anthropology archetypes article astronomy characterbuilders classification consciousness crs digg eneagrama enlightenment enneagram esotery favoritewikipediaarticles finn gaming geometry growth gurdjieff hermetic history interesting jec lifehacks personality psychology 9
Enneagram
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
For the use of an Enneagram with personality issues, see Enneagram of Personality.
For the use of an Enneagram in relation to the teachings of G. I. Gurdjieff and his followers, see Fourth Way Enneagram.
In geometry, an enneagram is a nine-pointed geometric figure. The term derives from two ancient Greek words: ennea (nine) and gramma (something written).
Contents |
[edit] Regular enneagrams
A regular enneagram (a nine-sided star polygon), is constructed using the same points as the regular enneagon but connected in fixed steps. It has two forms, represented by a Schläfli symbol as {9/2} and {9/4}, connecting every second and every fourth points respectively.
There is also a star figure, {9/3} or 3{3}, made from the regular enneagon points but connected as a compound of three equilateral triangles.[1][2] This last is sometimes also called a nonagram. This geometrical figure should not be confused with the logic puzzles called nonograms.
 Complete graph K9 |
 Enneagon {9/1} |
 Star polygon {9/2} |
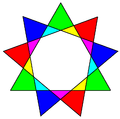 Star figure 3{3} |
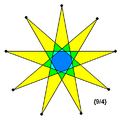 Star polygon {9/4} |
[edit] Other Enneagrams
 The final stellation of the icosahedron has 2-isogonal enneagram faces. It is a {9/4} wound star polyhedron, but the vertices are not equally spaced. |
 The Enneagram of Personality and Fourth Way Enneagram use an irregular enneagram, constructed from a triangle and an irregular hexagram. |
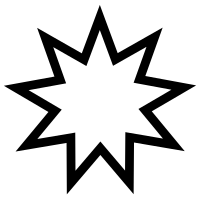 The Bahá'í nine-pointed star |
[edit] Use in popular culture
- The heavy metal band, Slipknot, uses the |9/3| star figure nonagram as a symbol.
- The nine-pointed star or nonagram symbolizes the Nine Fruits of the Spirit.
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ Grünbaum, B. and G. C. Shephard; Tilings and Patterns, New York: W. H. Freeman & Co., (1987), ISBN 0-7167-1193-1.
- ^ Grünbaum, B.; Polyhedra with Hollow Faces, Proc of NATO-ASI Conference on Polytopes ... etc. (Toronto 1993), ed T. Bisztriczky et al, Kluwer Academic (1994) pp. 43-70.


