GUID Partition Table
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In computer hardware, GUID Partition Table (GPT) is a standard for the layout of the partition table on a physical hard disk. It is a part of the Extensible Firmware Interface (EFI) standard proposed by Intel as a replacement for the PC BIOS, one of the few remaining parts of the original IBM PC. EFI uses GPT whereas BIOS uses a Master Boot Record (MBR).
Contents |
[edit] Features
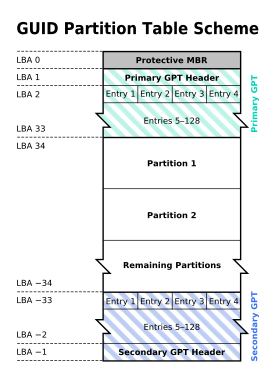
Current PC BIOS schemes use a master boot record (MBR) to begin the process of initializing the disk. The MBR begins with an entry called the Master Boot Code, which contains an executable binary for the purpose of identifying and booting the active partition. EFI instead contains this capability itself, but to maintain backwards compatibility, GPT retains the MBR entry as the first sector on the disk followed by a Primary Partition Table Header, the actual beginning of GPT.
GPT uses modern logical block addressing (LBA) in place of the cylinder-head-sector (CHS) addressing used with old MBRs (modern MBRs can use LBA). Legacy MBR information is contained in LBA 0, the GPT header is in LBA 1, and the partition table itself follows. In 64-bit Windows operating systems, 16,384 bytes, or 32 sectors, are reserved for the GPT, leaving LBA 34 as the first usable sector on the disk.
According to Apple,[1] "Do not assume that the {LBA} size is always going to be 512 bytes." When booting an Intel-based Mac from a hard drive that is partitioned, the hard disk must be partitioned according to GPT, rather than Apple Partition Map.
GPT also provides for redundancy. The GPT header and partition table are written at both the beginning and the end of the disk.
[edit] Legacy MBR (LBA 0)
The primary purpose of the MBR at the beginning of the disk is to prevent MBR-based disk utilities from mis-recognizing, and possibly over-writing, GPT disks. A single partition type of 0xEE, encompassing the entire GPT drive, is indicated and identifies it as GPT. Some 32-bit OSes which cannot read GPT disks nevertheless recognize this ID and present the disk as an inaccessible GPT disk. Older OSes will generally recognize the disk as containing one partition of unknown type and no empty space, and will typically refuse to modify the disk unless the user explicitly requests and confirms the deletion of this partition. This minimizes accidental erasures.
If the disk is larger than two terabytes (the maximum partition size in the legacy MBR), the size of this partition is marked as 2 TB, ignoring the rest of disk.
[edit] Partition table header (LBA 1)
The partition table header defines the blocks on the disk that can be utilized by the user (the usable blocks). It also defines the number and size of the partition entries that make up the partition table. On 64-bit Windows Server 2003 machines, there are 128 partition entries reserved, each 128 bytes long. Thus, 128 partitions can be created.
The header contains the disk GUID (Globally Unique Identifier). It records its own size and location (always LBA 1) and the size and location of the secondary GPT header and table (always the last sectors on the disk). Importantly, it also contains a CRC32 checksum for itself and for the partition table, which is verified by EFI processes on boot. Because EFI uses and verifies this checksum, hex editors should not be used to modify the contents of the GPT. Such modification would render the checksum invalid. In this case, EFI would overwrite the primary GPT with the secondary one, or, if both GPTs contained invalid checksums, would be unable to access the disk.
| Offset | Length | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 8 bytes | Signature ("EFI PART", 45 46 49 20 50 41 52 54) |
| 8 | 4 bytes | Revision (For version 1.0, the value is 00 00 01 00) |
| 12 | 4 bytes | Header size (in bytes, usually 5C 00 00 00 meaning 92 bytes) |
| 16 | 4 bytes | CRC32 of header (0 to header size), with this field zeroed during calculation |
| 20 | 4 bytes | reserved, must be zero |
| 24 | 8 bytes | Current LBA (location of this header copy) |
| 32 | 8 bytes | Backup LBA (location of the other header copy) |
| 40 | 8 bytes | First usable LBA for partitions (primary partition table last LBA + 1) |
| 48 | 8 bytes | Last usable LBA (secondary partition table first LBA - 1) |
| 56 | 16 bytes | Disk GUID (also referred as UUID on UNIXes) |
| 72 | 8 bytes | Partition entries starting LBA (always 2 in primary copy) |
| 80 | 4 bytes | Number of partition entries |
| 84 | 4 bytes | Size of a partition entry (usually 128) |
| 88 | 4 bytes | CRC32 of partition array |
| 92 | * | reserved, must be zeroes for the rest of the block (420 bytes for a 512-byte LBA) |
| LBA Size | TOTAL | |
The values for current and backup LBAs of the primary header should be the second sector of the disk (1) and the last sector of the disk, respectively. In the secondary header the same values are in reverse order.
[edit] Partition entries (LBA 2–33)
Partition entries are simple and straightforward. The first 16 bytes designate the partition type GUID. For example, the GUID for an EFI System partition is {C12A7328-F81F-11D2-BA4B-00A0C93EC93B}. The second 16 bytes contain a GUID unique to the partition. Starting and ending 64-bit LBAs are also recorded here, and space is allocated for partition names and attributes. There is no central registry for GUID partition type designators (needed), either de jure or de facto.
| Offset | Length | Contents |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 16 bytes | Partition type GUID |
| 16 | 16 bytes | Unique partition GUID |
| 32 | 8 bytes | First LBA (little-endian) |
| 40 | 8 bytes | Last LBA (inclusive, usually odd) |
| 48 | 8 bytes | Attribute flags (e.g. bit 60 denotes read-only) |
| 56 | 72 bytes | Partition name (36 UTF-16LE code units) |
| 128 | TOTAL | |
According to Apple, "Do not hardwire the current size of the partition entry (128 bytes)." Microsoft TechNet says that attributes are divided into two halves: the lower 4 bytes representing partition independent attributes, and the upper 4 bytes are partition type dependent. This seems odd, because Microsoft use the following bits in general:[clarification needed]
| Bit | Content |
|---|---|
| 0 | system partition (disk partitioning utilities must reserve the partition as is) |
| 60 | read-only |
| 62 | hidden |
| 63 | do not automount (eg. do not assign drive letter) |
[edit] Partition type GUIDs
| Assoc. OS | Partition type | Globally-Unique Identifier (GUID) |
|---|---|---|
| (None) | Unused entry | 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000 |
| MBR partition scheme | 024DEE41-33E7-11D3-9D69-0008C781F39F | |
| EFI System Partition | C12A7328-F81F-11D2-BA4B-00A0C93EC93B | |
| BIOS Boot Partition | 21686148-6449-6E6F-744E-656564454649 | |
| Windows | Microsoft Reserved Partition | E3C9E316-0B5C-4DB8-817D-F92DF00215AE |
| Basic Data Partition[2] | EBD0A0A2-B9E5-4433-87C0-68B6B72699C7 | |
| Logical Disk Manager metadata partition | 5808C8AA-7E8F-42E0-85D2-E1E90434CFB3 | |
| Logical Disk Manager data partition | AF9B60A0-1431-4F62-BC68-3311714A69AD | |
| HP-UX | Data partition | 75894C1E-3AEB-11D3-B7C1-7B03A0000000 |
| Service Partition | E2A1E728-32E3-11D6-A682-7B03A0000000 | |
| Linux | Data partition[2] | EBD0A0A2-B9E5-4433-87C0-68B6B72699C7 |
| RAID partition | A19D880F-05FC-4D3B-A006-743F0F84911E | |
| Swap partition | 0657FD6D-A4AB-43C4-84E5-0933C84B4F4F | |
| Logical Volume Manager (LVM) partition | E6D6D379-F507-44C2-A23C-238F2A3DF928 | |
| Reserved | 8DA63339-0007-60C0-C436-083AC8230908 | |
| FreeBSD | Boot partition | 83BD6B9D-7F41-11DC-BE0B-001560B84F0F |
| Data partition | 516E7CB4-6ECF-11D6-8FF8-00022D09712B | |
| Swap partition | 516E7CB5-6ECF-11D6-8FF8-00022D09712B | |
| Unix File System (UFS) partition | 516E7CB6-6ECF-11D6-8FF8-00022D09712B | |
| Vinum volume manager partition | 516E7CB8-6ECF-11D6-8FF8-00022D09712B | |
| ZFS partition | 516E7CBA-6ECF-11D6-8FF8-00022D09712B | |
| Mac OS X | Hierarchical File System (HFS+) partition | 48465300-0000-11AA-AA11-00306543ECAC |
| Apple UFS | 55465300-0000-11AA-AA11-00306543ECAC | |
| ZFS[3] | 6A898CC3-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | |
| Apple RAID partition | 52414944-0000-11AA-AA11-00306543ECAC | |
| Apple RAID partition, offline | 52414944-5F4F-11AA-AA11-00306543ECAC | |
| Apple Boot partition | 426F6F74-0000-11AA-AA11-00306543ECAC | |
| Apple Label | 4C616265-6C00-11AA-AA11-00306543ECAC | |
| Apple TV Recovery partition | 5265636F-7665-11AA-AA11-00306543ECAC | |
| Solaris | Boot partition | 6A82CB45-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 |
| Root partition | 6A85CF4D-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | |
| Swap partition | 6A87C46F-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | |
| Backup partition | 6A8B642B-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | |
| /usr partition[3] | 6A898CC3-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | |
| /var partition | 6A8EF2E9-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | |
| /home partition | 6A90BA39-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | |
| EFI_ALTSCTR | 6A9283A5-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | |
| Reserved partition | 6A945A3B-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | |
| 6A9630D1-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | ||
| 6A980767-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | ||
| 6A96237F-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | ||
| 6A8D2AC7-1DD2-11B2-99A6-080020736631 | ||
| NetBSD[4] | Swap partition | 49F48D32-B10E-11DC-B99B-0019D1879648 |
| FFS partition | 49F48D5A-B10E-11DC-B99B-0019D1879648 | |
| LFS partition | 49F48D82-B10E-11DC-B99B-0019D1879648 | |
| RAID partition | 49F48DAA-B10E-11DC-B99B-0019D1879648 | |
| concatenated partition | 2DB519C4-B10F-11DC-B99B-0019D1879648 | |
| encrypted partition | 2DB519EC-B10F-11DC-B99B-0019D1879648 |
- ^ The GUIDs in this table are written assuming a little-endian byte order. For example, the GUID for an EFI System partition is written as C12A7328-F81F-11D2-BA4B-00A0C93EC93B here, which corresponds to the 16 byte sequence 28 73 2A C1 1F F8 D2 11 BA 4B 00 A0 C9 3E C9 3B — only the first three blocks are byte-swapped.
- a b Linux and Windows use the same GUID for their respective data partitions.
- a b The GUID for
/usron Solaris is used as a generic GUID for ZFS by Mac OS X. - ^ Definitions are in src/sys/sys/disklabel_gpt.h. NetBSD had used the FreeBSD GUIDs before unique NetBSD-specific GUIDs were created.
[edit] References
[edit] See also
[edit] External links
- Microsoft TechNet: Disk Sectors on GPT Disks
- Microsoft TechNet: Using GPT Drives on x86-64 Systems
- Apple Developer Connection: Secrets of the GPT