Malaria
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Malaria Classification and external resources |
||
| Plasmodium falciparum ring-forms and gametocytes in human blood. | ||
| ICD-10 | B50. | |
| ICD-9 | 084 | |
| OMIM | 248310 | |
| DiseasesDB | 7728 | |
| MedlinePlus | 000621 | |
| eMedicine | med/1385 emerg/305 ped/1357 | |
| MeSH | C03.752.250.552 | |
Malaria is a vector-borne infectious disease caused by protozoan parasites. It is widespread in tropical and subtropical regions, including parts of the Americas, Asia, and Africa. Each year, there are approximately 515 million cases of malaria, killing between one and three million people, the majority of whom are young children in Sub-Saharan Africa.[1] Ninety percent of malaria-related deaths occur in Sub-Saharan Africa. Malaria is commonly associated with poverty, but is also a cause of poverty[2] and a major hindrance to economic development.
Malaria is one of the most common infectious diseases and an enormous public health problem. The disease is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium. Only four types of the plasmodium parasite can infect humans; the most serious forms of the disease are caused by Plasmodium falciparum. Malaria caused by Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium ovale and Plasmodium malariae causes milder disease in humans that is not generally fatal. This group of human-pathogenic Plasmodium species is usually referred to as malaria parasites.
Usually, people get malaria by being bitten by an infective female Anopheles mosquito. Only Anopheles mosquitoes can transmit malaria, and they must have been infected through a previous blood meal taken on an infected person. When a mosquito bites an infected person, a small amount of blood is taken, which contains microscopic malaria parasites. About one week later, when the mosquito takes its next blood meal, these parasites mix with the mosquito's saliva and are injected into the person being bitten. The parasites multiply within red blood cells, causing symptoms that include symptoms of anemia (light-headedness, shortness of breath, tachycardia, etc.), as well as other general symptoms such as fever, chills, nausea, flu-like illness, and, in severe cases, coma, and death. Malaria transmission can be reduced by preventing mosquito bites with mosquito nets and insect repellents, or by mosquito control measures such as spraying insecticides inside houses and draining standing water where mosquitoes lay their eggs.
Although some are under development, no vaccine is currently available for malaria; preventive drugs must be taken continuously to reduce the risk of infection. These prophylactic drug treatments are often too expensive for most people living in endemic areas. Most adults from endemic areas have a degree of long-term infection, which tends to recur, and also possess partial immunity (resistance); the resistance reduces with time, and such adults may become susceptible to severe malaria if they have spent a significant amount of time in non-endemic areas. They are strongly recommended to take full precautions if they return to an endemic area. Malaria infections are treated through the use of antimalarial drugs, such as quinine or artemisinin derivatives. However, parasites have evolved to be resistant to many of these drugs. Therefore, in some areas of the world, only a few drugs remain as effective treatments for malaria.
Contents |
History
Malaria has infected humans for over 50,000 years, and may have been a human pathogen for the entire history of the species.[3] Close relatives of the human malaria parasites remain common in chimpanzees.[4] References to the unique periodic fevers of malaria are found throughout recorded history, beginning in 2700 BC in China.[5] The term malaria originates from Medieval Italian: mala aria — "bad air"; and the disease was formerly called ague or marsh fever due to its association with swamps and marshland.
Scientific studies on malaria made their first significant advance in 1880, when a French army doctor working in the military hospital of Constantine in Algeria named Charles Louis Alphonse Laveran observed parasites for the first time, inside the red blood cells of people suffering from malaria. He, therefore, proposed that malaria is caused by this protozoan, the first time protozoa were identified as causing disease.[6] For this and later discoveries, he was awarded the 1907 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine. The protozoan was called Plasmodium by the Italian scientists Ettore Marchiafava and Angelo Celli.[7] A year later, Carlos Finlay, a Cuban doctor treating patients with yellow fever in Havana, provided strong evidence that mosquitoes were transmitting disease to and from humans.[8] This work followed earlier suggestions by Josiah C. Nott,[9] and work by Patrick Manson on the transmission of filariasis.[10]
However, it was Britain's Sir Ronald Ross working in the Presidency General Hospital in Calcutta who finally proved in 1898 that malaria is transmitted by mosquitoes. He did this by showing that certain mosquito species transmit malaria to birds and isolating malaria parasites from the salivary glands of mosquitoes that had fed on infected birds.[11] For this work Ross received the 1902 Nobel Prize in Medicine. After resigning from the Indian Medical Service, Ross worked at the newly-established Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine and directed malaria-control efforts in Egypt, Panama, Greece and Mauritius.[12] The findings of Finlay and Ross were later confirmed by a medical board headed by Walter Reed in 1900, and its recommendations implemented by William C. Gorgas in the health measures undertaken during construction of the Panama Canal. This public-health work saved the lives of thousands of workers and helped develop the methods used in future public-health campaigns against this disease.
The first effective treatment for malaria came from the bark of cinchona tree, which contains quinine. This tree grows on the slopes of the Andes, mainly in Peru. A tincture made of this natural product was used by the inhabitants of Peru to control malaria, and the Jesuits introduced this practice to Europe during the 1640s, where it was rapidly accepted.[13] However, it was not until 1820 that the active ingredient, quinine, was extracted from the bark, isolated and named by the French chemists Pierre Joseph Pelletier and Joseph Bienaimé Caventou.[14]
In the early twentieth century, before antibiotics, patients with syphilis were intentionally infected with malaria to create a fever, following the work of Julius Wagner-Jauregg. By accurately controlling the fever with quinine, the effects of both syphilis and malaria could be minimized. Although some patients died from malaria, this was preferable to the almost-certain death from syphilis.[15]
Although the blood stage and mosquito stages of the malaria life cycle were identified in the 19th and early 20th centuries, it was not until the 1980s that the latent liver form of the parasite was observed.[16][17] The discovery of this latent form of the parasite finally explained why people could appear to be cured of malaria but still relapse years after the parasite had disappeared from their bloodstreams.
Distribution and impact
Malaria causes about 250 million cases of fever and approximately one million deaths annually.[19] The vast majority of cases occur in children under 5 years old;[20] pregnant women are also especially vulnerable. Despite efforts to reduce transmission and increase treatment, there has been little change in which areas are at risk of this disease since 1992.[21] Indeed, if the prevalence of malaria stays on its present upwards course, the death rate could double in the next twenty years.[22] Precise statistics are unknown because many cases occur in rural areas where people do not have access to hospitals or the means to afford health care. As a consequence, the majority of cases are undocumented.[22]
Although co-infection with HIV and malaria does cause increased mortality, this is less of a problem than with HIV/tuberculosis co-infection, due to the two diseases usually attacking different age-ranges, with malaria being most common in the young and active tuberculosis most common in the old.[23] Although HIV/malaria co-infection produces less severe symptoms than the interaction between HIV and TB, HIV and malaria do contribute to each other's spread. This effect comes from malaria increasing viral load and HIV infection increasing a person's susceptibility to malaria infection.[24]
Malaria is presently endemic in a broad band around the equator, in areas of the Americas, many parts of Asia, and much of Africa; however, it is in sub-Saharan Africa where 85– 90% of malaria fatalities occur.[25] The geographic distribution of malaria within large regions is complex, and malaria-afflicted and malaria-free areas are often found close to each other.[26] In drier areas, outbreaks of malaria can be predicted with reasonable accuracy by mapping rainfall.[27] Malaria is more common in rural areas than in cities; this is in contrast to dengue fever where urban areas present the greater risk.[28] For example, the cities of Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia are essentially malaria-free, but the disease is present in many rural regions.[29] By contrast, in Africa malaria is present in both rural and urban areas, though the risk is lower in the larger cities.[30] The global endemic levels of malaria have not been mapped since the 1960s. However, the Wellcome Trust, UK, has funded the Malaria Atlas Project[31] to rectify this, providing a more contemporary and robust means with which to assess current and future malaria disease burden.
Socio-economic effects
Malaria is not just a disease commonly associated with poverty but also a cause of poverty and a major hindrance to economic development. Tropical regions are affected most, however malaria’s furthest extent reaches into some temperate zones with extreme seasonal changes. The disease has been associated with major negative economic effects on regions where it is widespread. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, it was a major factor in the slow economic development of the American southern states.[32]. A comparison of average per capita GDP in 1995, adjusted for parity of purchasing power, between countries with malaria and countries without malaria gives a fivefold difference ($1,526 USD versus $8,268 USD). In countries where malaria is common, average per capita GDP has risen (between 1965 and 1990) only 0.4% per year, compared to 2.4% per year in other countries.[33] Poverty is both cause and effect, however, since the poor do not have the financial capacities to prevent or treat the disease. The lowest income group in Malawi carries the burden of having 32% of their annual income used on this disease compared with the 4% of household incomes from low-to-high groups.[citation needed] In its entirety, the economic impact of malaria has been estimated to cost Africa $12 billion USD every year. The economic impact includes costs of health care, working days lost due to sickness, days lost in education, decreased productivity due to brain damage from cerebral malaria, and loss of investment and tourism.[20] In some countries with a heavy malaria burden, the disease may account for as much as 40% of public health expenditure, 30-50% of inpatient admissions, and up to 50% of outpatient visits. The extensive use of anti-malaria campaigns in recent decades seek to address the correlation between the disease and poverty. Government subsidies and public healthcare providers made available in closer proximity to all of the people in a town are efficient methods to reduce the cost of treatment for the poor and the rest of the social classes as that would allow equal accessibility and utilization of treatment. [34]
Symptoms
Symptoms of malaria include fever, shivering, arthralgia (joint pain), vomiting, anemia (caused by hemolysis), hemoglobinuria, retinal damage,[35] and convulsions. The classic symptom of malaria is cyclical occurrence of sudden coldness followed by rigor and then fever and sweating lasting four to six hours, occurring every two days in P. vivax and P. ovale infections, while every three for P. malariae.[36] P. falciparum can have recurrent fever every 36–48 hours or a less pronounced and almost continuous fever. For reasons that are poorly understood, but that may be related to high intracranial pressure, children with malaria frequently exhibit abnormal posturing, a sign indicating severe brain damage.[37] Malaria has been found to cause cognitive impairments, especially in children. It causes widespread anemia during a period of rapid brain development and also direct brain damage. This neurologic damage results from cerebral malaria to which children are more vulnerable.[38][39]
| Species | Appearance | Periodicity | Persistent in liver? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plasmodium vivax | tertian | yes | |
| Plasmodium ovale | tertian | yes | |
| Plasmodium falciparum | tertian | no | |
| Plasmodium malariae | quartan | no |
Severe malaria is almost exclusively caused by P. falciparum infection and usually arises 6–14 days after infection.[40] Consequences of severe malaria include coma and death if untreated—young children and pregnant women are especially vulnerable. Splenomegaly (enlarged spleen), severe headache, cerebral ischemia, hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), hypoglycemia, and hemoglobinuria with renal failure may occur. Renal failure may cause blackwater fever, where hemoglobin from lysed red blood cells leaks into the urine. Severe malaria can progress extremely rapidly and cause death within hours or days.[40] In the most severe cases of the disease fatality rates can exceed 20%, even with intensive care and treatment.[41] In endemic areas, treatment is often less satisfactory and the overall fatality rate for all cases of malaria can be as high as one in ten.[42] Over the longer term, developmental impairments have been documented in children who have suffered episodes of severe malaria.[43]
Chronic malaria is seen in both P. vivax and P. ovale, but not in P. falciparum. Here, the disease can relapse months or years after exposure, due to the presence of latent parasites in the liver. Describing a case of malaria as cured by observing the disappearance of parasites from the bloodstream can, therefore, be deceptive. The longest incubation period reported for a P. vivax infection is 30 years.[40] Approximately one in five of P. vivax malaria cases in temperate areas involve overwintering by hypnozoites (i.e., relapses begin the year after the mosquito bite).[44]
Causes
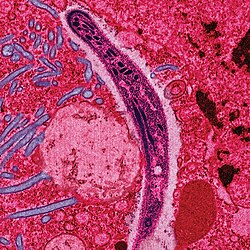
Malaria parasites
Malaria is caused by protozoan parasites of the genus Plasmodium (phylum Apicomplexa). In humans malaria is caused by P. falciparum, P. malariae, P. ovale, P. vivax and P. knowlesi.[45][46] P. falciparum is the most common cause of infection and is responsible for about 80% of all malaria cases, and is also responsible for about 90% of the deaths from malaria.[47] Parasitic Plasmodium species also infect birds, reptiles, monkeys, chimpanzees and rodents.[48] There have been documented human infections with several simian species of malaria, namely P. knowlesi, P. inui, P. cynomolgi,[49] P. simiovale, P. brazilianum, P. schwetzi and P. simium; however, with the exception of P. knowlesi, these are mostly of limited public health importance.[50] Although avian malaria can kill chickens and turkeys, this disease does not cause serious economic losses to poultry farmers.[51] However, since being accidentally introduced by humans it has decimated the endemic birds of Hawaii, which evolved in its absence and lack any resistance to it.[52]
Mosquito vectors and the Plasmodium life cycle
The parasite's primary (definitive) hosts and transmission vectors are female mosquitoes of the Anopheles genus. Young mosquitoes first ingest the malaria parasite by feeding on an infected human carrier and the infected Anopheles mosquitoes carry Plasmodium sporozoites in their salivary glands. A mosquito becomes infected when it takes a blood meal from an infected human. Once ingested, the parasite gametocytes taken up in the blood will further differentiate into male or female gametes and then fuse in the mosquito gut. This produces an ookinete that penetrates the gut lining and produces an oocyst in the gut wall. When the oocyst ruptures, it releases sporozoites that migrate through the mosquito's body to the salivary glands, where they are then ready to infect a new human host. This type of transmission is occasionally referred to as anterior station transfer.[53] The sporozoites are injected into the skin, alongside saliva, when the mosquito takes a subsequent blood meal.
Only female mosquitoes feed on blood, thus males do not transmit the disease. The females of the Anopheles genus of mosquito prefer to feed at night. They usually start searching for a meal at dusk, and will continue throughout the night until taking a meal. Malaria parasites can also be transmitted by blood transfusions, although this is rare.[54]
Pathogenesis

Malaria in humans develops via two phases: an exoerythrocytic and an erythrocytic phase. The exoerythrocytic phase involves infection of the hepatic system, or liver, whereas the erythrocytic phase involves infection of the erythrocytes, or red blood cells. When an infected mosquito pierces a person's skin to take a blood meal, sporozoites in the mosquito's saliva enter the bloodstream and migrate to the liver. Within 30 minutes of being introduced into the human host, the sporozoites infect hepatocytes, multiplying asexually and asymptomatically for a period of 6–15 days. Once in the liver, these organisms differentiate to yield thousands of merozoites, which, following rupture of their host cells, escape into the blood and infect red blood cells, thus beginning the erythrocytic stage of the life cycle.[55] The parasite escapes from the liver undetected by wrapping itself in the cell membrane of the infected host liver cell.[56]
Within the red blood cells, the parasites multiply further, again asexually, periodically breaking out of their hosts to invade fresh red blood cells. Several such amplification cycles occur. Thus, classical descriptions of waves of fever arise from simultaneous waves of merozoites escaping and infecting red blood cells.
Some P. vivax and P. ovale sporozoites do not immediately develop into exoerythrocytic-phase merozoites, but instead produce hypnozoites that remain dormant for periods ranging from several months (6–12 months is typical) to as long as three years. After a period of dormancy, they reactivate and produce merozoites. Hypnozoites are responsible for long incubation and late relapses in these two species of malaria.[57]
The parasite is relatively protected from attack by the body's immune system because for most of its human life cycle it resides within the liver and blood cells and is relatively invisible to immune surveillance. However, circulating infected blood cells are destroyed in the spleen. To avoid this fate, the P. falciparum parasite displays adhesive proteins on the surface of the infected blood cells, causing the blood cells to stick to the walls of small blood vessels, thereby sequestering the parasite from passage through the general circulation and the spleen.[58] This "stickiness" is the main factor giving rise to hemorrhagic complications of malaria. High endothelial venules (the smallest branches of the circulatory system) can be blocked by the attachment of masses of these infected red blood cells. The blockage of these vessels causes symptoms such as in placental and cerebral malaria. In cerebral malaria the sequestrated red blood cells can breach the blood brain barrier possibly leading to coma.[59]
Although the red blood cell surface adhesive proteins (called PfEMP1, for Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1) are exposed to the immune system, they do not serve as good immune targets because of their extreme diversity; there are at least 60 variations of the protein within a single parasite and perhaps limitless versions within parasite populations.[58] Like a thief changing disguises or a spy with multiple passports, the parasite switches between a broad repertoire of PfEMP1 surface proteins, thus staying one step ahead of the pursuing immune system.
Some merozoites turn into male and female gametocytes. If a mosquito pierces the skin of an infected person, it potentially picks up gametocytes within the blood. Fertilization and sexual recombination of the parasite occurs in the mosquito's gut, thereby defining the mosquito as the definitive host of the disease. New sporozoites develop and travel to the mosquito's salivary gland, completing the cycle. Pregnant women are especially attractive to the mosquitoes,[60] and malaria in pregnant women is an important cause of stillbirths, infant mortality and low birth weight,[61] particularly in P. falciparum infection, but also in other species infection, such as P. vivax.[62]
Evolutionary pressure of malaria on human genes
Malaria is thought to have been the greatest selective pressure on the human genome in recent history.[63] This is due to the high levels of mortality and morbidity caused by malaria, especially the P. falciparum species.
Sickle-cell disease
| This article may contain original research or unverified claims. Please improve the article by adding references. See the talk page for details. (April 2009) |
| This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (April 2009) |
The most-studied influence of the malaria parasite upon the human genome is a hereditary blood disease, sickle-cell disease. The sickle-cell trait causes disease, but even those only partially affected by sickle-cell have substantial protection against malaria.
In sickle-cell disease, there is a mutation in the HBB gene, which encodes the beta-globin subunit of haemoglobin. The normal allele encodes a glutamate at position six of the beta-globin protein, whereas the sickle-cell allele encodes a valine. This change from a hydrophilic to a hydrophobic amino acid encourages binding between haemoglobin molecules, with polymerization of haemoglobin deforming red blood cells into a "sickle" shape. Such deformed cells are cleared rapidly from the blood, mainly in the spleen, for destruction and recycling.
In the merozoite stage of its life cycle, the malaria parasite lives inside red blood cells, and its metabolism changes the internal chemistry of the red blood cell. Infected cells normally survive until the parasite reproduces, but, if the red cell contains a mixture of sickle and normal haemoglobin, it is likely to become deformed and be destroyed before the daughter parasites emerge. Thus, individuals heterozygous for the mutated allele, known as sickle-cell trait, may have a low and usually-unimportant level of anaemia, but also have a greatly reduced chance of serious malaria infection. This is a classic example of heterozygote advantage.
Individuals homozygous for the mutation have full sickle-cell disease and in traditional societies rarely live beyond adolescence. However, in populations where malaria is endemic, the frequency of sickle-cell genes is around 10%. The existence of four haplotypes of sickle-type hemoglobin suggests that this mutation has emerged independently at least four times in malaria-endemic areas, further demonstrating its evolutionary advantage in such affected regions. There are also other mutations of the HBB gene that produce haemoglobin molecules capable of conferring similar resistance to malaria infection. These mutations produce haemoglobin types HbE and HbC, which are common in Southeast Asia and Western Africa, respectively.
Thalassaemias
Another well-documented set of mutations found in the human genome associated with malaria are those involved in causing blood disorders known as thalassaemias. Studies in Sardinia and Papua New Guinea have found that the gene frequency of β-thalassaemias is related to the level of malarial endemicity in a given population. A study on more than 500 children in Liberia found that those with β-thalassaemia had a 50% decreased chance of getting clinical malaria. Similar studies have found links between gene frequency and malaria endemicity in the α+ form of α-thalassaemia. Presumably these genes have also been selected in the course of human evolution.
Duffy antigens
The Duffy antigens are antigens expressed on red blood cells and other cells in the body acting as a chemokine receptor. The expression of Duffy antigens on blood cells is encoded by Fy genes (Fya, Fyb, Fyc etc.). Plasmodium vivax malaria uses the Duffy antigen to enter blood cells. However, it is possible to express no Duffy antigen on red blood cells (Fy-/Fy-). This genotype confers complete resistance to P. vivax infection. The genotype is very rare in European, Asian and American populations, but is found in almost all of the indigenous population of West and Central Africa.[64] This is thought to be due to very high exposure to P. vivax in Africa in the last few thousand years.
G6PD
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is an enzyme that normally protects from the effects of oxidative stress in red blood cells. However, a genetic deficiency in this enzyme results in increased protection against severe malaria.
HLA and interleukin-4
HLA-B53 is associated with low risk of severe malaria. This MHC class I molecule presents liver stage and sporozoite antigens to T-Cells. Interleukin-4, encoded by IL4, is produced by activated T cells and promotes proliferation and differentiation of antibody-producing B cells. A study of the Fulani of Burkina Faso, who have both fewer malaria attacks and higher levels of antimalarial antibodies than do neighboring ethnic groups, found that the IL4-524 T allele was associated with elevated antibody levels against malaria antigens, which raises the possibility that this might be a factor in increased resistance to malaria.[65]
Diagnosis

Severe malaria is commonly misdiagnosed in Africa, leading to a failure to treat other life-threatening illnesses. In malaria-endemic areas, parasitemia does not ensure a diagnosis of severe malaria because parasitemia can be incidental to other concurrent disease. Recent investigations suggest that malarial retinopathy is better (collective sensitivity of 95% and specificity of 90%) than any other clinical or laboratory feature in distinguishing malarial from non-malarial coma.[66]
Symptomatic diagnosis
Areas that cannot afford even simple laboratory diagnostic tests often use only a history of subjective fever as the indication to treat for malaria. Using Giemsa-stained blood smears from children in Malawi, one study showed that unnecessary treatment for malaria was significantly decreased when clinical predictors (rectal temperature, nailbed pallor, and splenomegaly) were used as treatment indications, rather than the current national policy of using only a history of subjective fevers (sensitivity increased from 21% to 41%).[67]
Microscopic examination of blood films
The most economic, preferred, and reliable diagnosis of malaria is microscopic examination of blood films because each of the four major parasite species has distinguishing characteristics. Two sorts of blood film are traditionally used. Thin films are similar to usual blood films and allow species identification because the parasite's appearance is best preserved in this preparation. Thick films allow the microscopist to screen a larger volume of blood and are about eleven times more sensitive than the thin film, so picking up low levels of infection is easier on the thick film, but the appearance of the parasite is much more distorted and therefore distinguishing between the different species can be much more difficult. With the pros and cons of both thick and thin smears taken into consideration, it is imperative to utilize both smears while attempting to make a definitive diagnosis.[68]
From the thick film, an experienced microscopist can detect parasite levels (or parasitemia) down to as low as 0.0000001% of red blood cells. Diagnosis of species can be difficult because the early trophozoites ("ring form") of all four species look identical and it is never possible to diagnose species on the basis of a single ring form; species identification is always based on several trophozoites.
Field tests
In areas where microscopy is not available, or where laboratory staff are not experienced at malaria diagnosis, there are antigen detection tests that require only a drop of blood.[69] Immunochromatographic tests (also called: Malaria Rapid Diagnostic Tests, Antigen-Capture Assay or "Dipsticks") have been developed, distributed and fieldtested. These tests use finger-stick or venous blood, the completed test takes a total of 15–20 minutes, and a laboratory is not needed. The threshold of detection by these rapid diagnostic tests is in the range of 100 parasites/µl of blood compared to 5 by thick film microscopy. The first rapid diagnostic tests were using P. falciparum glutamate dehydrogenase as antigen.[70] PGluDH was soon replaced by P.falciparum lactate dehydrogenase, a 33 kDa oxidoreductase [EC 1.1.1.27]. It is the last enzyme of the glycolytic pathway, essential for ATP generation and one of the most abundant enzymes expressed by P.falciparum. PLDH does not persist in the blood but clears about the same time as the parasites following successful treatment. The lack of antigen persistence after treatment makes the pLDH test useful in predicting treatment failure. In this respect, pLDH is similar to pGluDH. The OptiMAL-IT assay can distinguish between P. falciparum and P. vivax because of antigenic differences between their pLDH isoenzymes. OptiMAL-IT will reliably detect falciparum down to 0.01% parasitemia and non-falciparum down to 0.1%. Paracheck-Pf will detect parasitemias down to 0.002% but will not distinguish between falciparum and non-falciparum malaria. Parasite nucleic acids are detected using polymerase chain reaction. This technique is more accurate than microscopy. However, it is expensive, and requires a specialized laboratory. Moreover, levels of parasitemia are not necessarily correlative with the progression of disease, particularly when the parasite is able to adhere to blood vessel walls. Therefore more sensitive, low-tech diagnosis tools need to be developed in order to detect low levels of parasitaemia in the field. Areas that cannot afford even simple laboratory diagnostic tests often use only a history of subjective fever as the indication to treat for malaria. Using Giemsa-stained blood smears from children in Malawi, one study showed that unnecessary treatment for malaria was significantly decreased when clinical predictors (rectal temperature, nailbed pallor, and splenomegaly) were used as treatment indications, rather than the current national policy of using only a history of subjective fevers (sensitivity increased from 21% to 41%).[71]
Molecular methods
Molecular methods are available in some clinical laboratories and rapid real-time assays (for example, QT-NASBA based on the polymerase chain reaction)[72] are being developed with the hope of being able to deploy them in endemic areas.
Laboratory tests
OptiMAL-IT will reliably detect falciparum down to 0.01% parasitemia and non-falciparum down to 0.1%. Paracheck-Pf will detect parasitemias down to 0.002% but will not distinguish between falciparum and non-falciparum malaria. Parasite nucleic acids are detected using polymerase chain reaction. This technique is more accurate than microscopy. However, it is expensive, and requires a specialized laboratory. Moreover, levels of parasitemia are not necessarily correlative with the progression of disease, particularly when the parasite is able to adhere to blood vessel walls. Therefore more sensitive, low-tech diagnosis tools need to be developed in order to detect low levels of parasitaemia in the field. [73]
Treatment
Active malaria infection with P. falciparum is a medical emergency requiring hospitalization. Infection with P. vivax, P. ovale or P. malariae can often be treated on an outpatient basis. Treatment of malaria involves supportive measures as well as specific antimalarial drugs. When properly treated, someone with malaria can expect a complete recovery.[74]
Antimalarial drugs
There are several families of drugs used to treat malaria. Chloroquine is very cheap and, until recently, was very effective, which made it the antimalarial drug of choice for many years in most parts of the world. However, resistance of Plasmodium falciparum to chloroquine has spread recently from Asia to Africa, making the drug ineffective against the most dangerous Plasmodium strain in many affected regions of the world.[75] In those areas where chloroquine is still effective it remains the first choice. Unfortunately, chloroquine-resistance is associated with reduced sensitivity to other drugs such as quinine and amodiaquine.[76]
There are several other substances which are used for treatment and, partially, for prevention (prophylaxis). Many drugs may be used for both purposes; larger doses are used to treat cases of malaria. Their deployment depends mainly on the frequency of resistant parasites in the area where the drug is used. One drug currently[update] being investigated for possible use as an anti-malarial, especially for treatment of drug-resistant strains, is the beta blocker propranolol. Propranolol has been shown to block both Plasmodium's ability to enter red blood cell and establish an infection, as well as parasite replication. A December 2006 study by Northwestern University researchers suggested that propranolol may reduce the dosages required for existing drugs to be effective against P. falciparum by 5- to 10-fold, suggesting a role in combination therapies.[77]
Currently available anti-malarial drugs include:[78]
- Artemether-lumefantrine (Therapy only, commercial names Coartem and Riamet)
- Artesunate-amodiaquine (Therapy only)
- Artesunate-mefloquine (Therapy only)
- Artesunate-Sulfadoxine/pyrimethamine (Therapy only)
- Atovaquone-proguanil, trade name Malarone (Therapy and prophylaxis)
- Quinine (Therapy only)
- Chloroquine (Therapy and prophylaxis; usefulness now reduced due to resistance)
- Cotrifazid (Therapy and prophylaxis)
- Doxycycline (Therapy and prophylaxis)
- Mefloquine, trade name Lariam (Therapy and prophylaxis)
- Primaquine (Therapy in P. vivax and P. ovale only; not for prophylaxis)
- Proguanil (Prophylaxis only)
- Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (Therapy; prophylaxis for semi-immune pregnant women in endemic countries as "Intermittent Preventive Treatment" - IPT)
- Hydroxychloroquine, trade name Plaquenil (Therapy and prophylaxis)
The development of drugs was facilitated when Plasmodium falciparum was successfully cultured.[79] This allowed in vitro testing of new drug candidates.
Extracts of the plant Artemisia annua, containing the compound artemisinin or semi-synthetic derivatives (a substance unrelated to quinine), offer over 90% efficacy rates, but their supply is not meeting demand.[80] In 2007, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation contributed $13.6m to support research at the University of York to develop fast and high-yield strains of artemisia, with researchers predicting an increase in yield of up to 1000% compared to current varieties.[81] One study in Rwanda showed that children with uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria demonstrated fewer clinical and parasitological failures on post-treatment day 28 when amodiaquine was combined with artesunate, rather than administered alone (OR = 0.34). However, increased resistance to amodiaquine during this study period was also noted.[82] Since 2001 the World Health Organization has recommended using artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) as first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria in areas experiencing resistance to older medications. The most recent WHO treatment guidelines for malaria recommend four different ACTs. While numerous countries, including most African nations, have adopted the change in their official malaria treatment policies, cost remains a major barrier to ACT implementation. Because ACTs cost up to twenty times as much as older medications, they remain unaffordable in many malaria-endemic countries. The molecular target of artemisinin is controversial, although recent studies suggest that SERCA, a calcium pump in the endoplasmic reticulum may be associated with artemisinin resistance.[83] Malaria parasites can develop resistance to artemisinin and resistance can be produced by mutation of SERCA.[84] However, other studies suggest the mitochondrion is the major target for artemisinin and its analogs.[85]
In February 2002, the journal Science and other press outlets[86] announced progress on a new treatment for infected individuals. A team of French and South African researchers had identified a new drug they were calling "G25".[87] It cured malaria in test primates by blocking the ability of the parasite to copy itself within the red blood cells of its victims. In 2005 the same team of researchers published their research on achieving an oral form, which they refer to as "TE3" or "te3".[88] As of early 2006, there is no information in the mainstream press as to when this family of drugs will become commercially available.
In 1996, Professor Geoff McFadden stumbled upon the work of British biologist Ian Wilson, who had discovered that the plasmodia responsible for causing malaria retained parts of chloroplasts,[89] an organelle usually found in plants, complete with their own functioning genomes. This led Professor McFadden to the realisation that any number of herbicides may in fact be successful in the fight against malaria, and so he set about trialing large numbers of them, and enjoyed a 75% success rate.
These "apicoplasts" are thought to have originated through the endosymbiosis of algae[90] and play a crucial role in fatty acid bio-synthesis in plasmodia.[91] To date, 466 proteins have been found to be produced by apicoplasts[92] and these are now being looked at as possible targets for novel anti-malarial drugs.
Although effective anti-malarial drugs are on the market, the disease remains a threat to people living in endemic areas who have no proper and prompt access to effective drugs. Access to pharmacies and health facilities, as well as drug costs, are major obstacles. Médecins Sans Frontières estimates that the cost of treating a malaria-infected person in an endemic country was between US$0.25 and $2.40 per dose in 2002.[93]
Counterfeit drugs
Sophisticated counterfeits have been found in several Asian countries such as Cambodia,[94] China,[95] Indonesia, Laos, Thailand, Vietnam and are an important cause of avoidable death in these countries.[96] WHO have said that studies indicate that up to 40% of artesunate based malaria medications are counterfeit, especially in the Greater Mekong region and have established a rapid alert system to enable information about counterfeit drugs to be rapidly reported to the relevant authorities in participating countries.[97] There is no reliable way for doctors or lay people to detect counterfeit drugs without help from a laboratory. Companies are attempting to combat the persistence of counterfeit drugs by using new technology to provide security from source to distribution.
Prevention and disease control

Methods used to prevent the spread of disease, or to protect individuals in areas where malaria is endemic, include prophylactic drugs, mosquito eradication, and the prevention of mosquito bites. The continued existence of malaria in an area requires a combination of high human population density, high mosquito population density, and high rates of transmission from humans to mosquitoes and from mosquitoes to humans. If any of these is lowered sufficiently, the parasite will sooner or later disappear from that area, as happened in North America, Europe and much of Middle East. However, unless the parasite is eliminated from the whole world, it could become re-established if conditions revert to a combination that favors the parasite's reproduction. Many countries are seeing an increasing number of imported malaria cases due to extensive travel and migration. (See Anopheles.)
There is currently no vaccine that will prevent malaria, but this is an active field of research.
Many researchers argue that prevention of malaria may be more cost-effective than treatment of the disease in the long run, but the capital costs required are out of reach of many of the world's poorest people. Economic adviser Jeffrey Sachs estimates that malaria can be controlled for US$3 billion in aid per year. It has been argued that, in order to meet the Millennium Development Goals, money should be redirected from HIV/AIDS treatment to malaria prevention, which for the same amount of money would provide greater benefit to African economies.[98]
The distribution of funding varies among countries. Countries with large populations do not receive the same amount of support. The 34 countries that received a per capita annual support of less than $1 included some of the poorest countries in Africa.
Brazil, Eritrea, India, and Vietnam have, unlike many other developing nations, successfully reduced the malaria burden. Common success factors included conducive country conditions, a targeted technical approach using a package of effective tools, data-driven decision-making, active leadership at all levels of government, involvement of communities, decentralized implementation and control of finances, skilled technical and managerial capacity at national and sub-national levels, hands-on technical and programmatic support from partner agencies, and sufficient and flexible financing.[99]
Vector control
Before DDT, malaria was successfully eradicated or controlled also in several tropical areas by removing or poisoning the breeding grounds of the mosquitoes or the aquatic habitats of the larva stages, for example by filling or applying oil to places with standing water. These methods have seen little application in Africa for more than half a century.[100]
Efforts to eradicate malaria by eliminating mosquitoes have been successful in some areas. Malaria was once common in the United States and southern Europe, but the draining of wetland breeding grounds and better sanitation, in conjunction with the monitoring and treatment of infected humans, eliminated it from affluent regions. In 2002, there were 1,059 cases of malaria reported in the US, including eight deaths. In five of those cases, the disease was contracted in the United States. Malaria was eliminated from the northern parts of the USA in the early twentieth century, and the use of the pesticide DDT eliminated it from the South by 1951. In the 1950s and 1960s, there was a major public health effort to eradicate malaria worldwide by selectively targeting mosquitoes in areas where malaria was rampant.[101] However, these efforts have so far failed to eradicate malaria in many parts of the developing world - the problem is most prevalent in Africa.
Sterile insect technique is emerging as a potential mosquito control method. Progress towards transgenic, or genetically modified, insects suggest that wild mosquito populations could be made malaria-resistant. Researchers at Imperial College London created the world's first transgenic malaria mosquito,[102] with the first plasmodium-resistant species announced by a team at Case Western Reserve University in Ohio in 2002.[103] Successful replacement of existent populations with genetically modified populations, relies upon a drive mechanism, such as transposable elements to allow for non-Mendelian inheritance of the gene of interest. However, this approach contains many difficulties and 34% of the malaria research and control community say that such an approach “will never fly” <Knols et al., 2007>. Furthermore, such an approach is at least 5 to 10 years away from introduction and the progress which has been made in developing a vaccine could influence further research in genetic modification of malaria mosquitoes negatively <Knols et al., 2007>.
On December 21, 2007, a study published in PLoS Pathogens found that the hemolytic C-type lectin CEL-III from Cucumaria echinata, a sea cucumber found in the Bay of Bengal, impaired the development of the malaria parasite when produced by transgenic mosquitoes.[104][105] This could potentially be used one day to control malaria by using genetically modified mosquitoes refractory to the parasites, although the authors of the study recognize that there are numerous scientific and ethical problems to be overcome before such a control strategy could be implemented.
Prophylactic drugs
Several drugs, most of which are also used for treatment of malaria, can be taken preventively. Generally, these drugs are taken daily or weekly, at a lower dose than would be used for treatment of a person who had actually contracted the disease. Use of prophylactic drugs is seldom practical for full-time residents of malaria-endemic areas, and their use is usually restricted to short-term visitors and travelers to malarial regions. This is due to the cost of purchasing the drugs, negative side effects from long-term use, and because some effective anti-malarial drugs are difficult to obtain outside of wealthy nations.
Quinine was used starting in the seventeenth century as a prophylactic against malaria. The development of more effective alternatives such as quinacrine, chloroquine, and primaquine in the twentieth century reduced the reliance on quinine. Today, quinine is still used to treat chloroquine resistant Plasmodium falciparum, as well as severe and cerebral stages of malaria, but is not generally used for prophylaxis. Samuel Hahnemann in the late 18th century noted that over-dosing of quinine leads to a symptomatic state very similar to that of malaria. This led him to develop the Law of Similars and homeopathy.
Modern drugs used preventively include mefloquine (Lariam), doxycycline (available generically), and the combination of atovaquone and proguanil hydrochloride (Malarone). The choice of which drug to use depends on which drugs the parasites in the area are resistant to, as well as side-effects and other considerations. The prophylactic effect does not begin immediately upon starting taking the drugs, so people temporarily visiting malaria-endemic areas usually begin taking the drugs one to two weeks before arriving and must continue taking them for 4 weeks after leaving (with the exception of atovaquone proguanil that only needs be started 2 days prior and continued for 7 days afterwards).
Indoor residual spraying
Indoor residual spraying (IRS) is the practice of spraying insecticides on the interior walls of homes in malaria affected areas. After feeding, many mosquito species rest on a nearby surface while digesting the bloodmeal, so if the walls of dwellings have been coated with insecticides, the resting mosquitos will be killed before they can bite another victim, transferring the malaria parasite.
The first and historically the most popular insecticide used for IRS is DDT. While it was initially used exclusively to combat malaria, its use quickly spread to agriculture. In time, pest-control, rather than disease-control, came to dominate DDT use, and this large-scale agricultural use led to the evolution of resistant mosquitoes in many regions. If the use of DDT was limited agriculturally, DDT may be more effective now as a method of disease-control. The DDT resistance shown by Anopheles mosquitoes can be compared to antibiotic resistance shown by bacteria. The overuse of anti-bacterial soaps and antibiotics have led to antibiotic resistance in bacteria, similar to how overspraying of DDT on crops have led to DDT resistance in Anopheles mosquitoes. During the 1960s, awareness of the negative consequences of its indiscriminate use increased ultimately leading to bans on agricultural applications of DDT in many countries in the 1970s.
Though DDT has never been banned for use in malaria control and there are several other insecticides suitable for IRS, some advocates have claimed that bans are responsible for tens of millions of deaths in tropical countries where DDT had once been effective in controlling malaria. Furthermore, most of the problems associated with DDT use stem specifically from its industrial-scale application in agriculture, rather than its use in public health.[106]
The World Health Organization (WHO) currently advises the use of 12 different insecticides in IRS operations. These include DDT and a series of alternative insecticides (such as the pyrethroids permethrin and deltamethrin) to both combat malaria in areas where mosquitoes are DDT-resistant, and to slow the evolution of resistance.[107] This public health use of small amounts of DDT is permitted under the Stockholm Convention on Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs), which prohibits the agricultural use of DDT.[108] However, because of its legacy, many developed countries discourage DDT use even in small quantities.[109][110]
One problem with all forms of Indoor Residual Spraying is insecticide resistance via evolution of mosquitos. According to a study published on Mosquito Behavior and Vector Control, mosquito breeds that are affected by IRS are endophilic species(Species which tend to rest and live indoors), and due to the irritation caused by spraying, their evolutionary descendants are trending towards becoming exophilic(Species which tend to rest and live out of doors), meaning that they are not as affected--if affected at all-- by the IRS, rendering it somewhat useless as a defense mechanism [111].
Mosquito nets and bedclothes
Mosquito nets help keep mosquitoes away from people, and thus greatly reduce the infection and transmission of malaria. The nets are not a perfect barrier, so they are often treated with an insecticide designed to kill the mosquito before it has time to search for a way past the net. Insecticide-treated nets (ITN) are estimated to be twice as effective as untreated nets,[98] and offer greater than 70% protection compared with no net.[112]. Although ITN are proven to be very effective against malaria, less than 2% of children in urban areas in Sub-Saharan Africa are protected by ITNs. Since the Anopheles mosquitoes feed at night, the preferred method is to hang a large "bed net" above the center of a bed such that it drapes down and covers the bed completely.
The distribution of mosquito nets impregnated with insecticide (often permethrin or deltamethrin) has been shown to be an extremely effective method of malaria prevention, and it is also one of the most cost-effective methods of prevention. These nets can often be obtained for around US$2.50 - $3.50 (2-3 euro) from the United Nations, the World Health Organization (WHO), and others. ITNs have been shown to be the most cost-effective prevention method against malaria and are actively part of WHO’s Millennium Development Goals (MDGs).
For maximum effectiveness, the nets should be re-impregnated with insecticide every six months. This process poses a significant logistical problem in rural areas. New technologies like Olyset or DawaPlus allow for production of long-lasting insecticidal mosquito nets (LLINs), which release insecticide for approximately 5 years,[113] and cost about US$5.50. ITNs have the advantage of protecting people sleeping under the net and simultaneously killing mosquitoes that contact the net. This has the effect of killing the most dangerous mosquitoes. Some protection is also provided to others, including people sleeping in the same room but not under the net.
Unfortunately, the cost of treating malaria is high relative to income, and the illness results in lost wages. Consequently, the financial burden means that the cost of a mosquito net is often unaffordable to people in developing countries, especially for those most at risk. Only 1 out of 20 people in Africa own a bed net.[98] Although shipped into Africa mainly from Europe as free development help, the nets quickly become expensive trade goods. They are mainly used for fishing, and by combining hundreds of donated mosquito nets, whole river sections can be completely shut off, catching even the smallest fish.[114] Nets are also often distributed though vaccine campaigns using vouchers subsidies, such as the measles campaign for children. Vouchers subsidies are an effective way of getting protective nets to those who cannot afford them off the market.
A study among Afghan refugees in Pakistan found that treating top-sheets and chaddars (head coverings) with permethrin has similar effectiveness to using a treated net, but is much cheaper.[115]
A new approach, announced in Science on June 10, 2005, uses spores of the fungus Beauveria bassiana, sprayed on walls and bed nets, to kill mosquitoes. While some mosquitoes have developed resistance to chemicals, they have not been found to develop a resistance to fungal infections.[116]
Vaccination
Vaccines for malaria are under development, with no completely effective vaccine yet available. The first promising studies demonstrating the potential for a malaria vaccine were performed in 1967 by immunizing mice with live, radiation-attenuated sporozoites, providing protection to about 60% of the mice upon subsequent injection with normal, viable sporozoites.[117] Since the 1970s, there has been a considerable effort to develop similar vaccination strategies within humans. It was determined that an individual can be protected from a P. falciparum infection if they receive over 1000 bites from infected, irradiated mosquitoes.[118]
It has been generally accepted that it is impractical to provide at-risk individuals with this vaccination strategy, but that has been recently challenged with work being done by Dr. Stephen Hoffman of Sanaria, one of the key researchers who originally sequenced the genome of Plasmodium falciparum. His work most recently has revolved around solving the logistical problem of isolating and preparing the parasites equivalent to 1000 irradiated mosquitoes for mass storage and inoculation of human beings. The company has recently received several multi-million dollar grants from the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation and the U.S. government to begin early clinical studies in 2007 and 2008.[119] The Seattle Biomedical Research Institute (SBRI), funded by the Malaria Vaccine Initiative, assures potential volunteers that "the [2009] clinical trials won't be a life-threatening experience. While many volunteers [in Seattle] will actually contract malaria, the cloned strain used in the experiments can be quickly cured, and does not cause a recurring form of the disease." "Some participants will get experimental drugs or vaccines, while others will get placebo."[120]
Instead, much work has been performed to try and understand the immunological processes that provide protection after immunization with irradiated sporozoites. After the mouse vaccination study in 1967,[117] it was hypothesized that the injected sporozoites themselves were being recognized by the immune system, which was in turn creating antibodies against the parasite. It was determined that the immune system was creating antibodies against the circumsporozoite protein (CSP) which coated the sporozoite.[121] Moreover, antibodies against CSP prevented the sporozoite from invading hepatocytes.[122] CSP was therefore chosen as the most promising protein on which to develop a vaccine against the malaria sporozoite. It is for these historical reasons that vaccines based on CSP are the most numerous of all malaria vaccines.
Presently, there is a huge variety of vaccine candidates on the table. Pre-erythrocytic vaccines (vaccines that target the parasite before it reaches the blood), in particular vaccines based on CSP, make up the largest group of research for the malaria vaccine. Other vaccine candidates include: those that seek to induce immunity to the blood stages of the infection; those that seek to avoid more severe pathologies of malaria by preventing adherence of the parasite to blood venules and placenta; and transmission-blocking vaccines that would stop the development of the parasite in the mosquito right after the mosquito has taken a bloodmeal from an infected person.[123] It is hoped that the sequencing of the P. falciparum genome will provide targets for new drugs or vaccines.[124]
The first vaccine developed that has undergone field trials, is the SPf66, developed by Manuel Elkin Patarroyo in 1987. It presents a combination of antigens from the sporozoite (using CS repeats) and merozoite parasites. During phase I trials a 75% efficacy rate was demonstrated and the vaccine appeared to be well tolerated by subjects and immunogenic. The phase IIb and III trials were less promising, with the efficacy falling to between 38.8% and 60.2%. A trial was carried out in Tanzania in 1993 demonstrating the efficacy to be 31% after a years follow up, however the most recent (though controversial) study in The Gambia did not show any effect. Despite the relatively long trial periods and the number of studies carried out, it is still not known how the SPf66 vaccine confers immunity; it therefore remains an unlikely solution to malaria. The CSP was the next vaccine developed that initially appeared promising enough to undergo trials. It is also based on the circumsporoziote protein, but additionally has the recombinant (Asn-Ala-Pro15Asn-Val-Asp-Pro)2-Leu-Arg(R32LR) protein covalently bound to a purified Pseudomonas aeruginosa toxin (A9). However at an early stage a complete lack of protective immunity was demonstrated in those inoculated. The study group used in Kenya had an 82% incidence of parasitaemia whilst the control group only had an 89% incidence. The vaccine intended to cause an increased T-lymphocyte response in those exposed, this was also not observed.
The efficacy of Patarroyo's vaccine has been disputed with some US scientists concluding in The Lancet (1997) that "the vaccine was not effective and should be dropped" while the Colombian accused them of "arrogance" putting down their assertions to the fact that he came from a developing country.
The RTS,S/AS02A vaccine is the candidate furthest along in vaccine trials. It is being developed by a partnership between the PATH Malaria Vaccine Initiative (a grantee of the Gates Foundation), the pharmaceutical company, GlaxoSmithKline, and the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research[125] In the vaccine, a portion of CSP has been fused to the immunogenic "S antigen" of the hepatitis B virus; this recombinant protein is injected alongside the potent AS02A adjuvant.[123] In October 2004, the RTS,S/AS02A researchers announced results of a Phase IIb trial, indicating the vaccine reduced infection risk by approximately 30% and severity of infection by over 50%. The study looked at over 2,000 Mozambican children.[126] More recent testing of the RTS,S/AS02A vaccine has focused on the safety and efficacy of administering it earlier in infancy: In October 2007, the researchers announced results of a phase I/IIb trial conducted on 214 Mozambican infants between the ages of 10 and 18 months in which the full three-dose course of the vaccine led to a 62% reduction of infection with no serious side-effects save some pain at the point of injection.[127] Further research will delay this vaccine from commercial release until around 2011.[128]
Other methods
Education in recognizing the symptoms of malaria has reduced the number of cases in some areas of the developing world by as much as 20%. Recognizing the disease in the early stages can also stop the disease from becoming a killer. Education can also inform people to cover over areas of stagnant, still water e.g. Water Tanks which are ideal breeding grounds for the parasite and mosquito, thus cutting down the risk of the transmission between people. This is most put in practice in urban areas where there are large centers of population in a confined space and transmission would be most likely in these areas.
The Malaria Control Project is currently using downtime computing power donated by individual volunteers around the world (see Volunteer computing and BOINC) to simulate models of the health effects and transmission dynamics in order to find the best method or combination of methods for malaria control. This modeling is extremely computer intensive due to the simulations of large human populations with a vast range of parameters related to biological and social factors that influence the spread of the disease. It is expected to take a few months using volunteered computing power compared to the 40 years it would have taken with the current resources available to the scientists who developed the program.[129]
An example of the importance of computer modeling in planning malaria eradication programs is shown in the paper by Águas and others. They showed that eradication of malaria is crucially dependent on finding and treating the large number of people in endemic areas with asymptomatic malaria, who act as a reservoir for infection.[130] The malaria parasites do not affect animal species and therefore eradication of the disease from the human population would be expected to be effective.
See also
References
- ^ Snow RW, Guerra CA, Noor AM, Myint HY, Hay SI (2005). "The global distribution of clinical episodes of Plasmodium falciparum malaria". Nature 434 (7030): 214–7. doi:. PMID 15759000.
- ^ "Malaria: Disease Impacts and Long-Run Income Differences" (PDF). Institute for the Study of Labor. http://ftp.iza.org/dp2997.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-12-10.
- ^ Joy D, Feng X, Mu J, et al (2003). "Early origin and recent expansion of Plasmodium falciparum". Science 300 (5617): 318–21. doi:. PMID 12690197.
- ^ Escalante A, Freeland D, Collins W, Lal A (1998). "The evolution of primate malaria parasites based on the gene encoding cytochrome b from the linear mitochondrial genome". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95 (14): 8124–9. doi:. PMID 9653151.
- ^ Cox F (2002). "History of human parasitology". Clin Microbiol Rev 15 (4): 595–612. doi:. PMID 12364371.
- ^ "Biography of Alphonse Laveran". The Nobel Foundation. http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/1907/laveran-bio.html. Retrieved on 2007-06-15. ] Nobel foundation. Accessed 25 Oct 2006
- ^ "Ettore Marchiafava". http://www.whonamedit.com/doctor.cfm/2478.html. Retrieved on 2007-06-15.
- ^ Tan SY, Sung H (May 2008). "Carlos Juan Finlay (1833–1915): of mosquitoes and yellow fever" (PDF). Singapore Med J 49 (5): 370–1. PMID 18465043. http://smj.sma.org.sg/4905/4905ms1.pdf.
- ^ Chernin E (November 1983). "Josiah Clark Nott, insects, and yellow fever". Bull N Y Acad Med 59 (9): 790–802. PMID 6140039.
- ^ Chernin E (September 1977). "Patrick Manson (1844–1922) and the transmission of filariasis". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 26 (5 Pt 2 Suppl): 1065–70. PMID 20786. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=20786.
- ^ "Biography of Ronald Ross". The Nobel Foundation. http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/medicine/laureates/1902/ross-bio.html. Retrieved on 2007-06-15.
- ^ "Ross and the Discovery that Mosquitoes Transmit Malaria Parasites". CDC Malaria website. http://www.cdc.gov/malaria/history/ross.htm. Retrieved on 2007-06-15.
- ^ Kaufman T, Rúveda E (2005). "The quest for quinine: those who won the battles and those who won the war". Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 44 (6): 854–85. doi:. PMID 15669029.
- ^ Kyle R, Shampe M (1974). "Discoverers of quinine". JAMA 229 (4): e320. doi:. PMID 4600403.
- ^ Raju T (2006). "Hot brains: manipulating body heat to save the brain". Pediatrics 117 (2): e320–1. doi:. PMID 16452338. http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/content/full/117/2/e320.
- ^ Krotoski W, Collins W, Bray R, et al (1982). "Demonstration of hypnozoites in sporozoite-transmitted Plasmodium vivax infection". Am J Trop Med Hyg 31 (6): 1291–3. PMID 6816080.
- ^ Meis J, Verhave J, Jap P, Sinden R, Meuwissen J (1983). "Malaria parasites--discovery of the early liver form". Nature 302 (5907): 424–6. doi:. PMID 6339945.
- ^ "Malaria". US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 2003. http://www.dpd.cdc.gov/dpdx/HTML/ImageLibrary/Malaria_il.htm. Retrieved on 2008-07-20.
- ^ 2005 WHO World Malaria Report 2008
- ^ a b Greenwood BM, Bojang K, Whitty CJ, Targett GA (2005). "Malaria". Lancet 365: 1487–1498. doi:. PMID 15850634.
- ^ Hay S, Guerra C, Tatem A, Noor A, Snow R (2004). "The global distribution and population at risk of malaria: past, present, and future". Lancet Infect Dis 4 (6): 327–36. doi:. PMID 15172341.
- ^ a b Breman J (January 1, 2001). "The ears of the hippopotamus: manifestations, determinants, and estimates of the malaria burden". Am J Trop Med Hyg 64 (1-2 Suppl): 1–11. PMID 11425172. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/content/abstract/64/1_suppl/1.
- ^ Korenromp E, Williams B, de Vlas S, Gouws E, Gilks C, Ghys P, Nahlen B (2005). "Malaria attributable to the HIV-1 epidemic, sub-Saharan Africa". Emerg Infect Dis 11 (9): 1410–9. PMID 16229771. http://www.cdc.gov/ncidod/EID/vol11no09/05-0337.htm.
- ^ Abu-Raddad L, Patnaik P, Kublin J (2006). "Dual infection with HIV and malaria fuels the spread of both diseases in sub-Saharan Africa". Science 314 (5805): 1603–6. doi:. PMID 17158329.
- ^ Layne SP. "Principles of Infectious Disease Epidemiology /" (PDF). EPI 220. UCLA Department of Epidemiology. http://web.archive.org/web/20060220083223/http://www.ph.ucla.edu/epi/layne/Epidemiology+220/07.malaria.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-06-15.
- ^ Greenwood B, Mutabingwa T (2002). "Malaria in 2002". Nature 415: 670–2. doi:. PMID 11832954.
- ^ Grover-Kopec E, Kawano M, Klaver R, Blumenthal B, Ceccato P, Connor S (2005). "An online operational rainfall-monitoring resource for epidemic malaria early warning systems in Africa". Malar J 4: 6. doi:. PMID 15663795.
- ^ Van Benthem B, Vanwambeke S, Khantikul N, Burghoorn-Maas C, Panart K, Oskam L, Lambin E, Somboon P (February 1, 2005). "Spatial patterns of and risk factors for seropositivity for dengue infection". Am J Trop Med Hyg 72 (2): 201–8. PMID 15741558. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/content/full/72/2/201.
- ^ Trung H, Van Bortel W, Sochantha T, Keokenchanh K, Quang N, Cong L, Coosemans M (2004). "Malaria transmission and major malaria vectors in different geographical areas of Southeast Asia". Trop Med Int Health 9 (2): e473. doi:. PMID 15040560.
- ^ Keiser J, Utzinger J, Caldas de Castro M, Smith T, Tanner M, Singer B (August 1, 2004). "Urbanization in sub-saharan Africa and implication for malaria control". Am J Trop Med Hyg 71 (2 Suppl): 118–27. PMID 15331827. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/content/full/71/2_suppl/118.
- ^ Hay SI, Snow RW (2006). "The Malaria Atlas Project: Developing Global Maps of Malaria Risk". PLoS Medicine 3 (12): e473. doi:. PMID 17147467.
- ^ Humphreys, M. 2001. Malaria: Poverty, Race, and Public Health in the United States. John Hopkins University Press. ISBN 0-8018-6637-5
- ^ Sachs J, Malaney P (2002). "The economic and social burden of malaria". Nature 415: 680–5. doi:. PMID 11832956.
- ^ Roll Back Malaria. "Economic costs of malaria". WHO. http://www.rbm.who.int/cmc_upload/0/000/015/363/RBMInfosheet_10.htm. Retrieved on 2006-09-21.
- ^ Beare NA, Taylor TE, Harding SP, Lewallen S, Molyneux ME (November 1, 2006). "Malarial retinopathy: a newly established diagnostic sign in severe malaria". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 75 (5): 790–7. PMID 17123967. PMC: 2367432. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17123967.
- ^ Malaria life cycle & pathogenesis. Malaria in Armenia. Accessed October 31, 2006.
- ^ Idro, R; Otieno G, White S, Kahindi A, Fegan G, Ogutu B, Mithwani S, Maitland K, Neville BG, Newton CR. "Decorticate, decerebrate and opisthotonic posturing and seizures in Kenyan children with cerebral malaria". Malaria Journal 4 (57): 57. doi:. PMID 16336645.
- ^ Boivin MJ (October 2002). "Effects of early cerebral malaria on cognitive ability in Senegalese children". J Dev Behav Pediatr 23 (5): 353–64. PMID 12394524. http://meta.wkhealth.com/pt/pt-core/template-journal/lwwgateway/media/landingpage.htm?issn=0196-206X&volume=23&issue=5&spage=353.
- ^ Holding PA, Snow RW (2001). "Impact of Plasmodium falciparum malaria on performance and learning: review of the evidence". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 64 (1-2 Suppl): 68–75. PMID 11425179. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/content/abstract/64/1_suppl/68. – Scholar search}}
- ^ a b c Trampuz A, Jereb M, Muzlovic I, Prabhu R (2003). "Clinical review: Severe malaria". Crit Care 7 (4): 315–23. doi:. PMID 12930555.
- ^ Kain K, Harrington M, Tennyson S, Keystone J (1998). "Imported malaria: prospective analysis of problems in diagnosis and management". Clin Infect Dis 27 (1): 142–9. doi:. PMID 9675468.
- ^ Mockenhaupt F, Ehrhardt S, Burkhardt J, Bosomtwe S, Laryea S, Anemana S, Otchwemah R, Cramer J, Dietz E, Gellert S, Bienzle U (2004). "Manifestation and outcome of severe malaria in children in northern Ghana". Am J Trop Med Hyg 71 (2): 167–72. PMID 15306705.
- ^ Carter JA, Ross AJ, Neville BG, Obiero E, Katana K, Mung'ala-Odera V, Lees JA, Newton CR (2005). "Developmental impairments following severe falciparum malaria in children". Trop Med Int Health 10: 3–10. doi:. PMID 15655008.
- ^ Adak T, Sharma V, Orlov V (1998). "Studies on the Plasmodium vivax relapse pattern in Delhi, India". Am J Trop Med Hyg 59 (1): 175–9. PMID 9684649.
- ^ Mueller I, Zimmerman PA, Reeder JC (June 2007). "Plasmodium malariae and Plasmodium ovale--the "bashful" malaria parasites". Trends Parasitol. 23 (6): 278–83. doi:. PMID 17459775.
- ^ Singh B, Kim Sung L, Matusop A, et al (March 2004). "A large focus of naturally acquired Plasmodium knowlesi infections in human beings". Lancet 363 (9414): 1017–24. doi:. PMID 15051281.
- ^ Mendis K, Sina B, Marchesini P, Carter R (2001). "The neglected burden of Plasmodium vivax malaria" (PDF). Am J Trop Med Hyg 64 (1-2 Suppl): 97–106. PMID 11425182. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/reprint/64/1_suppl/97.pdf.
- ^ Escalante A, Ayala F (1994). "Phylogeny of the malarial genus Plasmodium, derived from rRNA gene sequences". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91 (24): 11373–7. doi:. PMID 7972067.
- ^ Garnham, PCC (1966). Malaria parasites and other haemosporidia. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
- ^ Collins WE & Barnwell JW (2009). "Plasmodium knowlesi: Finally being recognized". J Infect Dis 199: 1107–1108. doi:.
- ^ Investing in Animal Health Research to Alleviate Poverty. International Livestock Research Institute. Permin A. and Madsen M. (2001) Appendix 2: review on disease occurrence and impact (smallholder poultry). Accessed 29 Oct 2006
- ^ Atkinson CT, Woods KL, Dusek RJ, Sileo LS, Iko WM (1995). "Wildlife disease and conservation in Hawaii: pathogenicity of avian malaria (Plasmodium relictum) in experimentally infected iiwi (Vestiaria coccinea)". Parasitology 111 Suppl: S59–69. PMID 8632925.
- ^ Talman A, Domarle O, McKenzie F, Ariey F, Robert V (2004). "Gametocytogenesis: the puberty of Plasmodium falciparum". Malar J 3: 24. doi:. PMID 15253774.
- ^ Marcucci C, Madjdpour C, Spahn D (2004). "Allogeneic blood transfusions: benefit, risks and clinical indications in countries with a low or high human development index". Br Med Bull 70: 15–28. doi:. PMID 15339855.
- ^ Bledsoe, G. H. (December 2005) "Malaria primer for clinicians in the United States" Southern Medical Journal 98(12): pp. 1197–204, (PMID: 16440920);
- ^ Sturm A, Amino R, van de Sand C, Regen T, Retzlaff S, Rennenberg A, Krueger A, Pollok JM, Menard R, Heussler VT (2006). "Manipulation of host hepatocytes by the malaria parasite for delivery into liver sinusoids". Science 313: 1287–1490. doi:. PMID 16888102.
- ^ Cogswell FB (January 1992). "The hypnozoite and relapse in primate malaria". Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 5 (1): 26–35. PMID 1735093. PMC: 358221. http://cmr.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=1735093.
- ^ a b Chen Q, Schlichtherle M, Wahlgren M (July 2000). "Molecular aspects of severe malaria". Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 13 (3): 439–50. doi:. PMID 10885986. PMC: 88942. http://cmr.asm.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=10885986.
- ^ Adams S, Brown H, Turner G (2002). "Breaking down the blood-brain barrier: signaling a path to cerebral malaria?". Trends Parasitol 18 (8): 360–6. doi:. PMID 12377286.
- ^ Lindsay S, Ansell J, Selman C, Cox V, Hamilton K, Walraven G (2000). "Effect of pregnancy on exposure to malaria mosquitoes". Lancet 355 (9219): 1972. doi:. PMID 10859048.
- ^ van Geertruyden J, Thomas F, Erhart A, D'Alessandro U (August 1, 2004). "The contribution of malaria in pregnancy to perinatal mortality". Am J Trop Med Hyg 71 (2 Suppl): 35–40. PMID 15331817. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/content/full/71/2_suppl/35.
- ^ Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Sanchez E, Vargas M, Piccolo C, Colina R, Arria M, Franco-Paredes C (2006). "Pregnancy outcomes associated with Plasmodium vivax malaria in northeastern Venezuela". Am J Trop Med Hyg 74: 755–757. PMID 16687675.
- ^ Kwiatkowski DP (August 2005). "How malaria has affected the human genome and what human genetics can teach us about malaria". Am J Hum Genet. 77 (2): 171–92. doi:. PMID 16001361.
- ^ Carter R, Mendis KN (2002). "Evolutionary and historical aspects of the burden of malaria". Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 15 (4): 564–94. doi:. PMID 12364370. http://cmr.asm.org/cgi/content/full/15/4/564?view=long&pmid=12364370#RBC%20Duffy%20Negativity.
- ^ Verra F, Luoni G, Calissano C, Troye-Blomberg M, Perlmann P, Perlmann H, Arcà B, Sirima B, Konaté A, Coluzzi M, Kwiatkowski D, Modiano D (2004). "IL4-589C/T polymorphism and IgE levels in severe malaria". Acta Trop. 90 (2): 205–9. doi:. PMID 15177147.
- ^ Beare NA, Taylor TE, Harding SP, Lewallen S, Molyneux ME (November 2006). "Malarial retinopathy: a newly established diagnostic sign in severe malaria". Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 75 (5): 790–7. PMID 17123967. PMC: 2367432. http://www.ajtmh.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17123967.
- ^ Redd S, Kazembe P, Luby S, Nwanyanwu O, Hightower A, Ziba C, Wirima J, Chitsulo L, Franco C, Olivar M (2006). "Clinical algorithm for treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children". Lancet 347 (8996): 80. doi:. PMID 8551881..
- ^ Warhurst DC, Williams JE (1996). "Laboratory diagnosis of malaria". J Clin Pathol 49: 533–38. doi:. PMID 8813948.
- ^ Pattanasin S, Proux S, Chompasuk D, Luwiradaj K, Jacquier P, Looareesuwan S, Nosten F (2003). "Evaluation of a new Plasmodium lactate dehydrogenase assay (OptiMAL-IT) for the detection of malaria". Transact Royal Soc Trop Med 97: 672–4. doi:. PMID 16117960.
- ^ Ling IT., Cooksley S., Bates PA., Hempelmann E., Wilson RJM. (1986). "Antibodies to the glutamate dehydrogenase of Plasmodium falciparum". Parasitology 92,: 313–24. PMID 3086819.
- ^ Redd S, Kazembe P, Luby S, Nwanyanwu O, Hightower A, Ziba C, Wirima J, Chitsulo L, Franco C, Olivar M (2006). "Clinical algorithm for treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children". Lancet 347 (8996): 80. doi:. PMID 8551881..
- ^ Mens PF, Schoone GJ, Kager PA, Schallig HDFH. (2006). "Detection and identification of human Plasmodium species with real-time quantitative nucleic acid sequence-based amplification". Malaria Journal 5 (80): 80. doi:.
- ^ Redd S, Kazembe P, Luby S, Nwanyanwu O, Hightower A, Ziba C, Wirima J, Chitsulo L, Franco C, Olivar M (2006). "Clinical algorithm for treatment of Plasmodium falciparum malaria in children". Lancet 347 (8996): 80. doi:. PMID 8551881..
- ^ If I get malaria, will I have it for the rest of my life? CDC publication, Accessed 14 Nov 2006
- ^ White NJ (April 2004). "Antimalarial drug resistance". J Clin Invest. 113 (8): 1084–92. doi:. PMID 15085184.
- ^ Tinto H, Rwagacondo C, Karema C, et al. (2006). "In-vitro susceptibility of Plasmodium falciparum to monodesethylamodiaquine, dihydroartemsinin and quinine in an area of high chloroquine resistance in Rwanda". Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 100 (6): 509–14. doi:.
- ^ Murphy S, Harrison T, Hamm H, Lomasney J, Mohandas N, Haldar K (December 2006). "Erythrocyte G protein as a novel target for malarial chemotherapy". PLoS Med 3 (12): e528. doi:. PMID 17194200.
- ^ Prescription drugs for malaria Retrieved February 27, 2007.
- ^ Trager W, Jensen JB (1976). "Human malaria parasites in continuous culture". Science 193 (4254): 673–5. doi:. PMID 781840.
- ^ Senior K (2005). "Shortfall in front-line antimalarial drug likely in 2005". Lancet Infect Dis 5 (2): 75. PMID 15702504.
- ^ York CNAP Artemisia Project Retrieved August 30, 2008
- ^ Rwagacondo C, Karema C, Mugisha V, Erhart A, Dujardin J, Van Overmeir C, Ringwald P, D'Alessandro U (2004). "Is amodiaquine failing in Rwanda? Efficacy of amodiaquine alone and combined with artesunate in children with uncomplicated malaria". Trop Med Int Health 9 (10): 1091–8. doi:. PMID 15482401..
- ^ Eckstein-Ludwig U, Webb R, Van Goethem I, East J, Lee A, Kimura M, O'Neill P, Bray P, Ward S, Krishna S (2003). "Artemisinins target the SERCA of Plasmodium falciparum". Nature 424 (6951): 957–61. doi:. PMID 12931192.
- ^ Uhlemann A, Cameron A, Eckstein-Ludwig U, Fischbarg J, Iserovich P, Zuniga F, East M, Lee A, Brady L, Haynes R, Krishna S (2005). "A single amino acid residue may determine the sensitivity of SER`CAs to artemisinins". Nat Struct Mol Biol 12 (7): 628–9. doi:. PMID 15937493.
- ^ Li W, Mo W, Shen D, Sun L, Wang J, Lu S, Gitschier J, Zhou B (2005). "Yeast model uncovers dual roles of mitochondria in action of artemisinin". PLoS Genet 1 (3): e36. doi:. PMID 16170412.
- ^ Malaria drug offers new hope. BBC News 2002-02-15.
- ^ One step closer to conquering malaria
- ^ Salom-Roig, X. et al. (2005) Dual molecules as new antimalarials. Combinatorial Chemistry & High Throughput Screening 8:49-62.
- ^ "Herbicides as a treatment for malaria". http://www.abc.net.au/rn/scienceshow/stories/2007/1902657.htm. Retrieved on 2007-09-25.
- ^ Khöler, Sabine (March 1997). "A Plastid of Probable Green Algal Origin in Apicomplexan Parasites". Science 275 (5305): 1485–1489. doi:. PMID 9045615.
- ^ Gardner, Malcom (November 1998). "Chromosome 2 Sequence of the Human Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum". Science 282 (5391): 1126–1132. doi:. PMID 9804551.
- ^ Foth, Bernado (January 2003). "Dissecting Apicoplast Targeting in the Malaria Parasite Plasmodium falciparum". Science 299 (5607): 705–708. doi:. PMID 12560551. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/abstract/299/5607/705?maxtoshow=&HITS=10&hits=10&RESULTFORMAT=&fulltext=apicoplast&searchid=1&FIRSTINDEX=0&resourcetype=HWCIT.
- ^ Medecins Sans Frontieres, "What is the Cost and Who Will Pay?"
- ^ Lon CT, Tsuyuoka R, Phanouvong S, et al. (2006). "Counterfeit and substandard antimalarial drugs in Cambodia". Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 100 (11): 1019–24. doi:. PMID 16765399.
- ^ U. S. Pharmacopeia (2004). "Fake antimalarials found in Yunan province, China" (PDF). http://www.uspdqi.org/pubs/other/FakeAntimalarialsinChina.pdf. Retrieved on 2006-10-06.
- ^ Newton PN Green MD, Fernández FM, Day NPJ, White NJ. (2006). "Counterfeit anti-infective drugs". Lancet Infect Dis 6 (9): 602–13. doi:. PMID 16931411.
- ^ Jane Parry (2005). "WHO combats counterfeit malaria drugs in Asia". http://www.bmj.com/cgi/content/full/330/7499/1044-d. Retrieved on 2008-07-19.
- ^ a b c Hull, Kevin. (2006) "Malaria: Fever Wars". PBS Documentary
- ^ Barat L (2006). "Four malaria success stories: how malaria burden was successfully reduced in Brazil, Eritrea, India, and Vietnam". Am J Trop Med Hyg 74 (1): 12–6. PMID 16407339.
- ^ Killeen G, Fillinger U, Kiche I, Gouagna L, Knols B (2002). "Eradication of Anopheles gambiae from Brazil: lessons for malaria control in Africa?". Lancet Infect Dis 2 (10): e192. doi:. PMID 12383612.
- ^ Gladwell, Malcolm. (2001-07-02). "The Mosquito Killer". The New Yorker. http://www.gladwell.com/2001/2001_07_02_a_ddt.htm.
- ^ Imperial College, London, "Scientists create first transgenic malaria mosquito", 2000-06-22.
- ^ Ito J, Ghosh A, Moreira LA, Wimmer EA, Jacobs-Lorena M (2002). "Transgenic anopheline mosquitoes impaired in transmission of a malaria parasite". Nature 417: 387–8. doi:. PMID 12024215.
- ^ BBC NEWS, Sea cucumber 'new malaria weapon'
- ^ Yoshida S, Shimada Y, Kondoh D, et al (2007). "Hemolytic C-type lectin CEL-III from sea cucumber expressed in transgenic mosquitoes impairs malaria parasite development". PLoS Pathog. 3 (12): e192. doi:. PMID 18159942. http://www.plospathogens.org/article/info:doi/10.1371/journal.ppat.0030192.
- ^ Tia E, Akogbeto M, Koffi A, et al (2006). "[Pyrethroid and DDT resistance of Anopheles gambiae s.s. (Diptera: Culicidae) in five agricultural ecosystems from Côte-d'Ivoire]" (in French). Bulletin de la Société de pathologie exotique (1990) 99 (4): 278–82. PMID 17111979.
- ^ Indoor Residual Spraying: Use of Indoor Residual Spraying for Scaling Up Global Malaria Control and Elimination. World Health Organization, 2006.
- ^ 10 Things You Need to Know about DDT Use under The Stockholm Convention
- ^ The Stockholm Convention on persistent organic pollutants
- ^ Rosenberg, Tina (2007-04-11). ""What the world needs now is DDT"". New York Times. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?sec=health&res=9F0DEEDA1738F932A25757C0A9629C8B63. Retrieved on 2008-11-03.
- ^ Pates, H & Curtis, C.:"Mosquito behavior and vector control", page 53-70. Annual Review on Entomology, 50, 2005.
- ^ Bachou H, Tylleskär T, Kaddu-Mulindwa DH, Tumwine JK (2006). "Bacteraemia among severely malnourished children infected and uninfected with the human immunodeficiency virus-1 in Kampala, Uganda". BMC Infect. Dis. 6: 160. doi:. PMID 17090299.
- ^ New Mosquito Nets Could Help Fight Malaria in Africa
- ^ The Economist (2007). "Traditional Economy of the Kavango". Economist Documentary. http://www.economist.com.na/2002/15mar/03-15-22.htm.
- ^ Rowland M, Durrani N, Hewitt S, Mohammed N, Bouma M, Carneiro I, Rozendaal J, Schapira A (1999). "Permethrin-treated chaddars and top-sheets: appropriate technology for protection against malaria in Afghanistan and other complex emergencies". Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 93 (5): 465–72. doi:. PMID 10696399.
- ^ "Fungus 'may help malaria fight'", BBC News, 2005-06-09
- ^ a b Nussenzweig R, Vanderberg J, Most H, Orton C (1967). "Protective immunity produced by the injection of x-irradiated sporozoites of plasmodium berghei". Nature 216 (5111): 160–2. doi:. PMID 6057225.
- ^ Hoffman SL, Goh LM, Luke TC, et al (2002). "Protection of humans against malaria by immunization with radiation-attenuated Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites". J. Infect. Dis. 185 (8): 1155–64. doi:. PMID 11930326.
- ^ Sanaria Press and Publications
- ^ Health | You can get paid to catch malaria | Seattle Times Newspaper
- ^ Zavala F, Cochrane A, Nardin E, Nussenzweig R, Nussenzweig V (1983). "Circumsporozoite proteins of malaria parasites contain a single immunodominant region with two or more identical epitopes". J Exp Med 157 (6): 1947–57. doi:. PMID 6189951.
- ^ Hollingdale M, Nardin E, Tharavanij S, Schwartz A, Nussenzweig R (1984). "Inhibition of entry of Plasmodium falciparum and P. vivax sporozoites into cultured cells; an in vitro assay of protective antibodies". J Immunol 132 (2): 909–13. PMID 6317752.
- ^ a b Matuschewski K (2006). "Vaccine development against malaria". Curr Opin Immunol 18 (4): 449–57. doi:. PMID 16765576.
- ^ Gardner M, Hall N, Fung E, et al (2002). "Genome sequence of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum". Nature 370 (6906): 1543. doi:. PMID 12368864.
- ^ Heppner DG, Kester KE, Ockenhouse CF, et al (2005). "Towards an RTS,S-based, multi-stage, multi-antigen vaccine against falciparum malaria: progress at the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research". Vaccine 23 (17-18): 2243–50. doi:. PMID 15755604.
- ^ Alonso PL, Sacarlal J, Aponte JJ, et al (2004). "Efficacy of the RTS,S/AS02A vaccine against Plasmodium falciparum infection and disease in young African children: randomised controlled trial". Lancet 364 (9443): 1411–20. doi:. PMID 15488216.
- ^ Aponte JJ, Aide P, Renom M, et al (November 2007). "Safety of the RTS,S/AS02D candidate malaria vaccine in infants living in a highly endemic area of Mozambique: a double blind randomised controlled phase I/IIb trial". Lancet 370 (9598): 1543–51. doi:. PMID 17949807.
- ^ Africa: Malaria - Vaccine Expected in 2011. Accra Mail. 9 January 2007. Accessed 15 January 2007.
- ^ "What is Malariacontrol.net". AFRICA@home. http://africa-at-home.web.cern.ch/africa%2Dat%2Dhome/malariacontrol.html. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- ^ Águas R, White LJ, Snow RW, Gomes MG (2008). "Prospects for malaria eradication in sub-Saharan Africa". PLoS ONE 3 (3): e1767. doi:. PMID 18335042.
External links
General information
- WHO site on malaria
- Medicines for Malaria Venture (MMV)
- World Malaria Report 2005
- Doctors Without Borders/Medecins Sans Frontieres - Malaria information pages
- Medline Plus - Malaria
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||








