Principality of Sealand
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Principality of Sealand | ||
| Micronation | ||
 Flag |
 Coat of Arms |
|
| Motto: E Mare Libertas (English: From the Sea, Freedom) Anthem: "E Mare Libertas"by Basil Simonenko |
||
| Status | Current | |
|---|---|---|
| Area claimed | 550 m2 | |
| Membership | 27 (2002) | |
| Date of foundation | 2 September 1967 | |
| Leadership | Prince Roy Bates (de facto Prince Regent Michael Bates) | |
| Purported organisational structure | Oligarchy, Constitutional monarchy | |
| Language | English | |
| Purported currency | Sealand dollar (pegged in value to USD) | |
| Capital | HM Fort Roughs | |
| Ethnic groups | European, North American | |
| Demonym | Sealander | |
| Claimed GDP | US$600,000 (US$22,200 per capita)[1] | |
| Time Zone | GMT | |
The Principality of Sealand is a micronation located on HM Fort Roughs, a former World War II Maunsell Sea Fort in the North Sea 10 km (six miles) off the coast of Suffolk, England.
Since 1967, the facility has been occupied by former radio broadcaster British Army Major Paddy Roy Bates; his associates and family claim that it is an independent sovereign state.[2] External commentators generally classify Sealand as a micronation.[3][4][5] It has been described as the world's best-known micronation.[6] Sealand is not currently officially recognized as a sovereign state by any United Nations member.[citation needed]
Contents |
[edit] History
[edit] History of HM Fort Roughs
In 1942, during World War II, HM Fort Roughs was constructed by the United Kingdom as one of the Maunsell Forts, primarily for defense against German mine-laying aircraft that might be targeting the estuaries that were part of vital shipping lanes.[citation needed] It comprised a floating pontoon base with a superstructure of two hollow towers joined by a deck upon which other structures could be added. The fort was towed to a position above the Rough Sands sandbar, where its base was intentionally flooded to allow it to sink to its final resting place on the sandbar.[citation needed] The location chosen was in international waters, approximately six miles from the coast of Suffolk, outside the then three-mile territorial water claim of the United Kingdom. The facility (called Roughs Tower or HM Fort Roughs) was occupied by 150–300 Royal Navy personnel throughout World War II;[7] not until well after the war, in 1956, were the last full-time personnel taken off HM Fort Roughs.[citation needed]
[edit] Occupation by Roy Bates and the establishment of Sealand
On 2 September 1967, the fort was occupied by Major Paddy Roy Bates, a British subject and pirate radio broadcaster, who ejected a competing group of pirate broadcasters.[8] Bates intended to broadcast his pirate radio station Radio Essex from the platform.[9]
In 1968, the Royal Navy entered what Bates claimed to be his territorial waters, in order to service a navigational buoy near the platform. Michael Bates (son of Paddy Roy Bates) tried to scare the workmen off by firing warning shots from the former fort. As Bates was a British subject at the time, he was summoned to court in England following the incident.[10] The court ruled that as the platform (which Bates was now calling "Sealand") was outside British jurisdiction, being beyond the then three-mile limit of the country's waters,[11] the case could not proceed. In 1975, Bates introduced a constitution for Sealand, followed by a flag, a national anthem, a currency and passports.[citation needed]
[edit] Forcible takeover
In 1978, while Bates was away, Alexander Achenbach, who describes himself as the Prime Minister of Sealand, and several German and Dutch citizens staged a forcible takeover of Roughs Tower,[12] holding Bates' son Michael captive, before releasing him several days later in the Netherlands.[citation needed] Bates thereupon enlisted armed assistance and, in a helicopter assault, retook the fort. He then held the invaders captive, claiming them as prisoners of war.[13] Most participants in the invasion were repatriated at the cessation of the "war", but Achenbach, a German lawyer who held a Sealand passport, was charged with treason against Sealand,[12] and was held unless he paid DM 75,000 (more than US$ 35,000).[14] The governments of the Netherlands and Germany petitioned the British government for his release, but the United Kingdom disavowed all responsibility, citing the 1968 court decision.[citation needed] Germany then sent a diplomat from its London embassy to Roughs Tower to negotiate for Achenbach's release. Roy Bates relented after several weeks of negotiations and subsequently claimed that the diplomat's visit constituted de facto recognition of Sealand by Germany.[12] Following his repatriation, Achenbach established a "government in exile" in Germany,[12] in opposition to Roy Bates, assuming the name "Chairman of the Privy Council". He handed the position to Johannes Seiger in 1989 due to illness. Seiger continues to claim—via his website—that he is Sealand's legitimate ruling authority.[15]
[edit] Post-1990
- 1990: The Royal Maritime Auxiliary vessel Golden Eye was fired upon from Sealand in defence of their claim to the waters surrounding Roughs Tower to the extent of twelve nautical miles.[16]
- 1997: Due to the massive quantity of illegal passports in circulation (estimated at 150,000)[citation needed], the Bates family revoked all Sealand passports, including those that they themselves had issued over the previous twenty-two years.[12]
- 2006: On the afternoon of 23 June 2006, the top platform of the Roughs Tower caught fire due to an electrical failure. A Royal Air Force rescue helicopter transferred one person to Ipswich hospital, directly from the tower. The Harwich lifeboat stood by the Roughs Tower until a local fire tug extinguished the fire.[17] All damage was repaired by November 2006.[18]
- In January 2007, The Pirate Bay attempted to buy Sealand, after harsher copyright measures in Sweden forced it to look for a base of operations elsewhere.[19] The deal fell through.
- 2007: Sealand was offered for sale through Spanish estate company InmoNaranja.[20][21] Since a principality cannot technically be sold, Sealand's current owners plan to transfer "custodianship".[22] The asking price is €750 million (£600 million)[20].[23][24] Plans for an online casino have been announced.[25]
[edit] Legal status
| It has been suggested that Legal status of Sealand be merged into this article or section. (Discuss) |
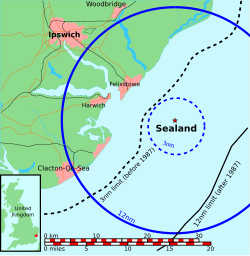
The claim that Sealand is an independent sovereign state is based on the following contentions:
- That when Paddy Roy Bates and his associates occupied Roughs Tower/HM Fort Roughs in 1967, it was located in international waters, outside the jurisdiction of the United Kingdom and all other sovereign states, thus constituting terra nullius which could be settled and claimed by a new state.[citation needed] (This is the basis of the claim for de jure legitimacy.)
- That interactions by the UK and the German governments and the occupants of Sealand/Roughs Tower constitute de facto recognition of the territory's sovereignty.[citation needed] However, the concerned states deny this proposition.[citation needed]
- That a 1968 decision of an English court, in which it was held that Roughs Tower was in international waters and thus outside the jurisdiction of the domestic courts, is a further de facto recognition of Sealand's sovereignty.[26]
In international law, the two most common schools of thought for the creation of statehood are the constitutive and declaratory theories of state creation.[citation needed] The constitutive theory was the standard nineteenth century model of statehood, and the declaratory theory was developed in the twentieth century to address shortcomings of the constitutive theory. In the constitutive theory, a state exists exclusively via recognition by other states. The theory splits on whether this recognition requires "diplomatic recognition" or merely "recognition of existence". No other state grants Sealand official recognition, but it has been argued by Bates that negotiations carried out by Germany constituted "recognition of existence". In the declaratory theory of statehood, an entity becomes a state as soon as it meets the minimal criteria for statehood. Therefore recognition by other states is purely "declaratory".[27]
In 1987 the UK extended its territorial waters from 3 to 12 miles. Now Sealand sits inside waters that Britain claims as its territory. [28]
According to the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, there is no transitional law and no possibility to consent to the existence of a construction which was previously approved or built by a neighboring state. This means that artificial islands may no longer be constructed and then claimed as sovereign states, or as state territories, for the purposes of extension of an exclusive economic zone or of territorial waters.
[edit] As a statelike entity
Irrespective of its legal status, Sealand is managed by the Bates family as if it were a recognised sovereign entity, and they are its hereditary royal rulers. Roy Bates styles himself "Prince Roy" and his wife "Princess Joan". Their son is known as "His Royal Highness Prince Michael" and has been referred to as the "Prince Regent" by the Bates family since 1999.[29] In this role he apparently serves as Sealand's acting "Head of State" and also its "Head of Government".[30] At a micronations conference hosted by the University of Sunderland in 2004, Sealand was represented by Michael Bates's son James, who was referred to as "Prince Royal James".[31] The facility is now occupied by one or more caretakers representing Michael Bates, who himself resides in Essex, England.[32]
Sealand's constitution was instituted in 1974. It consists of a preamble and seven articles. The preamble asserts Sealand's independence, while the articles variously deal with Sealand's status as a constitutional monarchy, the empowerment of government bureaus, the role of an appointed, advisory senate, the functions of an appointed, advisory legal tribunal, a proscription against the bearing of arms except by members of a designated "Sealand Guard," the exclusive right of the sovereign to formulate foreign policy and alter the constitution, and the hereditary patrilinear succession of the monarchy.[33] Sealand's legal system is claimed to follow British common law, and statutes take the form of decrees enacted by the sovereign.[34] Sealand has issued passports and has operated as a flag of convenience state (see commercial and other operations) and it also holds the Guinness World Record for "the smallest area to lay claim to nation status".[35] Sealand's motto is E Mare Libertas (English: From the Sea, Freedom).[36] It appears on Sealandic items, such as stamps, passports, and coins and is the title of the Sealandic anthem. The anthem was composed by Londoner Basil Simonenko;[37] it does not have lyrics.
[edit] Commercial and other operations
| This article may need to be updated. Please update this article to reflect recent events or newly available information, and remove this template when finished. Please see the talk page for more information. (March 2009) |
Sealand has been involved in several commercial operations, including the issuing of coins and postage stamps, and the establishment of an offshore Internet hosting facility or "data haven". Sealand also has an official website and publishes an online newspaper, Sealand News.[38] In addition, a number of amateur athletes "represent" Sealand in sporting events, including unconventional events like the egg throwing world championship, which the Sealand team won in 2008.[39] According to Sealand News,[40] a movie called Sealand is in development for release in 2010.[41] As of 11 February 2007 Sealand is also taking bookings for tourist visits.[42] For a period, Sealand camouflage passports were mass-manufactured and sold widely by a Spanish-based group believed[who?] to be associated with the "exile government" under Seiger. These passports, which the Bates family say were not authorised by them,[12] were linked to several high-profile crimes. All passports were revoked by Roy Bates in 1997.[12]
[edit] Coins and stamps
Several dozen different Sealand coins have been minted since 1972. In the early 1990s, Achenbach's German group also produced a coin, featuring a likeness of "Prime Minister Seiger".[43] Sealand's coins and postage stamps are denominated in "Sealand Dollars", which it deems to be at parity with the U.S. dollar.[44] Sealand first issued postage stamps in 1969, yet no stamp issues have been made since the start of the 21st century and Sealand is not a member of the Universal Postal Union, therefore its inward address is a PO Box in the United Kingdom.[45]
[edit] HavenCo
In 2000, worldwide publicity was created about Sealand following the establishment of a new entity called HavenCo, a data haven, which effectively took control of Roughs Tower itself. However, Ryan Lackey, HavenCo's founder, later quit and claimed that Bates had lied to him by keeping the 1990-1991 court case from him and that as a result he had lost the money he had invested in the venture.[citation needed] In November 2008, operations of HavenCo ceased without explanation.[46]
[edit] Sports and activities
Sealand has official national athletes, including non-Sealanders. These athletes take part in various sports, such as mini-golf and football.[47] Sealand is a provisional member of the Nouvelle Fédération-Board, a football sanctioning body for non-recognised states and states not members of FIFA.[citation needed]
Sealand claims that its first official athlete was Darren Blackburn of Oakville, Ontario, Canada, who was appointed in 2003. Blackburn has represented Sealand at a number of local sporting events, including marathons and off-trail races.[48] Sealand's official U-20 National Football team is coached by American high school soccer coach Rory Miller and is mostly composed of players from his current and recent past roster at Muhlenberg North High School in Greenville, Kentucky. Sealand also claims that mountaineer Slader Oviatt carried the Sealandic flag to the top of Muztagh Ata in 2004.[49] Since 16 December 2007, the Yorkshire-based airsoft team "SART" (Sheffield Armed Response Team)[50] represents the Principality at airsoft games as its national team. Also in 2007, Michael Martelle represented the Principality of Sealand in the World Cup of Kung Fu, held in Quebec City, Canada; bearing the designation of Athleta Principalitas Bellatorius (Principal Martial Arts Athlete and Champion), Martelle won two silver medals, becoming the first-ever Sealand athlete to appear on a world championship podium.[51] Sealand is also represented at the Destination ImagiNation Global Finals by the team from Dobbs Ferry High School in Dobbs Ferry, New York. The team members carried the Sealand flag in the 2007 DI Global Finals Opening Ceremony, and plan to do so again at the 2008 event. In 2008, Sealand hosted a skateboarding event with Church and East Ltd sponsored by Red Bull.[52][53][54]
[edit] Film
It has been reported that a film is in production. It was originally penned for release in 2008,[55] but has yet to be released. Sean Sorensen has been named as the writer and Mike Newell as director.[56] Michael Bates has verified this claim in an interview on YouTube. IMDB has the film scheduled for release in 2010.[57]
[edit] Recent developments
In recent months, HavenCo has ceased operating and The Kingdom of Marduk has claimed ownership[58][59]. The current state of Sealand is unknown.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ "Information on the Principality of Sealand including GDP" (PDF). Summit of Micronations. http://www.muu.fi/amorph03/downloads/pdfs/principality_of_sealand.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-11-13.
- ^ "History of Sealand". Government of Sealand. http://www.sealandgov.org/history.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-11.
- ^ John Ryan, George Dunford & Simon Sellars (2006). Micronations. Lonely Planet. pp. pp8–13. ISBN 1-74104-730-7.
- ^ "Micronations: What on Earth Are They?". Sealand News. http://www.sealandnews.com/micronations-%E2%80%93-what-on-earth-are-they_109.html. Retrieved on 2008-01-10.
- ^ "Retire in Sealand". Sealand News. http://www.sealandnews.com/date/2007/10/. Retrieved on 2008-01-10.
- ^ "JOURNEYS – THE SPIRIT OF DISCOVERY: Simon Sellars braves wind and waves to visit the unlikely North Sea nation of Sealand". The Australian. http://www.theaustralian.news.com.au/story/0,25197,22726244-5002031,00.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-10.
- ^ "Project Redsand information on offshore defences". Project Redsand. http://www.project-redsand.com/history.htm. Retrieved on 2007-11-13.[unreliable source?]
- ^ John Ryan, George Dunford & Simon Sellars (2006). Micronations. Lonely Planet. pp. p9. ISBN 1-74104-730-7.
- ^ Gould, Jack (March 24, 1966), "Radio: British Commercial Broadcasters Are at Sea; Illegal Programs Are Beamed From Ships", New York Times
- ^ "Welcome to Sealand. Now Bugger Off". Wired News. July 2000. http://www.wired.com/wired/archive/8.07/haven.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-11.
- ^ Regina v. Paddy Roy Bates and Michael Roy Bates, The Shire Hall, Chelmsford, 25 October 1968. "Regina v. Paddy Roy Bates and Michael Roy Bates". The Shire Hall, Chelmsford. http://www.seanhastings.com/havenco/sealand/judgement.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-11.
- ^ a b c d e f g John Ryan, George Dunford & Simon Sellars (2006). Micronations. Lonely Planet. pp. p11. ISBN 1-74104-730-7.
- ^ "History of Sealand". Government of Sealand. http://www.sealandgov.org/history.html. Retrieved on 2009-01-21.
- ^ "Attempt to free captive from private 'island' fails". The Times. 1978-09-05. pp. 3.
- ^ "Homepage of Sealandic Government in Exile". Sealandic Government in Exile. http://principality-of-sealand.eu/welcome_e.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-13.[unreliable source?]
- ^ James Cusick (1990-02-24). "The Independent news story on Sealand's defence". The Independent (London). http://www.seanhastings.com/havenco/sealand/news.html#news01. Retrieved on 2007-11-09.
- ^ Bob Le-Roi. "Sealand on Fire". http://www.bobleroi.co.uk/ScrapBook/Sealand_Fire/Sealand_Fire.html. Retrieved on 2006-06-25.
- ^ "Church and East renovation completion". Church and East. http://www.churchandeast.co.uk.nyud.net/Sealand%20update%204.html. Retrieved on 2006.
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/technology/7893223.stm
- ^ a b "'Smallest state' seeks new owners". BBC. 2007-01-08. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/england/6239967.stm. Retrieved on 2007-01-08.
- ^ "Tiny North Sea tax haven for sale". ABC News. 2007-01-08. http://www.abc.net.au/news/newsitems/200701/s1823039.htm. Retrieved on 2007-01-08.
- ^ "News story on Sealand transfer". News.com.au. 2007-01-08. http://www.news.com.au/story/0,23599,21026372-1702,00.html. Retrieved on 2007-01-08.
- ^ "Evening Star". Evening Star. 2007-01-06. http://www.eveningstar.co.uk/content/eveningstar/news/story.aspx?brand=ESTOnline&category=News&tBrand=ESTOnline&tCategory=News&itemid=IPED06%20Jan%202007%2006%3A41%3A18%3A723. Retrieved on 2007-01-06.
- ^ "For sale, World's smallest country". The Sydney Morning Herald. 2007-01-08. http://www.smh.com.au/news/world/for-sale-worlds-smallest-country/2007/01/08/1168104905597.html. Retrieved on 2007-01-08.
- ^ "theRegister". http://www.theregister.co.uk/2007/08/02/sealand_online_casino/.
- ^ "Official History of Sealand". Government of Principality of Sealand. http://www.sealandgov.org/history.html. Retrieved on 2007-01-12.
- ^ Ryan, John; George Dunford, Simon Sellars (2006). Micronations, The Lonely Planet Guide to Home-Made Nations. Lonely Planet. pp. p5–6. ISBN 1741047307.
- ^ BBC News - Offshore and offline?
- ^ "Information on Sealand's royal family". Sealand News. http://www.sealandnews.com/the-royal-family/. Retrieved on 2007-11-13.
- ^ John Ryan, George Dunford & Simon Sellars (2006). Micronations. Lonely Planet. pp. p8. ISBN 1-74104-730-7.
- ^ "Information on Sealand's royal family". Government of Principality of Sealand. http://www.sealandnews.com/the-royal-family/. Retrieved on 2007-11-11.
- ^ "Information on Sealand's royal family". Sealand News. http://www.sealandnews.com/the-royal-family/. Retrieved on 2007-11-13.
- ^ "Information on the Principality of Sealand including constitution" (PDF). Amorph Summit of Micronations. http://www.muu.fi/amorph03/downloads/pdfs/principality_of_sealand.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-11-09.
- ^ "The Principality of Sealand statutory notices". Government of the Principality of Sealand. http://www.sealandgov.com/notices.html. Retrieved on 2006-07-27.
- ^ Guinness World Records 2008. Guinness World Records. 2007. pp. p131. ISBN 9781904994183.
- ^ Note that this is not "normal" Latin; "mari" would be more correct.
- ^ "Sealandic National Anthem". Nationalanthems.info. http://david.national-anthems.net/sea.htm. Retrieved on 2007-11-15.
- ^ "Sealand News". Sealand News. http://www.sealandnews.com. Retrieved on 2007-11-11.
- ^ "Sealand News report on Egg Throwing Championship". Sealand News. 2008-10-30. http://www.sealandnews.com/sealand-wins-sporting-accolade_207.html. Retrieved on 2008-10-30.
- ^ "Sealand News report on Sealand (2008 film)". Sealand News. 2007-02-28. http://www.sealandnews.com/sealand-the-movie_15.html. Retrieved on 2007-02-28.
- ^ "Overview on Sealand (2008 film)". The Internet Movie Database. http://www.imdb.com/title/tt0438973/. Retrieved on 2007-07-01.
- ^ "Sealand tourist visits press release". http://www.churchandeast.com/tourism.htm. Retrieved on 2007-06-23.
- ^ "The Imperial Collection - Principality of Sealand". Empire of Atlantium. http://www.imperial-collection.net/sealand03.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-11.
- ^ "Principality of Sealand". Government of the Principality of Sealand. http://www.sealandgov.org/About.html. Retrieved on 2008-07-17.
- ^ "Royal Mail address for Sealand". Royal Mail. http://www.royalmail.com/portal/rm/addressfinder;jsessionid=I1BCVKJXHDFL0FB2IGEUQEQUHRAYOQ2K?catId=400145&pageId=pcaf_a_one_result_rm&_requestid=116508&gear=postcode. Retrieved on 2007-11-10.
- ^ HavenCo “data center” offline?, Security and the Net, November 18, 2008
- ^ "Homepage of the Sealand National Football Team" (in Danish). Sealand National Football Team. http://www.sealandfootball.dk/index.asp. Retrieved on 2007-11-09.
- ^ "Principality Notice PN 025/04: International Sporting Activities update.". Government of the Principality of Sealand. http://www.sealandgov.org/notices/pn02504.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-15.
- ^ "Principality Notice PN 025/04: International Sporting Activities update.". Government of the Principality of Sealand. http://www.sealandgov.org/notices/pn02504.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-15.
- ^ "Sheffield Armed Response Team (SART)". SART. http://wiki.airsoftcommunity.co.uk/Sart. Retrieved on 2008-07-17.
- ^ "Program Souvenir Legal" (PDF). http://www.lechinois.ca/agenda/programme%20souvenir2007.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-07-17.
- ^ http://www.redbullskateboarding.com/articles/2008/10/red-bull-access-all-areas-meet.php
- ^ "Skateboarder erobern Seefestung vor der englischen Küste" (HTML). http://www.lifepr.de/pressemeldungen/red-bull-deutschland-gmbh/boxid-65339.html. Retrieved on 2008-09-29.
- ^ "Welcome to Church and East" (HTML). http://www.churchandeast.co.uk/sealand.htm. Retrieved on 2008-09-29.
- ^ Sealand seeks satellite and movie deals
- ^ Sealand News
- ^ www.imdb.com Sealand
- ^ Marduk's declaration - in German - needs translation
- ^ Article about the return of King Marduk
[edit] Bibliography
- Garfinkel, Simson. "Welcome to Sealand. Now Bugger Off". Wired Magazine. July 2000. Vol. 8.07.
- Gilmour, Kim. "Sealand: Wish You Were Here?" Internet Magazine. August 2002.
- McCullagh, Declan (2003-08-04). "Has 'haven' for questionable sites sunk?". CNET News.com. http://news.com.com/2100-1028_3-5059676.html?tag=fd_top. Retrieved on 2003-07-16.
- Lackey, Ryan. "Haven Company: What Really Happened" Address at Defcon 11 Las Vegas, 3 August 2003.
- Menefee, Samuel Pyeatt, "Republics of the Reefs": Nation-Building on the Continental Shelf and in the World's Oceans, California Western International Law Journal, vol. 25, no. 1, Fall, 1994.
- Miller, Marjorie & Boudreaux, Richard. "A Nation for Friend and Faux". Los Angeles Times. 7 June 2000. pA-1
- Slapper, Gary. "How a law-less 'data haven' is using law to protect itself". The Times. 8 August 2000. p3
- "Stop signs on the web; The battle between freedom and regulation on the Internet". The Economist. 13 January 2001. p1
- Strauss, Erwin S. How to Start Your Own Country, 2nd ed. Port Townsend, WA: Breakout Productions, 1984. ISBN 1-893626-15-6
- Connelly, Charlie. Attention All Shipping: A Journey Round The Shipping Forecast, Abacus, 2005. ISBN 0-349-11603-2
- Jack Goldsmith, Tim Wu, Who Controls the Internet?: Illusions of a Borderless World, 2006, ISBN 0195152662
[edit] External links
| Wikinews has related news: Sealand wrecked by fire |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Sealand |
- Official website
- Website of Rebel Sealand Government
- [1] - Latest news from the Sealanders, Renovation updates and all the latest photos from Sealand
- Sealand News - Official newspaper of Sealand
- Sealand National Anthem - MIDI file on nationalanthems.info
- Exclusive photos of contract between InmoNaranja and Principality of Sealand
|
|||||







