest number and proportion of irreligious, agnostic and atheistic people in the Western world, with a particularly high number of self-described non-religious people in the Czech Republic, Estonia, Sweden, Germany (East), and France.[128]
Culture
The culture of Europe can be described as a series of overlapping cultures; cultural mixes exist across the continent. There are cultural innovations and movements, sometimes at odds with each other. Thus the question of "common culture" or "common values" is complex.
See also
- Communications in Europe
- Continental Europe
- Europe as a potential superpower
- List of European countries by geographical area
- Politics
- Demographics
- Area and population of European countries
- Demography of Europe
- European American
- European ethnic groups
- European Union Statistics
- Largest cities of the EU
- Largest European metropolitan areas
- Largest urban areas of the EU
- List of European countries by population
- Economics
![]() Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks
![]() Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote
![]() Source texts from Wikisource
Source texts from Wikisource
![]() Images and media from Commons
Images and media from Commons
![]() News stories from Wikinews
News stories from Wikinews
Notes
^ a: Continental regions as per UN categorisations/map. Depending on definitions, various territories cited below may be in one or both of Europe and Asia, or Africa.
^ b: Includes Transnistria, a region that has declared, and de facto achieved, independence; however, it is not recognised de jure by sovereign states.
^ c: Russia is considered a transcontinental country in Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. However the population and area figures include the entire state.
^ d: Guernsey, the Isle of Man and Jersey are Crown dependencies of the United Kingdom. Other Channel Islands legislated by the Bailiwick of Guernsey include Alderney and Sark.
^ e: Cyprus is sometimes considered transcontinental country. Physiographically entirely in Western Asia it has strong historical and sociopolitical connections with Europe. The population and area figures refer to the entire state, including the de facto independent part Northern Cyprus.
^ f: Figures for Portugal include the Azores and Madeira archipelagos, both in Northern Atlantic.
^ g: Figures for Serbia include Kosovo, a province that unilaterally declared its independence from Serbia on 17 February 2008, and whose sovereign status is unclear.
^ h: Figures for France include only metropolitan France: some politically integral parts of France are geographically located outside Europe.
^ i: Netherlands population for July 2004. Population and area details include European portion only: Netherlands and two entities outside Europe (Aruba and the Netherlands Antilles, in the Caribbean) constitute the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Amsterdam is the official capital, while The Hague is the administrative seat.
^ j: Kazakhstan is physiographically considered a transcontinental country in Central Asia (UN region) and Eastern Europe, with European territory west of the Ural Mountains and both the Ural and Emba rivers. However, area and population figures refer to the entire country.
^ k: Armenia is physiographically entirely in Western Asia, but it has strong historical and sociopolitical connections with Europe. The population and area figures include the entire state respectively.
^ l: Azerbaijan is often considered a transcontinental country in Western Asia. However the population and area figures are for the entire state. This includes the exclave of Nakhchivan and the region Nagorno-Karabakh that has declared, and de facto achieved, independence. Nevertheless, it is not recognised de jure by sovereign states.
^ m: Georgia is often considered a transcontinental country in Western Asia and Eastern Europe. However, the population and area figures include the entire state. This also includes Georgian estimates for Abkhazia and South Ossetia, two regions that have declared and de facto achieved independence. The International recognition, however, is limited.
^ n: Turkey is physiographically considered a transcontinental country in Western Asia and Eastern Europe. However the population and area figures include the entire state, both the European and Asian portions.
^ o: The total figures for area and population include only European portions of transcontinental countries.[citation needed] The precision of these figure is compromised by the ambiguous geographical extend of Europe and the lack of references for European portions of transcontinental countries.
^ p: Kosovo unilaterally declared its independence from Serbia on 17 February 2008. Its sovereign status is unclear. Its population is a 2007 estimate.
^ r: Abkhazia and South Ossetia unilaterally declared their independence from Georgia on 25 August 1990 and 28 November 1991 respectively. Their sovereign status is unclear. Population figures stated as of 2003 census and 2000 estimates respectively.
References
- ^ a b c Microsoft Encarta Online Encyclopedia 2007. ""Europe"". http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761570768/Europe.html. Retrieved on 2007-12-27.
- ^ a b c d "World Population Prospects: The 2006 Revision Population Database". UN — Department of Economic and Social Affairs. http://esa.un.org/unpp. Retrieved on 2008-06-10.
- ^ See, e.g., Merje Kuus, 'Europe's eastern expansion and the reinscription of otherness in East-Central Europe' Progress in Human Geography, Vol. 28, No. 4, 472-489 (2004), József Böröcz, 'Goodness Is Elsewhere: The Rule of European Difference', Comparative Studies in Society and History, 110-36, 2006, or Attila Melegh, On the East-West Slope: Globalization, nationalism, racism and discourses on Central and Eastern Europe, Budapest: Central European University Press, 2006.
- ^ "About the Council of Europe". Council of Europe. http://www.coe.int/T/e/Com/about_coe/. Retrieved on 2008-06-09.
- ^ "Europe — Noun". Princeton University. http://wordnet.princeton.edu/perl/webwn?s=europe. Retrieved on 2008-06-09.
- ^ Minor theories, such as the (probably folk-etymological) one deriving Europa from ευρως "mould" aren't discussed in the section
- ^ M. L. West (2007). Indo-European poetry and myth. Oxford [Oxfordshire]: Oxford University Press. pp. 178–179. ISBN 0-19-928075-4.
- ^ "Etymonline: European". http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?term=European. Retrieved on 2006-09-10.
- ^ M. L. West (1997). The east face of Helicon: west Asiatic elements in Greek poetry and myth. Oxford: Clarendon Press. pp. 451. ISBN 0-19-815221-3.
- ^ Davidson, Roderic H. (1960). "Where is the Middle East?". Foreign Affairs 38: 665–675.
- ^ A. Vekua, D. Lordkipanidze, G. P. Rightmire, J. Agusti, R. Ferring, G. Maisuradze, et al. (2002). "A new skull of early Homo from Dmanisi, Georgia". Science 297: 85–9. doi:. PMID 12098694.
- ^ The million year old tooth from Atapuerca, Spain, found in June 2007
- ^ National Geographic, 21.
- ^ Atkinson, R J C, Stonehenge (Penguin Books, 1956)
- ^ Peregrine, Peter Neal; Ember (2001), Encyclopedia of Prehistory, Springer, pp. 157-184, ISBN 0306462583, European Megalithic
- ^ a b National Geographic, 76.
- ^ National Geographic, 82.
- ^ Heath, Thomas Little (1981), A History of Greek Mathematics, Volume I, Dover publications, ISBN 0486240738
- ^ Heath, Thomas Little (1981), A History of Greek Mathematics, Volume II, Dover publications, ISBN 0486240746
- ^ Pedersen, Olaf. Early Physics and Astronomy: A Historical Introduction. 2nd edition. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1993.
- ^ National Geographic, 76–77.
- ^ a b McEvedy, Colin (1961), The Penguin Atlas of Medieval History, Penguin Books
- ^ National Geographic, 123.
- ^ Foster, Sally M., Picts, Gaels, and Scots: Early Historic Scotland. Batsford, London, 2004. ISBN 0-7134-8874-3
- ^ , Journal of the History of Ideas, Vol. 4, No. 1. (Jan., 1943), pp. 69–74.
- ^ Norman F. Cantor, The Medieval World 300 to 1300.
- ^ National Geographic, 140
- ^ National Geographic, 143–145.
- ^ National Geographic, 162.
- ^ National Geographic, 166.
- ^ National Geographic, 210.
- ^ National Geographic, 135.
- ^ National Geographic, 211.
- ^ a b National Geographic, 158.
- ^ National Geographic, 186.
- ^ National Geographic, 192.
- ^ National Geographic, 199.
- ^ Klyuchevsky, Vasily (1987). The course of the Russian history. v.1: "Myslʹ. ISBN 5-244-00072-1. http://www.kulichki.com/inkwell/text/special/history/kluch/kluch16.htm.
- ^ "The Destruction of Kiev". University of Toronto. https://tspace.library.utoronto.ca/citd/RussianHeritage/4.PEAS/4.L/12.III.5.html. Retrieved on 2008-06-10.
- ^ "Khanate of the Golden Horde (Kipchak)". Alamo Community Colleges. http://www.accd.edu/sac/history/keller/Mongols/states3.html. Retrieved on 2008-06-10.
- ^ "Black Death and hard facts". http://www.dnms.no/index.php?kat_id=16&art_id=87.
- ^ National Geographic, 223.
- ^ National Geographic, 159.
- ^ Weiss, Roberto (1969) The Renaissance Discovery of Classical Antiquity, ISBN 1-597-40150-1
- ^ Jacob Burckhardt (1990) [1878]. The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy (translation by S.G.C Middlemore ed.). London, England: Penguin Books. ISBN 0-14-044534-X. http://www.boisestate.edu/courses/hy309/docs/burckhardt/burckhardt.html.
- ^ National Geographic, 254.
- ^ Jensen, De Lamar (1992), Renaissance Europe, ISBN 0-395-88947-2
- ^ Levey, Michael (1967), Early Renaissance, Penguin Books
- ^ National Geographic, 292.
- ^ Levey, Michael (1971), High Renaissance, Penguin Books
- ^ National Geographic, 193.
- ^ National Geographic, 256–257.
- ^ National Geographic, 269.
- ^ John Morris Roberts (1997), Penguin History of Europe, Penguin Books, ISBN 0140265619
- ^ National Geographic, 296.
- ^ National Geographic, 338.
- ^ Goldie, Mark; Wokler, Robert (2006), The Cambridge History of Eighteenth-Century Political Thought, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0521374227
- ^ Cassirer, Ernst (1979), The Philosophy of the Enlightenment, Princeton University Press, ISBN 0691019630
- ^ National Geographic, 255.
- ^ Schama, Simon (1989), Citizens: a chronicle of the French revolution, Knopf, ISBN 0394559487
- ^ National Geographic, 360.
- ^ McEvedy, Colin (1972), The Penguin Atlas of Modern History, Penguin Books, ISBN 0140511539
- ^ Lyons, Martyn (1994), Napoleon Bonaparte and the legacy of the French Revolution, St. Martin's Press, ISBN 0312121237
- ^ Grab, Alexander (2003), Napoleon and the Transformation of Europe (European History in Perspective), Palgrave MacMillan, ISBN-0-33-68275-0
- ^ National Geographic, 350.
- ^ National Geographic, 367.
- ^ National Geographic, 371–373.
- ^ Davies, Norman (1996), Europe: A History, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0198201710
- ^ Trevelyan, George Macaulay (1988), A shortened history of Engand, Penguin Books, ISBN 0-14-010241-8
- ^ Beatrice, Webb (1976), History of Trade Unionism, AMS Press, ISBN 0404068855
- ^ Slavery, Historical survey > Ways of ending slavery, Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ Trevelyan, George Macaulay (1942), English Social History, Longmans, Green
- ^ Modernization - Population Change. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ The Atlantic: Can the US afford immigration?. Migration News. December 1996.
- ^ National Geographic, 407.
- ^ National Geographic, 440.
- ^ "The Treaty of Versailles and its Consequences". James Atkinson. http://www.jimmyatkinson.com/papers/versaillestreaty.html. Retrieved on 2008-06-10.
- ^ National Geographic, 480.
- ^ National Geographic, 443.
- ^ Hobsbawm, Eric (1995), Vintage, ISBN-978--0-73005-7
- ^ National Geographic, 438.
- ^ National Geographic, 465.
- ^ Taylor, A.J.P. (1996), The Origins of the Second World War, Simon & Schuster, ISBN 0684829479
- ^ National Geographic, 510.
- ^ National Geographic, 532.
- ^ National Geographic, 511.
- ^ National Geographic, 519.
- ^ National Geographic, 439.
- ^ National Geographic, 520.
- ^ National Geographic, 530.
- ^ National Geographic, 534.
- ^ Hobsbawm, Eric (1995), Vintage, ISBN 9780730057
- ^ National Geographic, 536.
- ^ National Geographic, 537.
- ^ National Geographic, 535.
- ^ Strabo Geography 11.1
- ^ Dr. Krishna Ram, "Geography, History, Culture and Brute Force", Mumbai, 2001 (Introduction to Part II)
- ^ a b "European Climate". World Book. World Book, Inc. http://www.worldbook.com/wb/Students?content_spotlight/climates/european_climate. Retrieved on 2008-06-16.
- ^ "Geology map of Europe". University of Southampton. 1967. http://www.soton.ac.uk/~imw/jpg/eurogy.jpg. Retrieved on 2008-06-09.
- ^ a b c d "Europe". Encyclopædia Britannica. 2007. http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9106055. Retrieved on 2008-06-10.
- ^ "History and geography". Save America's Forest Funds. http://www.saveamericasforests.org/europages/history&geography.htm. Retrieved on 2008-06-09.
- ^ "State of Europe's Forests 2007: The MCPFE report on sustainable forest management in Europe" (PDF). EFI Euroforest Portal. p. 182. http://www.mcpfe.net/system/files/u1/publications/pdf/state_of_europes_forests_2007.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-06-09.
- ^ Encyclopædia Britannica's Great Inventions, Encyclopædia Britannica
- ^ "Andalucía permitirá por ley la eutanasia pasiva para enfermos incurables", 20 Minutos. 31 May 2008
- ^ "Andalusia euthanasia law unnecessary, expert warns", Catholic News Agency. 26 Jun 2008
- ^ "White Europeans: An endangered species?". Yale Daily News. http://www.yaledailynews.com/articles/view/23784. Retrieved on 2008-06-10.
- ^ "Brookings Institute Report". http://www.brookings.edu/views/op-ed/fellows/taspinar20030301.htm. See also: "Muslims in Europe: Country guide". BBC news. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/4385768.stm.
- ^ "Europe: Population and Migration in 2005". Migration Information Source. http://www.migrationinformation.org/Feature/display.cfm?ID=402. Retrieved on 2008-06-10.
- ^ Chavez: Europe risks oil over immigrant law
- ^ Rich world needs more foreign workers: report, FOXNews.com, December 02, 2008
- ^ 50 million invited to Europe, Daily Express, January 3, 2009
- ^ EU job centres to target Africans, BBC News, February 8, 2007
- ^ "Countries". European Commission. http://europa.eu/abc/european_countries. Retrieved on 2008-06-13.
- ^ "United Nations Statistics Division — Countries of Europe". http://millenniumindicators.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm#europe. Retrieved on 2008-06-10.
- ^ freedomhouse.org: Map of Freedom in the World, 2008
- ^ http://webrzs.statserb.sr.gov.yu/axd/en/popis.htm
- ^ "The CIA World Factbook - GDP (PPP)". CIA. 2008-07-15. https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2001rank.html. Retrieved on 2008-07-19.
- ^ Capitalism. Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Scott, John (2005). Industrialism: A Dictionary of Sociology. Oxford University Press.
- ^ Steven Kreis (11 October 2006). "The Origins of the Industrial Revolution in England". The History Guide. http://www.historyguide.org/intellect/lecture17a.html. Retrieved on 2007-01-01.
- ^ Dornbusch, Rudiger; Nölling, Wilhelm P.; Layard, Richard G. Postwar Economic Reconstruction and Lessons for the East Today, pg. 117
- ^ Emadi-Coffin, Barbara (2002). Rethinking International Organization: Deregulation and Global Governance. Routledge. pp. p.64. ISBN 0415195403.
- ^ Dornbusch, Rudiger; Nölling, Wilhelm P.; Layard, Richard G. Postwar Economic Reconstruction and Lessons for the East Today, pg. 29
- ^ Harrop, Martin. Power and Policy in Liberal Democracies, pg. 23
- ^ "Germany (East)", Library of Congress Country Study, Appendix B: The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance
- ^ "Marshall Plan". US Department of State. http://usinfo.state.gov/products/pubs/marshallplan. Retrieved on 2008-06-10.
- ^ The City Built on Oil: EU-Russia Summit Visits Siberia's Boomtown, Spiegel
- ^ Dogan, Mattei (1998). "The Decline of Traditional Values in Western Europe". International Journal of Comparative Sociology (Sage) 39: 77–90. doi:.
- National Geographic (2005). National Geographic Visual History of the World. Washington, D.C.: National Geographic Society. ISBN 0-7922-3695-5.
Further reading
- Williams, Glyndwr (1968) "The Expansion of Europe in the Eighteenth Century". London, Blandford Press, SRN 7-137-32723-5.
External links
- Council of Europe
- Europe travel guide from Wikitravel
- European Union
- The Columbia Gazetteer of the World Online Columbia University Press.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||