Kenya
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding reliable references (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (September 2008) |
| Republic of Kenya
Jamhuri ya Kenya
|
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
||||||
| Motto: "Harambee" (Swahili) "Let us all pull together" |
||||||
| Anthem: Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu "O God of All Creation" |
||||||
| Capital (and largest city) |
Nairobi |
|||||
| Official languages | Swahili, English[1] | |||||
| Demonym | Kenyan | |||||
| Government | Semi-presidential Republic | |||||
| - | President | Mwai Kibaki | ||||
| - | Prime Minister | Raila Odinga | ||||
| Independence | from the United Kingdom | |||||
| - | Date | December 12, 1963 | ||||
| - | Republic declared | December 12, 1964 | ||||
| Area | ||||||
| - | Total | 580,367 km2 (47th) 224,080 sq mi |
||||
| - | Water (%) | 2.3 | ||||
| Population | ||||||
| - | July 2008 estimate | 37,953,8401 (36th) | ||||
| - | 8 February 2007 census | 31,138,735 | ||||
| - | Density | 59/km2 (140th) 153/sq mi |
||||
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $61.172 billion[2] | ||||
| - | Per capita | $1,734[2] | ||||
| GDP (nominal) | 2008 estimate | |||||
| - | Total | $31.418 billion[2] | ||||
| - | Per capita | $890[2] | ||||
| HDI (2007) | ▲ 0.521 (medium) (148th) | |||||
| Currency | Kenyan shilling (KES) |
|||||
| Time zone | EAT (UTC+3) | |||||
| - | Summer (DST) | not observed (UTC+3) | ||||
| Drives on the | left | |||||
| Internet TLD | .ke | |||||
| Calling code | 254 | |||||
| 1. According to cia.gov, estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality and death rates, lower population and growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex, than would otherwise be expected.[3] | ||||||
The Republic of Kenya is a country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia to the north, Somalia to the northeast, Tanzania to the south, Uganda to the west, and Sudan to the northwest, with the Indian Ocean running along the southeast border. The capital city is Nairobi. The country is named after Mount Kenya, a very significant landmark and the second among the highest mountain peaks of Africa,[4][5] and both were originally usually pronounced /ˈkiːnjə/[6] in English although the native pronunciation and the one intended by the original transcription Kenia was [ˈkenia].[7] During the presidency of Jomo Kenyatta in the 1960s, the current pronunciation /ˈkɛnjə/ became widespread in English because his name was pronounced according to the original native pronunciation.[8] Before 1920, the area now known as Kenya was known as the British East Africa Protectorate and so there was no need to mention mount when referring to the mountain.[4]
Contents |
History
Prehistory
Giant crocodile fossils have been discovered in Kenya, dating from the Mesozoic Era, over 200 million years ago. The fossils were found in an excavation conducted by a team from the University of Utah and the National Museums of Kenya in July–August 2004 at Lokitaung Gorge, near Lake Turkana.[9]
Fossils found in East Africa suggest that primates roamed the area more than 20 million years ago. Recent finds near Kenya's Lake Turkana indicate that hominids such as Homo habilis (1.8 and 2.5 million years ago) and Homo erectus (1.8 million to 350 000 years ago) are possible direct ancestors of modern Homo sapiens and lived in Kenya during the Pleistocene epoch. In 1984 one particular discovery made at Lake Turkana by famous palaeoanthropologist Richard Leakey and Kamoya Kimeu was the skeleton of a Turkana boy belonging to Homo erectus from 1.6 million years ago. Previous research on early hominids is particularly identified with Mary Leakey and Louis Leakey, who were responsible for the preliminary archaeological research at Olorgesailie and Hyrax Hill. Later work at the former was undertaken by Glynn Isaac.
Pre-colonial history

Cushitic-speaking people, as termed by Schloezer, from northern Africa, moved into the area that is now Kenya beginning around 2000 BCE.[10] Arab traders began frequenting the Kenya coast around the 1st century CE. Kenya's proximity to the Arabian Peninsula invited colonisation, and Arab and Persian settlements sprouted along the coast by the 8th century, though some of the "Arabs", like in much of East Africa, were Afro-Arabs. During the first millennium CE, Nilotic and Bantu-speaking peoples moved into the region, and the latter now comprise three-quarters of Kenya's population.[citation needed] The Kenyan coast had served host to communities of ironworkers and communities of subsistence farmers, hunters and fishers who supported the economy with agriculture, fishing, metal production and trade with foreign countries.[11] Around the 6th or 9th century CE Kenya switched to a maritime-based economy and began to specialize in shipbuilding to travel south by sea to other port cities such as Kilwa and Shanga along the East African coast. Mombasa became the major port city of pre-colonial Kenya in the Middle Ages and was used to trade with other African port cities, Persia, Arab traders, Yemen and even India.[12] 15th century Portuguese voyager Duarte Barbosa claimed, "[Mombasa] is a place of great traffic and has a good harbour in which there are always moored small craft of many kinds and also great ships, both of which are bound from Sofala and others which come from Cambay and Melinde and others which sail to the island of Zanzibar."[13]
In the centuries preceding colonisation, the Swahili coast of Kenya was part of the east African region which traded with the Arab world and India especially for ivory and slaves (the Ameru tribe is said to have originated from slaves escaping from Arab lands some time around the year 1700. Initially these traders came mainly from Arab states, but later many also came from Zanzibar (such as Tippu Tip).
Swahili, a Bantu language with Arabic, Persian and other Middle Eastern and South Asian loan words, later developed as a lingua franca for trade between the different peoples.[14]
The Luo of Kenya descend from early agricultural and herding communities from western Kenya's early pre-colonial history. The Luo along with other tribes associated with the Nilotic language group, are known to have originated from the north of Kenya, probably the northern regions of modern Sudan. The Nilots as they are known, are an anthropological group that originated from the northeastern regions of Africa. They may have moved south due to the wars that characterized the growth of territories such as Kush and Egypt. In Kenya, this group comprises the Luo, Kalenjin, the Turkana and the Maasai as the main groups. This is clearly evidenced by the presence of similar dialects among certain tribes in modern day Sudan. These tribes, include the Acoli and Lwo (not same as Luo) who occupy modern Darfur region.[citation needed]
There are also other tribes belonging to this group in Uganda and Tanzania. This is attributed mainly to the Luo's affinity to Lake Victoria, which they have stuck to throughout the three countries (Uganda, Tanzania and Kenya). In Uganda, they are known to have established the Buganda Kingdom and the Toro Kingdom. The Luo in Kenya are known to have fought numerous wars with their neighbors, notably the Kalenjin, for control of the lake.[citation needed]
Throughout the centuries, the Kenyan Coast has played host to many merchants and explorers. Among the cities that line the Kenyan coast is the City of Malindi. It has remained an important Swahili settlement since the 14th century and once rivaled Mombasa for dominance in this part of East Africa. Malindi has traditionally been a friendly port city for foreign powers. In 1414, the Arab Sultan of Malindi initiated diplomatic relations with Ming Dynasty China during the voyages of the explorer Zheng He.[15] Malindi authorities welcomed the great Portuguese explorer, Vasco da Gama, in 1498.
Colonial history
| This article does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (November 2008) |
The Portuguese were the first Europeans to explore the region of current-day Kenya, Vasco da Gama having visited Mombasa in 1498. Gama's voyage was successful in reaching India and this permitted the Portuguese to trade with the Far East directly by sea, thus challenging older trading networks of mixed land and sea routes, such as the Spice trade routes that utilized the Persian Gulf, Red Sea and caravans to reach the eastern Mediterranean. The Republic of Venice had gained control over much of the trade routes between Europe and Asia. After traditional land routes to India had been closed by the Ottoman Turks, Portugal hoped to use the sea route pioneered by Gama to break the once Venetian trading monopoly. Portuguese rule in East Africa focused mainly on a coastal strip centred in Mombasa. The Portuguese presence in East Africa officially began after 1505, when flagships under the command of Don Francisco de Almeida conquered Kilwa, an island located in what is now southern Tanzania.
The Portuguese presence in East Africa served the purpose of control trade within the Indian Ocean and secure the sea routes linking Europe to Asia. Portuguese naval vessels were very disruptive to the commerce of Portugal's enemies within the western Indian Ocean and were able to demand high tariffs on items transported through the sea due to their strategic control of ports and shipping lanes. The construction of Fort Jesus in Mombasa in 1593 was meant to solidify Portuguese hegemony in the region, but their influence was clipped by the British, Dutch Omani Arab incursions into the region during the 17th century. The Omani Arabs posed the most direct challenge to Portuguese influence in East Africa and besieged Portuguese fortresses, openly attacked naval vessels and expelled the remaining Portuguese from the Kenyan and Tanzanian coasts by 1730. By this time the Portuguese Empire had already lost its interest on the spice trade sea route due to the decreasing profitability of that business.
Omani Arab colonization of the Kenyan and Tanzanian coasts brought the once independent city-states under closer foreign scrutiny and domination than was experienced during the Portuguese period. Like their predecessors, the Omani Arabs were primarily able only to control the coastal areas, not the interior. However, the creation of clove plantations, intensification of the slave trade and relocation of the Omani capital to Zanzibar in 1839 by Seyyid Said had the effect of consolidating the Omani power in the region. Arab governance of all the major ports along the East African coast continued until British interests aimed particularly at ending the slave trade and creation of a wage-labour system began to put pressure on Omani rule. By the late nineteenth century, the slave trade on the open seas had been completely outlawed by the British and the Omani Arabs had little ability to resist the Royal Navy's ability to enforce the directive. The Omani presence continued in Zanzibar and Pemba until the 1964 revolution, but the official Omani Arab presence in Kenya was checked by German and British seizure of key ports and creation of crucial trade alliances with influential local leaders in the 1880s. However, the Omani Arab legacy in East Africa is currently found through their numerous descendants found along the coast that can directly trace ancestry to Oman and are typically the wealthiest and most politically influential members of the Kenyan coastal community.

However, most historians consider that the colonial history of Kenya dates from the establishment of a German protectorate over the Sultan of Zanzibar's coastal possessions in 1885, followed by the arrival of the Imperial British East Africa Company in 1888. Incipient imperial rivalry was forestalled when Germany handed its coastal holdings to Britain in 1890. This followed the building of the Kenya-Uganda railway passing through the country. This was resisted by some tribes — notably the Nandi led by Orkoiyot Koitalel Arap Samoei for ten years from 1895 to 1905 — still the British eventually built the railway. It is believed that the Nandi were the first tribe to be put in a native reserve to stop them from disrupting the building of the railway. During the railway construction era, there was a significant inflow of Indian peoples who provided the bulk of the skilled manpower required for construction. It was during this time, while building the railroad through the Tsavo National Park, that a number of the Indian railway workers and local African labourers were attacked by two lions known as the Tsavo maneaters. They and most of their descendants later remained in Kenya and formed the core of several distinct Indian communities such as the Ismaili Muslim and Sikh communities.[16][17]
At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, the governors of British East Africa (as the Protectorate was generally known) and German East Africa agreed a truce in an attempt to keep the young colonies out of direct hostilities. However Lt Col Paul von Lettow-Vorbeck took command of the German military forces, determined to tie down as many British resources as possible. Completely cut off from Germany by the Royal Navy, von Lettow conducted an effective guerilla warfare campaign, living off the land, capturing British supplies, and remaining undefeated. He eventually surrendered in Zambia eleven days after the Armistice was signed in 1918. To chase von Lettow the British deployed Indian Army troops from India and then needed large numbers of porters to overcome the formidable logistics of transporting supplies far into the interior by foot. The Carrier Corps was formed and ultimately mobilised over 400,000 Africans, contributing to their long-term politicisation.
During the early part of the 20th century, the interior central highlands were settled by British and other European farmers, who became wealthy farming coffee and tea. By the 1930s, approximately 30 000 white settlers lived in the area and were offered undue political powers because of their effects on the economy. The area was already home to over a million members of the Kikuyu tribe, most of whom had no land claims in European terms (but the land belonged to the ethnic group), and lived as itinerant farmers. To protect their interests, the settlers banned the growing of coffee, introduced a hut tax, and the landless were granted less and less land in exchange for their labour. A massive exodus to the cities ensued as their ability to provide a living from the land dwindled.
In 1951, Sir Horace Hector Hearne became Chief Justice in Kenya (coming from Ceylon, where he had also been Chief Justice) and sat in the Supreme Court in Nairobi. He held that position until 1954 when he became an Appeal Justice of the West African Court of Appeal. On the night of the death of King George VI, 5 February 1952, Hearne escorted The Princess Elizabeth, Duchess of Edinburgh, as she then was, to a state dinner at the Treetops Hotel, which is now a very popular tourist retreat. It was there that she "went up a princess and came down a Queen".[18] She returned immediately to England, accompanied by Hearne.
From October 1952 to December 1959, Kenya was under a state of emergency arising from the Mau Mau rebellion against British rule. The governor requested and obtained British and African troops, including the King's African Rifles. In January 1953, Major General Hinde was appointed as director of counter-insurgency operations. The situation did not improve for lack of intelligence, so General Sir George Erskine was appointed commander-in-chief of the colony's armed forces in May 1953, with the personal backing of Winston Churchill.
The capture of Warũhiũ Itote (aka General China) on 15 January 1954, and the subsequent interrogation led to a better understanding of the Mau Mau command structure. Operation Anvil opened on 24 April 1954, after weeks of planning by the army with the approval of the War Council. The operation effectively placed Nairobi under military siege, and the occupants were screened and the Mau Mau supporters moved to detention camps. May 1953 also saw the Home Guard officially recognized as a branch of the Security Forces. The Home Guard formed the core of the government's anti-Mau Mau strategy as it was composed of loyalist Africans, not foreign forces like the British Army and King's African Rifles. By the end of the emergency the Home Guard had killed 4686 Mau Mau, amounting to 42% of the total insurgents. The capture of Dedan Kimathi on 21 October 1956, in Nyeri signified the ultimate defeat of the Mau Mau and essentially ended the military offensive.
Post-colonial history
The first direct elections for Africans to the Legislative Council took place in 1957. Despite British hopes of handing power to "moderate" African rivals, it was the Kenya African National Union (KANU) of Jomo Kenyatta that formed a government shortly before Kenya became independent on 12 December 1963. During the same year, the Kenyan army fought the Shifta War against ethnic Somalis determined to see the NFD join with the Republic of Somalia. The Shiftas inflicted heavy casualties on the Kenyan armed forces but were defeated in 1967.
Kenya, fearing an invasion from militarily stronger Somalia, in 1969 signed a defence pact with Ethiopia which is still in effect.[19] Suffering from droughts and floods, the NFD is the least developed region in Kenya. However, since the 1990s, Somali refugees-turned-wealthy businessmen have managed to transform the one-time slum of Eastleigh into the most prosperous commercial centre of Eastlands and increasingly much of Nairobi.[20]
In 1964, Kenyatta became Kenya's first president. At Kenyatta's death in 1978, Daniel arap Moi became President. Daniel arap Moi retained the Presidency, being unopposed in elections held in 1979, 1983 (snap elections) and 1988, all of which were held under the single party constitution. The 1983 elections were held a year early, and were a direct result of an abortive military coup attempt on 1 August 1982.
The abortive coup was masterminded by a lowly ranked Air Force serviceman, Senior Private Hezekiah Ochuka and was staged mainly by enlisted men in the Air Force. The attempt was quickly suppressed by Loyalist forces led by the Army, the General Service Unit (GSU) — a paramilitary wing of the police — and later the regular police, but not without civilian casualties. This event led to the disbanding of the entire Air Force and a large number of its former members were either dismissed or court-martialled.
The election held in 1988 saw the advent of the mlolongo (queuing) system, where voters were supposed to line up behind their favoured candidates instead of a secret ballot[citation needed]. This was seen as the climax of a very undemocratic regime and it led to widespread agitation for constitutional reform. Several contentious clauses, including one that allowed for only one political party were changed in the following years[citation needed]. In democratic, multiparty elections in 1992 and 1997, Daniel arap Moi won re-election. In 2002, Moi was constitutionally barred from running, and Mwai Kǐbakǐ, running for the opposition coalition "National Rainbow Coalition" — NARC, was elected President. The elections, judged free and fair by local and international observers, marked a turning point in Kenya's democratic evolution.
Origins of the country's name
Until 1920 the area that is now Kenya was called the British East African Protectorate.[4] In 1920 Kenya Colony was formed, named after its highest peak, and pronounced /ˈkiːnjə/.[8]
At independence, in 1963, Jomo Kenyatta was elected as the first president.[21] He had previously assumed this name to reflect his commitment to freeing his country and his pronunciation of his name resulted in the pronunciation of Kenya in English changing back to an approximation of the original native pronunciation, pronounced /ˈkɛnjə/.[8]
Politics

Kenya is a presidential representative democratic republic, whereby the President was both the head of state and head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government. Legislative power is vested in both the government and the National Assembly. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. However, there was growing concern especially during former president Daniel arap Moi's tenure that the executive was increasingly meddling with the affairs of the judiciary.
Until the unrest occasioned by the disputed election results of December 2007, Kenya had hitherto maintained remarkable stability despite changes in its political system and crises in neighbouring countries. A cross-party parliamentary reform initiative in the fall of 1997 revised some oppressive laws inherited from the colonial era that had been used to limit freedom of speech and assembly. This improved public freedoms and contributed to generally credible national elections in December 1997.
In December 2002, Kenyans held democratic and open elections, most of which were judged free and fair by international observers. The 2002 elections marked an important turning point in Kenya's democratic evolution in that power was transferred peacefully from the Kenya African Union (KANU), which had ruled the country since independence to the National Rainbow Coalition (Narc), a coalition of political parties.
Under the presidency of Mwai Kibaki, the new ruling coalition promised to focus its efforts on generating economic growth, combating corruption, improving education, and rewriting its constitution. A few of these promises have been met. There is free primary education. In 2007 the government issued a statement declaring that from 2008, secondary education would be heavily subsidised, with the government footing all tuition fees.
2007 elections
The last general elections were held on December 27, 2007. In them, President Kibaki under the Party of National Unity ran for re-election against the main opposition party, the Orange Democratic Movement (ODM). The elections were largely believed to have been flawed with international observers saying that they did not meet regional or international standards, with observers stating that the tallying process was rigged in favor of president Mwai Kibaki. After a split which would take a crucial 8% of the votes away from the ODM to the newly formed Orange Democratic Movement-Kenya (ODM-K)'s candidate, Kalonzo Musyoka, the race tightened between ODM candidate Raila Odinga and Kibaki. As the count came in to the Kenyan Election Commission, Odinga was shown to have a slight, and then substantial lead. However, as the Electoral Commission of Kenya (ECK) continued to count the votes, Kibaki closed the gap and then overtook his opponent by a substantial margin amid largely substantiated claims of rigging from both sides of the political divide (notably by the EU Observers). This led to protests and riots, open discrediting of the ECK for complicity and to Odinga declaring himself the "people's president" and calling for a recount and Kibaki to resign.[citation needed]
The protests escalated into unprecedented violence and destruction of property, leading to Odinga claiming up to 1000 deaths as a result.[22] The government claimed nearly 700 deaths and the internal displacement of around 260,000 people. [23] A group of eminent persons of Africa, led by former United Nations secretary-general Kofi Annan, was called in to broker a peaceful solution to the political stalemate. This group enjoyed the backing of the UN, European Union, African Union and United States governments, as well as those of various other notable countries across the world. More information is available in clashes in Kenya (2007–present).
Annan requested mediation support for his team on the Panel Secretariat from the Swiss based conflict mediation organisation, the Centre for Humanitarian Dialogue.
2008
On 28 February 2008, Kibaki and Odinga signed an agreement on the formation of a coalition government in which Odinga would become Kenya's second prime Minister. Under the deal, the president would also appoint cabinet ministers from both PNU and ODM camps depending on each party's strength in Parliament. The agreement stipulated that the cabinet would also include a vice-president and two deputy Prime Ministers. After being debated and passed by Parliament, the coalition would hold until the end of the current Parliament or if either of the parties withdraws from the deal before then.
The new office of the PM will have power and authority to co-ordinate and supervise the functions of the Government and will be occupied by an elected MP who will also be the leader of the party or coalition with majority members in Parliament. The world watched Annan and his UN-backed panel and African Union chairman Jakaya Kikwete as they brought together the erstwhile rivals to the signing ceremony, beamed live on national TV from the steps of Nairobi's Harambee House. On February 29, 2008, representatives of PNU and ODM began working on the finer details of the power-sharing agreement.[24] Kenyan lawmakers unanimously approved a power-sharing deal March 18, 2008, aimed at salvaging a country once seen as one of the most stable and prosperous in Africa. The deal brought Kibaki's PNU and Odinga's ODM together and heralded the formation of the Grand Coalition, in which the two political parties would share power equally.[citation needed]
According to a report published by the Independent Review Commission (IREC) on the 2007 elections chaired by Justice Johann Kriegler, there were too many electoral malpractices from grassroot regions of all parties involved to conclusively establish which candidate won the December 2007 Presidential elections. Such malpractices included widespread bribery, vote buying, intimidation and ballot-stuffing as well as incompetence from the Electoral Commission of Kenya (ECK). The commission exonerated the ECK from tampering with the vote tallying at the ECK's Voter Tallying headquarters.[25] This was contrary to the claims of rigging by the ECK at the voter tallying headquarters.
Grand coalition
On April 13, 2008, President Kibaki named a Grand coalition cabinet of 41 Ministers- including the prime minister and his two deputies - after weeks of tension and uncertainty that had gripped the country following the failure of the president and prime minister designate, Raila Odinga, to agree on how some of the ministries should be shared. The cabinet, which also included 50 Assistant Ministers, was sworn in at the State House in Nairobi on Thursday, April 17, 2008 in the presence of Dr. Kofi Annan and other invited dignitaries.
Provinces, districts, and divisions
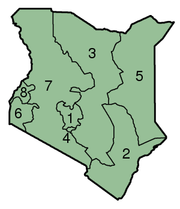
Kenya comprises eight provinces each headed by a Provincial Commissioner (centrally appointed by the president). The provinces (mkoa singular mikoa plural in Swahili) are subdivided into districts (wilaya). There were 69 districts as of 1999 census. Districts are then subdivided into 497 divisions (taarafa). The divisions are then subdivided into 2,427 locations (mtaa) and then 6,612 sublocations (mtaa mdogo).[26] The City of Nairobi enjoys the status of a full administrative province. The government supervises administration of districts and provinces. The provinces are:
Local governance in Kenya is practised through local authorities. Many urban centres host city, municipal or town councils. Local authorities in rural areas are known as county councils. Local councillors are elected by civic elections, held alongside general elections.
Constituencies are an electoral subdivision. There are 210 Constituencies in Kenya.[27]
Population of major cities
| City | Population |
|---|---|
| Nairobi | 2 940 911 |
| Mombasa | 707 400 |
| Nakuru | 337 200 |
| Kisumu | 273 400 |
| Eldoret | 249 100 |
| Nyeri | 213 000 |
| Machakos | 179 500 |
| Meru | 140 900 |
Geography and climate

At 224,961 square miles (582,646 km²), Kenya is the world's forty-seventh largest country (after Madagascar). From the coast on the Indian Ocean the Low plains rise to central highlands. The highlands are bisected by the Great Rift Valley; a fertile plateau in the east. The Kenyan Highlands comprise one of the most successful agricultural production regions in Africa. The highlands are the site of the highest point in Kenya (and the second highest in Africa): Mount Kenya, which reaches 5,199 metres (17,057 ft) and is also the site of glaciers. Climate varies from tropical along the coast to arid in the interior. Mount Kilimanjaro (5,895m - 19,341 ft) can be seen from Kenya to the South of the Tanzanian border.[30]
Kenya has considerable land area of wildlife habitat, including the Masai Mara, where Blue Wildebeest and other bovids participate in a large scale annual migration. Up to 250,000 blue wildebeest perish each year in the long and arduous movement to find forage in the dry season.[citation needed] The "Big Five" animals of Africa can also be found in Kenya: the lion, leopard, buffalo, rhinoceros and elephant. A significant population of other wild animals, reptiles and birds can be found in the national parks and game reserves in the country. The environment of Kenya is threatened by high population growth and its side effects.[citation needed]
Kenya has a tropical climate. It is hot and humid at the coast, temperate inland and very dry in the north and northeast parts of the country. There is however a lot of rain between March and May, and moderate rain in October and November. The temperature remains high throughout these months.
| City | Elevation (m) | Max (°C) | Min (°C) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mombasa | coastal town | 17 | 30.3 | 22.4 |
| Nairobi | capital city | 1,661 | 25.2 | 13.6 |
| Eldoret | 3,085 | 23.6 | 9.5 | |
| Lodwar | dry north plainlands | 506 | 34.8 | 23.7 |
| Mandera | dry north plainlands | 506 | 34.8 | 25.7 |
The country receives a great deal of sunshine all the year round and summer clothes are worn throughout the year. However, it is usually cool at night and early in the morning.
The long rain season occurs from April to June. The short rain season occurs from October to December. The rainfall is sometimes heavy and often falls in the afternoons and evenings. The hottest period is from February to March and coldest in July to August.
The annual animal migration - especially migration of the wildebeest - occurs between June and September with millions of animals taking part. It has been a popular event for filmmakers to capture.
Economy
After independence, Kenya promoted rapid economic growth through public investment, encouragement of smallholder agricultural production, and incentives for private (often foreign) industrial investment. Gross domestic product (GDP) grew at an annual average of 6.6% from 1963 to 1973. Agricultural production grew by 4.7% annually during the same period, stimulated by redistributing estates, diffusing new crop strains, and opening new areas to cultivation.
Between 1974 and 1990, however, Kenya's economic performance declined. Inappropriate agricultural policies, inadequate credit, and poor international terms of trade contributed to the decline in agriculture.
From 1991 to 1993, Kenya had its worst economic performance since independence. Growth in GDP stagnated, and agricultural production shrank at an annual rate of 3.9%. Inflation reached a record 100% in August 1993, and the government's budget deficit was over 10% of GDP. As a result of these combined problems, bilateral and multilateral donors suspended programme aid to Kenya in 1991.
In 1993, the Government of Kenya began a major programme of economic reform and liberalization. A new minister of finance and a new governor of the Central Bank of Kenya undertook a series of economic measures with the assistance of the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). As part of this programme, the government eliminated price controls and import licensing, removed foreign exchange controls, privatised a range of publicly owned companies, reduced the number of civil servants, and introduced conservative fiscal and monetary policies. From 1994 to 1996, Kenya's real GDP growth rate averaged just over 4% a year.
In 1997, however, the economy entered a period of slowing or stagnant growth, due in part to adverse weather conditions and reduced economic activity prior to general elections in December 1997. In 2000, GDP growth was negative, but improved slightly in 2001 as rainfall returned closer to normal levels. Economic growth continued to improve slightly in 2002 and reached 1.4% in 2003. it was 4.3% in 2004 and 5.8% in 2005.

In July 1997, the Government of Kenya refused to meet commitments made earlier to the IMF on governance reforms. As a result, the IMF suspended lending for 3 years, and the World Bank also put a $90-million structural adjustment credit on hold. Although many economic reforms put in place in 1993-94 remained, conservative economists believe that Kenya needs further reforms, particularly in governance, in order to increase GDP growth and combat the poverty that afflicts more than 57% of its population.
The Government of Kenya took some positive steps on reform, including the 1999 establishment of the Kenya Anti-Corruption Authority (KACA), and measures to improve the transparency of government procurements and reduce the government payroll. In July 2000, the IMF signed a $150 million Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility (PRGF), and the World Bank followed suit shortly after with a $157 million Economic and Public Sector Reform credit. The Anti-Corruption Authority was declared unconstitutional in December 2000, and other parts of the reform effort faltered in 2001. The IMF and World Bank again suspended their programmes. Various efforts to restart the programme through mid-2002 were unsuccessful.
Under the leadership of President Kibaki, who took over on December 30, 2002, the Government of Kenya began an ambitious economic reform programme and has resumed its cooperation with the World Bank and the IMF. The new National Rainbow Coalition (NARC) government enacted the Anti-Corruption and Economic Crimes Act and Public Officers Ethics Act in May 2003 aimed at fighting graft in public offices. Other reforms especially in the judiciary, public procurement etc., have led to the unlocking of donor aid and a renewed hope at economic revival. In November 2003, following the adoption of key anti-corruption laws and other reforms by the new government, donors reengaged as the IMF approved a three-year $250 million Poverty Reduction and Growth Facility and donors committed $4.2 billion in support over 4 years. The renewal of donor involvement has provided a much-needed boost to investor confidence.
The Privatisation Bill has been enacted although the setting up of a privatisation commission is yet to be finalised, civil service reform has been implemented and in 2007 the country won the UN Public Service reform award.[31][32] However a lot of work needs to be done to make the country catch up with the rest of economic giants especially the Far East. The main challenges include taking candid action on corruption, enacting anti-terrorism and money laundering laws, bridging budget deficits, rehabilitating and building infrastructure. This hopefully will help in maintaining sound macroeconomic policies, and speed up the rapidly accelerating economic growth, which is projected to grow to 7.2% in 2007.
In 2007, the Kenyan government unveiled Vision 2030, which is a very ambitious economic blueprint and which, if implemented in its entirety, has the potential of putting the country in the same league as the Asian Economic Tigers. However all these economic projections now hang in the balance following the political uncertainty occasioned by the aftermath of the 2007 disputed Presidential polls, which left the country economically dented.
Nairobi continues to be the primary communication and financial hub of East Africa. It enjoys the region's best transportation linkages, communications infrastructure, and trained personnel, although these advantages are less prominent than in past years. A wide range of foreign firms maintain regional branch or representative offices in the city. In March 1996, the Presidents of Kenya, Tanzania, and Uganda re-established the East African Community (EAC). The EAC's objectives include harmonizing tariffs and customs regimes, free movement of people, and improving regional infrastructures. In March 2004, the three East African countries signed a Customs Union Agreement.
| GDP | $17.43 billion (2005) at Market Price. $ 41.36 billion (Purchasing Power Parity, 2006)
There also exists a large, informal economy that is never counted as part of the official GDP figures. |
|---|---|
| Annual growth rate | 5.8% (2005): 2006 = 6.1% : Estimate for 2007 = 7.2% |
| Per capita income | Per Capita Income (PPP)= $1,200 |
| Natural resources | Wildlife, land (5% arable) |
| Agricultural produce | tea, coffee, sugarcane, horticultural products, corn, wheat, rice, sisal, pineapples, pyrethrum, dairy products, meat and meat products, hides, skins |
| Industry | petroleum products, grain and sugar milling, cement, beer, soft drinks, textiles, vehicle assembly, paper and light manufacturing, tourism |
| This article's factual accuracy may be compromised due to out-of-date information. Please help improve the article by updating it. There may be information on the talk page. |
| Exports | $2.2 billion | tea, coffee, horticultural products, petroleum products, cement, pyrethrum, soda ash, sisal, hides and skins, fluorspar |
|---|---|---|
| Major markets (2006)[3] | Uganda, United Kingdom, Tanzania, Netherlands, United States, Pakistan | |
| Imports | $3.2 billion | machinery, vehicles, crude petroleum, iron and steel, resins and plastic materials, refined petroleum products, pharmaceuticals, paper and paper products, fertilizers, wheat |
| Major suppliers | United Kingdom, Japan, South Africa, Germany, United Arab Emirates, Italy, India, France, United States, Saudi Arabia | |
Oil exploration
Early in 2006 Chinese President Hu Jintao signed an oil exploration contract with Kenya; the latest in a series of deals designed to keep Africa's natural resources flowing to China's rapidly-expanding economy.
The deal allowed for China's state-controlled offshore oil and gas company, CNOOC Ltd, to prospect for oil in Kenya, which is just beginning to drill its first exploratory wells on the borders of Sudan and Somalia and in coastal waters. No oil has been produced yet, and there has been no formal estimate of the possible reserves.[33]
Demographics
Kenya is a country of great ethnic diversity. Most Kenyans are bilingual in English and Swahili, also a large percentage speak the mother tongue of their ethnic tribe.
- Ethnic groups
- Kikuyu 22%, Luhya 14%, Luo 13%, Kalenjin 12%, Kamba 11%, Kisii 6%, Meru 6%, other African 15%, non-African (Asian, European, and Arab) 1%[3]
Religion in Kenya
| Religion in Kenya[34] | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| religion | percent | |||
| Protestant | 45% | |||
| Roman Catholic | 33% | |||
| Islam | 10% | |||
| Indigenous | 10% | |||
| Other | 2% | |||
The vast majority of Kenyans are Christian with 45% regarding themselves as Protestant and 33% as Roman Catholic. Sizeable minorities of other faiths do exist (Muslim 10%, indigenous beliefs 10%) but estimates for the percentage of the population that adheres to Islam or indigenous beliefs vary widely.[3] For example, according to some sources, estimates for the percentage of Muslims in Kenya range from 20% to as high as constituting 45% of the total population.[35]
Sixty percent of the Muslim population lives in Coast Province, comprising 50 percent of the total population there. Western areas of Coast Province are mostly Christian. The upper part of Eastern Province is home to 10 percent of the country's Muslims, where they are the majority religious group and apart from a small ethnic Somali population in Nairobi, the rest of the country is largely Christian.[36]
Education
| This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (March 2009) |
| It has been suggested that this article or section be merged into Education in Kenya. (Discuss) |
Kenya's education system consists of early childhood education, primary, secondary and college. Early childhood education takes at least three years, primary eight years, secondary four and university four or six years depending on the course. Preschooling, which targets children from age three to five, is an integral component of the education system and is a key requirement for admission to Standard One (First Grade). At the end of primary education, pupils sit the Kenya Certificate of Primary Education (KCPE), which determines those who proceed to secondary school or vocational training. Primary school age is 6/7-13/14 years. For those who proceed to secondary level, there is a national examination at the end of Form Four – the Kenya Certificate of Secondary Education (KCSE), which determines those proceeding to the universities, other professional training or employment. The Joint Admission Board (JAB) is responsible for selecting students joining the public universities. Other than the public schools, there are many private schools in the country, mainly in urban areas. Similarly, there are a number of international schools catering for various overseas educational systems.
Historical Background
The first Independent Kenya's system of education was introduced by British colonists. After Kenya's independence on December 12, 1963, an authority named Ominde Commission was formed to introduce changes that would reflect the nation's sovereignty.The commission focused on identity and unity, which were critical issues at the time. Changes in the subject content of history and geography were made to reflect national cohesion. Between 1964 and 1985, the 7-4-2-3-system was adopted – seven years of primary, four years of lower secondary, two years of upper secondary, and three years of university. All schools had a common curriculum.
In 1981, the Presidential Working Party on the Second University was commissioned to look at both the possibilities of setting up a second university in Kenya as well as the reforming of the entire education system. The committee recommended that the 7-4-2-3 system be changed to an 8-4-4 system (eight years in primary, four years in secondary, and four years in university education). The table under Present Day Education in Kenya below shows the structure of the 8-4-4 system. Although the 7-4-2-3 system theoretically ended with the introduction of the new 8-4-4 system in 1985, the last batch of students from the former system graduated from Kenyan Universities in 1992.
Present Day Education in Kenya
The current 8-4-4 system was launched in January 1985. It put more emphasis on vocational subjects in the assumption that the new structure would enable school dropouts at all levels to be either self-employed or to secure employment in the informal sector.
In January 2003, the Government of Kenya announced the introduction of free primary education. As a result, primary school enrolment increased by about 70%. However, secondary and tertiary education enrollment has not increased proportionally due to the fact that payment is still required for attendance.
In class eight of primary school the Kenya Certificate of Primary Examination (K.C.P.E.) is written. The result of this examination is needed for placement at secondary school. In form four of secondary schools the Kenya Certificate of Secondary Examination (K.C.S.E.) is written. Students sit examinations in eight subjects.
KCSE Grading System
Grade A A- B+ B B- C+ C C- D+ D D- E Points 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
The average grade is based on performance in the eight subjects. Where a candidate sits for more than eight subjects, the average grade is based on the best eight subjects. University matriculation is based on the best eight and performance in particular subjects relevant to degree courses. Example below:
Subject / Group / Grade / Points English / 1 / B+ / 10 Kiswahili / 1 / A- / 11 Mathematics / 1 / A / 12 History & Government / 3 / B / 9 Geography / 3 / A- / 11 Physics / 2 / B+ / 10 Chemistry / 2 / B- / 8 Biology 2 A- 11
The total number of points is 81.
The average grade is 81 divided by 8, which equals 10.1 (approximately 10.0 points) which is Grade B+ according to the grading system. This student qualifies to join one of the Public Universities due to his good score. Training institutions and faculties and departments determine their own minimum entry requirements.
Students who manage a grade of C+ qualify to do a degree course at the University. Due to competition, and fewer places at the University, those with B and in a few cases B-, and above are taken for degree courses at the Public Universities. The rest join private universities or middle colleges.
Criticism The Kenyan 8-4-4 system of education has weathered many storms in the 24 years of its existence. Immediately after the first batch of students of this system graduated in 1989, most of the country was up in arms, criticizing the government of "haphazard adoption of the system". Critics claimed that the system was producing "below par" graduates who could not effectively compete with their counterparts from other parts of the world. Others argued that the system had produced graduates who were either too young or ill-prepared for the job market. The government turned a deaf ear, probably because the prospect of overhauling the new system was unwelcome due the cost that the exercise would involve.
Culture


Kenya is a diverse country, with many different cultures represented. Notable cultures include the Swahili on the coast, pastoralist communities in the north, and several different communities in the central and western regions. Today, the Maasai culture is well known, due to its heavy exposure from tourism, however, Maasai make up a relatively minor percentage of the Kenyan population. The Maasai are known for their elaborate upper body adornment and jewelry.
Kenya has an extensive music, television and theatre scene.
Sports
Kenya is active in several sports, among them cricket, rallying, football (soccer), rugby union and boxing. But the country is known chiefly for its dominance in Middle-distance and long-distance athletics. Kenya has regularly produced Olympic and Commonwealth Games champions in various distance events, especially in 800 m, 1,500 m, 3,000 m steeplechase, 5,000 m, 10,000 m and the marathons. Kenyan athletes (particularly Kalenjin) continue to dominate the world of distance running, although competition from Morocco and Ethiopia has reduced this supremacy. Kenya's best-known athletes included the four-time women's Boston Marathon winner and two-time world champion Catherine Ndereba, former Marathon world record-holder Paul Tergat, and John Ngugi.
Kenya won several medals during the Beijing Olympics, 5 gold, 5 silver and 4 bronze, making it Africa's most successful Nation in the 2008 Olympics. New athletes gained attention, such as Pamela Jelimo, the women's 800m gold medalist who went ahead to win the Golden League jackpot, and Samuel Wanjiru who won the men's marathon.
Retired Olympic and Commonwealth Games champion Kipchoge Keino helped usher in Kenya's ongoing distance dynasty 1970s and was followed by Commonwealth Champion Henry Rono's spectacular string of world record performances.
Lately, there has been controversy in Kenyan athletics circles, with the defection of a number of Kenyan athletes to represent other countries, chiefly Bahrain and Qatar.[37] The Kenyan Ministry of Sports has tried to stop the defections, but they have continued anyway, with Bernard Lagat the latest, choosing to represent the United States.[37] Most of these defections occur due to economic or financial factors however some elite Kenyan runners who can't qualify for their country's strong national team also find it easier to qualify by running for other countries.
Kenya has also been a dominant force in ladies' volleyball within Africa, with both the clubs and the national team winning various continental championships in the past decade.[citation needed] The womens' team has also competed at the Olympics and World Championships but without any notable success.
Cricket is another popular and the most successful team sport. Kenya has competed in the Cricket World Cup since 1996. They upset some of the World's best teams and reached semi-finals of the 2003 tournament. They also won the inaugural World Cricket League Division 1 hosted in Nairobi and participated in the World T20. Their current captain is Steve Tikolo.
Kenya is making a name for itself in rugby union. It is popular in Kenya especially with the annual Safari Sevens tournament. Kenya sevens team ranked 9th in IRB Sevens World Series for the 2006 season.
Kenya was a regional power in soccer but its dominance has been eroded by wrangles within the Kenya Football Federation.[38] This has led to a suspension by FIFA which was lifted in March, 2007.
In the motor rallying arena, Kenya is home to the world famous Safari Rally, commonly acknowledged as one of the toughest rallies in the world,[39] and a part of the World Rally Championship for many years until its exclusion after the 2002 event due to financial difficulties. Some of the best rally drivers in the world have taken part in and won the rally, such as Bjorn Waldegaard, Hannu Mikkola, Tommi Makinen, Shekhar Mehta, Carlos Sainz and Colin McRae. Though the rally still runs annually as part of the Africa rally championship, the organisers are hoping to be allowed to rejoin the World Rally championship in the next couple of years.
Literary perspective
Ngugi wa Thiong'o is one of the best known writers of Kenya. His book, Weep Not, Child is an illustration of life in Kenya during the British occupation. This is a story about the effects of the Mau Mau on the lives of black Kenyans. Its combination of themes - colonialism, education, and love - help to make it one of the best-known novels in Africa.
M.G. Vassanji's 2003 novel The In-Between World of Vikram Lall won the Giller Prize in 2003. It is the fictional memoir of a Kenyan of Indian heritage and his family as they adjust to the changing political climates in colonial and post-colonial Kenya.
Since 2003, the literary journal Kwani? has been publishing Kenyan contemporary literature.
See also
|
|
References
- ^ Constitution (1998) art. 53 "the official languages of the National Assembly shall be Kiswahili and English and the business of the National Assembly may be conducted in either or both languages."
- ^ a b c d "Kenya". International Monetary Fund. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2008/02/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=52&pr.y=4&sy=2004&ey=2008&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=664&s=NGDPD%2CNGDPDPC%2CPPPGDP%2CPPPPC%2CLP&grp=0&a=. Retrieved on 2008-10-09.
- ^ a b c d cia.gov – The World Factbook Kenya
- ^ a b c Reuter."British East Africa Annexed--"Kenya Colony"" (News). The Times. Thursday, July 8, 1920. Issue 42457, col C, pg. 13.
- ^ "East Africa: Kenya: History: Kenya Colony". Encyclopedia Britannica. 17 (15 ed.). 2002. pp. 801, 1b. ISBN 0-85229-787-4.
- ^ "Kenya". Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. 2nd ed. 1989.
- ^ The Spelling of Kenya. B. J. Ratcliffe. Journal of the Royal African Society, Vol. 42, No. 166 (Jan., 1943), pp. 42-44
- ^ a b c Foottit, Claire (2006) [2004]. Kenya. The Brade Travel Guide. Bradt Travel Guides Ltd. ISBN 1-84162-066-1.
- ^ Kenya's first dinosaur dig yields fossil wealth, ABC News Online, 2005-03-10
- ^ Wonders of the African World - PBS
- ^ Wonders of the African World - PBS
- ^ Hybrid Urbanism By Nezar Al-Sayyad
- ^ The African Dispersal in the Deccan By Shanti Sadiq Ali
- ^ Wonders of the African World - PBS
- ^ Sultan of Malinda, PBS
- ^ Ismaili muslim
- ^ Sikh
- ^ Kenya, AfricaGenWeb
- ^ Post-Independence Low Intensity Conflict In Kenya
- ^ E. H., Campbell (2006). "Urban Refugees in Nairobi: Problems of Protection, Mechanisms of Survival, and Possibilities for Integration" (full text). Journal of Refugee Studies 19 (3): 396. doi:.
- ^ Castro, Alfonso Peter (1995). Facing Kirinyaga. London: Intermediat Technology Publications Ltd.. ISBN 1-85339-253-7.
- ^ http://www.reuters.com/article/homepageCrisis/idUSL0743589._CH_.2400
- ^ http://www.iol.co.za/index.php?set_id=1&click_id=68&art_id=nw20080113081804606C678503
- ^ 'Hope is back' for Kenya - CNN.com at edition.cnn.com
- ^ [1],IREC EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
- ^ Central Bureaus of Statistics (Kenya): Census cartography: The Kenyan Experience
- ^ Kenya Roads Board Constituency funding under the RMLF
- ^ Rough Guide. Rough Guide Map Kenya [map], 9 edition, 1:900,000, Rough Guide Map. Cartography by World Mapping Project. (2006) ISBN 1-84353-359-6.
- ^ Reuter."British East Africa Annexed--"Kenya Colony"" (News). The Times. Thursday, July 08, 1920. Issue 42457, col C, pg. 13.
- ^ Rough Guide. Rough Guide Map Kenya [map], 9 edition, 1:900,000, Rough Guide Map. Cartography by World Mapping Project. (2006) ISBN 1-84353-359-6.
- ^ http://www.7thglobalforum.org/Forum_Information/unpsa.htm
- ^ http://unpan1.un.org/intradoc/groups/public/documents/un/unpan026198.pdf
- ^ Barber, Lionel; Andrew England (August 10 2006). "China's scramble for Africa finds a welcome in Kenya". Financial Times. http://www.ft.com/cms/s/0/a51a39d2-280c-11db-b25c-0000779e2340.html. Retrieved on 2008-06-27.
- ^ the World Factbook
- ^ Islam and Politics in Kenya, By Arye Oded, pg. 11
- ^ U.S. Department of State
- ^ a b IAAF: Changes of Allegiance 1998 to 2005
- ^ New Vision, June 3, 2004: Wrangles land Kenya indefinite FIFA ban
- ^ The Auto Channel, July 21, 2001: FIA RALLY: Delecour takes points finish on Safari Rally debut
External links
![]() Textbooks from Wikibooks
Textbooks from Wikibooks
![]() Quotations from Wikiquote
Quotations from Wikiquote
![]() Source texts from Wikisource
Source texts from Wikisource
![]() Images and media from Commons
Images and media from Commons
![]() News stories from Wikinews
News stories from Wikinews
- Government
- Government Spokeperson Office of the Government Spokesperson of the Republic of Kenya.
- Government of Kenya Official site.
- Kenya Law Reports Kenyan Legislation, Case Law, Official Gazette Notices and legal Info.
- State House Kenya Official site State House, Kenya.
- Chief of State and Cabinet Members
- General
- Country Profile from BBC News
- Kenya from the Encyclopaedia Britannica
- Kenya entry at The World Factbook
- Kenya from UCB Libraries GovPubs
- Kenya at the Open Directory Project
- Wikimedia Atlas of Kenya
- Google Maps , interactive map of Kenya on the Web
- Media
- Kenya news media list from Stanford University
- Tourism
- Kenya Tourist Board (Magical Kenya) official travel and tourism guide
- Kenya travel guide from Wikitravel
- History
- 1911 Encyclopedia Britannica on the Kenya Colony
- 1911 Encyclopedia Britannica on the 1908 Demarcation of the Ethiopian-Kenyan Border
- Other
- Kimaiyo, Towett J. (2004). Ogiek Land Cases and Historical Injustices — 1902 – 2004. Nakuru, Kenya: Ogiek Welfare Council. pp. 127 pages + appendices. http://www.geocities.com/OgiekLand/. (Full text of book at link.)
- "Who Owns Kenya? — What is the Queen Doing in Parliament?". March 31, 2007. http://www.geocities.com/WhoOwnsKenya/.
- Rural poverty in Kenya (IFAD)
- Kenyan View A photographic approach to Kenya's beauty.
- UNESCO Nairobi Office - Education Sector Clearinghouse
- Solar cooking history and recent developments in Kenya
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||