Breast cancer
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Breast cancer Classification and external resources |
|
| Mammogram showing breast cancer (indicated by arrow) | |
| ICD-10 | C50. |
| ICD-9 | 174-175,V10.3 |
| OMIM | 114480 |
| DiseasesDB | 1598 |
| MedlinePlus | 000913 |
| eMedicine | med/2808 med/3287 radio/115 plastic/521 |
| MeSH | D001943 |
Breast cancer is a cancer that starts in the cells of the breast in women and men. Worldwide, breast cancer is the second most common type of cancer after lung cancer (10.4% of all cancer incidence, both sexes counted)[1] and the fifth most common cause of cancer death.[2] In 2004, breast cancer caused 519,000 deaths worldwide (7% of cancer deaths; almost 1% of all deaths).[2]
Breast cancer is about 100 times as frequent among women as among men, but survival rates are equal in both sexes.[3][4][5]
Contents |
[edit] Classification
Breast cancers are described along four different classification schemes, or groups, each based on different criteria and serving a different purpose:
- Pathology - Each tumor is classified by its histological (microscopic anatomy) appearance and other criteria.
- Grade of tumor - The histological grade of a tumor is determined by a pathologist under a microscope. A well-differentiated (low grade) tumor resembles normal tissue. A poorly differentiated (high grade) tumor is composed of disorganized cells and, therefore, does not look like normal tissue. Moderately differentiated (intermediate grade) tumors are somewhere in between.
- Protein & gene expression status - Currently, all breast cancers should be tested for expression, or detectable effect, of the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR) and HER2/neu proteins. These tests are usually done by immunohistochemistry and are presented in a pathologist's report. The profile of expression of a given tumor helps predict its prognosis, or outlook, and helps an oncologist choose the most appropriate treatment. More genes and/or proteins may be tested in the future.
- Stage of a tumor - The currently accepted staging scheme for breast cancer is the TNM classification. This considers the Tumor itself, whether it has spread to lymph Nodes, and whether there are any Metastases to locations other than the breast and lymph nodes.
Breast cancer is usually, but not always, primarily classified by its histological appearance. Rare variants are defined on the basis of physical exam findings. For example, inflammatory breast cancer (IBC), a form of ductal carcinoma or malignant cancer in the ducts, is distinguished from other carcinomas by the inflamed appearance of the affected breast.[6] In the future, some pathologic classifications may be changed. For example, a subset of ductal carcinomas may be re-named basal-like carcinoma (part of the "triple-negative" tumors).[citation needed]
[edit] Signs and symptoms
The first symptom, or subjective sign, of breast cancer is typically a lump that feels different from the surrounding breast tissue. According to the The Merck Manual, more than 80% of breast cancer cases are discovered when the woman feels a lump.[7] According to the American Cancer Society, the first medical sign, or objective indication of breast cancer as detected by a physician, is discovered by mammogram.[8] Lumps found in lymph nodes located in the armpits[7] and/or collarbone[citation needed] can also indicate breast cancer.
Indications of breast cancer other than a lump may include changes in breast size or shape, skin dimpling, nipple inversion, or spontaneous single-nipple discharge. Pain is an unreliable tool in determining the presence or absence of breast cancer, but may be indicative of other breast health issues such as mastodynia.[8][7][9]
When breast cancer cells invade the dermal lymphatics—small lymph vessels in the skin of the breast—its presentation can resemble skin inflammation and thus is known as inflammatory breast cancer (IBC). Symptoms of inflammatory breast cancer include pain, swelling, warmth and redness throughout the breast, as well as an orange-peel texture to the skin referred to as peau d'orange.[7]
Another reported symptom complex of breast cancer is Paget's disease of the breast. This syndrome presents as eczematoid skin changes such as redness and mild flaking of the nipple skin. As Paget's advances, symptoms may include tingling, itching, increased sensitivity, burning, and pain. There may also be discharge from the nipple. Approximately half of women diagnosed with Paget's also have a lump in the breast.[10]
Occasionally, breast cancer presents as metastatic disease, that is, cancer that has spread beyond the original organ. Metastatic breast cancer will cause symptoms that depend on the location of metastasis. Common sites of metastasis include bone, liver, lung and brain. Unexplained weight loss can occasionally herald an occult breast cancer, as can symptoms of fevers or chills. Bone or joint pains can sometimes be manifestations of metastatic breast cancer, as can jaundice or neurological symptoms. These symptoms are "non-specific", meaning they can also be manifestations of many other illnesses.[11]
Most symptoms of breast disorder do not turn out to represent underlying breast cancer. Benign breast diseases such as mastitis and fibroadenoma of the breast are more common causes of breast disorder symptoms. The appearance of a new symptom should be taken seriously by both patients and their doctors, because of the possibility of an underlying breast cancer at almost any age.[12]
[edit] Epidemiology and etiology
Epidemiological risk factors for a disease can provide important clues as to the etiology, or cause, of a disease. The first case-controlled study on breast cancer epidemiology was done by Janet Lane-Claypon, who published a comparative study in 1926 of 500 breast cancer cases and 500 control patients of the same background and lifestyle for the British Ministry of Health.[13][verification needed][14]
Today, breast cancer, like other forms of cancer, is considered to be the final outcome of multiple environmental and hereditary factors. Some of these factors include:
- Lesions to DNA such as genetic mutations. Mutations that can lead to breast cancer have been experimentally linked to estrogen exposure.[15] Beyond the contribution of estrogen, research has implicated viral transformation and the contribution of ionizing radiation in causing genetic mutations.[citation needed]
- Failure of immune surveillance, a theory in which the immune system removes malignant cells throughout one's life.[16]
- Abnormal growth factor signaling in the interaction between stromal cells and epithelial cells can facilitate malignant cell growth. For example, tumors can induce blood vessel growth (angiogenesis) by secreting various growth factors further facilitating cancer growth.[citation needed]
- Inherited defects in DNA repair genes, such as BRCA1, BRCA2[17] and p53.[citation needed] People in less-developed countries report lower incidence rates than in developed countries.
Experts believe that 95 percent of inherited breast cancer can be traced to one of two genes, which they call Breast Cancer 1 (BRCA1) and Breast Cancer 2 (BRCA2). Hereditary breast cancers can take the form of a site-specific hereditary breast cancer- cancers affecting the breast only- or breast- ovarian and other cancer syndromes. Breast cancer can be inherited both from female and male relatives. [18]
Although many epidemiological risk factors have been identified, the cause of any individual breast cancer is often unknowable. In other words, epidemiological research informs the patterns of breast cancer incidence across certain populations, but not in a given individual. Due to breast cancer is vary in different racial and ethnic group. The primary risk factors that have been identified are sex,[19] age,[20] childbearing, hormones,[21] a high-fat diet,[22] alcohol intake,[23][24] obesity,[25] and environmental factors such as tobacco use, radiation[17] and shiftwork.[26]
No etiology is known for 95% of breast cancer cases, while approximately 5% of new breast cancers are attributable to hereditary syndromes.[27] In particular, carriers of the breast cancer susceptibility genes, BRCA1 and BRCA2, are at a 30-40% increased risk for breast and ovarian cancer, depending on in which portion of the protein the mutation occurs.[28]
Worldwide, breast cancer is by far the most common cancer amongst women, with an incidence rate more than twice that of colorectal cancer and cervical cancer and about three times that of lung cancer. However breast cancer mortality worldwide is just 25% greater than that of lung cancer in women.[1] In 2004, breast cancer caused 519,000 deaths worldwide (7% of cancer deaths; almost 1% of all deaths).[2] The number of cases worldwide has significantly increased since the 1970s, a phenomenon partly blamed on modern lifestyles in the Western world.[29][30]
The incidence of breast cancer varies greatly around the world, being lower in less-developed countries and greatest in the more-developed countries. In the twelve world regions, the annual age-standardized incidence rates per 100,000 women are as follows: in Eastern Asia, 18; South Central Asia, 22; sub-Saharan Africa, 22; South-Eastern Asia, 26; North Africa and Western Asia, 28; South and Central America, 42; Eastern Europe, 49; Southern Europe, 56; Northern Europe, 73; Oceania, 74; Western Europe, 78; and in North America, 90.[31]
[edit] United States
Women in the United States have the highest incidence rates of breast cancer in the world; 141 among white women and 122 among African American women.[32][33] Among women in the US, breast cancer is the most common cancer and the second-most common cause of cancer death (after lung cancer).[33] Women in the US have a 1 in 8 (12.5%) lifetime chance of developing invasive breast cancer and a 1 in 35 (3%) chance of breast cancer causing their death.[33] In 2007, breast cancer was expected to cause 40,910 deaths in the US (7% of cancer deaths; almost 2% of all deaths).[8]
In the US, both incidence and death rates for breast cancer have been declining in the last few years in Native Americans and Alaskan Natives.[34][8] Nevertheless, a US study conducted in 2005 by the Society for Women's Health Research indicated that breast cancer remains the most feared disease,[35] even though heart disease is a much more common cause of death among women.[36] Many doctors say that women exaggerate their risk of breast cancer.[37]
[edit] Racial disparities in diagnosis and treatment
Several studies have found that black women in the U.S. are more likely to die from breast cancer even though white women are more likely to be diagnosed with the disease. Even after diagnosis, black women are less likely to get treatment compared to white women.[38][39][40] Scholars have advanced several theories for the disparities, including inadequate access to screening, reduced availability of the most advanced surgical and medical techniques, or some biological characteristic of the disease in the African American population.[41] Some studies suggest that the racial disparity in breast cancer outcomes may reflect cultural biases more than biological disease differences.[42] Research is currently ongoing to define the contribution of both biological and cultural factors.[43][39]
[edit] UK
45,000 cases diagnosed and 12,500 deaths per annum. 60% of cases are treated with Tamoxifen, of these the drug becomes ineffective in 35%.[44]
[edit] Prevention
Several factors can influence breast cancer incidence either positively or negatively. Those factors are discussed in a specific Wikipedia article.
[edit] Screening
Breast cancer screening is an attempt to find unsuspected cancers. The most common screening methods are self and clinical breast exams, x-ray mammography, and breast Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Genetic testing may also be used.
Breast self-examination involves examining one's own breasts using a specific palpation technique to detect any lumps in the breast tissue, which may be cancerous. Clinical exams are similar, except they are performed by a clinician or doctor.
X-ray mammography uses x-rays to examine the breast for any uncharacteristic masses or lumps. Regular mammograms -- the process of getting breast mammography -- is often recommended as a preventative measure, particularly for older women and at-risk individuals. A recent study involving 160,921 women recruited at age 39-41 showed that annual screening mammograms up to age 48 did decrease breast cancer mortality over an average of 10.7 years. This reduction, however, was not statistically significant. The results may be due to chance. According to these findings, about 2,500 women would need to be screened to prevent one breast cancer death during this time period.[45]
Breast MRIs are another imaging technique that can be used to spot potentially cancerous masses.
The most recent technology for breast cancer screening is ultrasound computed tomography, which uses sound waves to create a three-dimensional image and detect breast cancer without the use of dangerous radiation used in x-ray mammography. This method was discovered at Los Alamos National Laboratory.[46]
Genetic testing for breast cancer typically involves testing for mutations in the BRCA genes. This is not generally a recommended technique except for those at elevated risk for breast cancer.
several studies suggest that regular that vigorous excercise offers modest protections against breast cancer
[edit] Diagnosis
| This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (October 2007) |
While screening techniques discussed above are useful in determining the presence of cancer, they are not in and of themselves diagnostic of cancer. Pathology is the study and diagnosis of disease; only microscopic evaluation of a biopsy specimen can yield a cancer diagnosis. A number of procedures can obtain tissue or cells for histological or cytological examination. Such procedures include fine-needle aspiration, nipple aspirates, ductal lavage, core needle biopsy, and local surgical excision. Occasionally, pre-surgical procedures such as fine needle aspirate may not yield enough tissue to make a diagnosis, or may miss the cancer entirely.
[edit] Staging
Breast cancer is staged according to the TNM system, updated in the AJCC Staging Manual, now on its sixth edition. Prognosis is closely linked to results of staging, and staging is also used to allocate patients to treatments both in clinical trials and clinical practice. For a more detailed discussion on staging of breast cancer, see here.
Approximately 90% of new breast cancer cases in the US will be classified as "early-stage" cases (DCIS, Stage I,IIA, IIB or IIIA), due to early detection and prevention techniques. Early-stage treatment options are different from late-stage options.[47]
[edit] Hormone receptors
Breast lesions are examined for certain markers, notably sex steroid hormone receptors. About two thirds of postmenopausal breast cancers are estrogen receptor positive (ER+) and progesterone receptor positive (PR+).[48] Receptor status modifies the treatment as, for instance, only ER-positive tumors, not ER-negative tumors, are sensitive to hormonal therapy.
[edit] HER2
The breast cancer is also usually tested for the presence of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2, a protein also known as HER2, neu or erbB2. HER2 is a cell-surface protein involved in cell development. In normal cells, HER2 controls aspects of cell growth and division. When activated in cancer cells, HER2 accelerates tumor formation. About 20-30% of breast cancers overexpress HER2. Those patients may be candidates for the drug trastuzumab, both in the postsurgical setting (so-called "adjuvant" therapy), and in the metastatic setting.[49] HER2 status can be assessed by immunohistochemistry, fluorescent/chromogenic/silver in situ hybridization (FISH/CISH/SISH), or virtual karyotyping.
[edit] Treatment
The mainstay of breast cancer treatment is surgery when the tumor is localized, with possible adjuvant hormonal therapy (with tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor), chemotherapy, and/or radiotherapy. At present, the treatment recommendations after surgery (adjuvant therapy) follow a pattern. This pattern is subject to change, as every two years, a worldwide conference takes place in St. Gallen, Switzerland, to discuss the actual results of worldwide multi-center studies. Depending on clinical criteria (age, type of cancer, size, metastasis) patients are roughly divided to high risk and low risk cases, with each risk category following different rules for therapy. Treatment possibilities include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and immune therapy.
In planning treatment, doctors can also use PCR tests like Oncotype DX or microarray tests like MammaPrint that predict breast cancer recurrence risk based on gene expression. In February 2007, the MammaPrint test became the first breast cancer predictor to win formal approval from the Food and Drug Administration. This is a new gene test to help predict whether women with early-stage breast cancer will relapse in 5 or 10 years, this could help influence how aggressively the initial tumor is treated.[50]
Interstitial laser thermotherapy (ILT) is an innovative method of treating breast cancer in a minimally invasive manner and without the need for surgical removal, and with the absence of any adverse effect on the health and survival of the patient during intermediate followup.[51]
Radiation treatment is also used to help destroy cancer cells that may linger after surgery. Radiation can reduce the risk of recurrence by 50-66% (1/2 - 2/3rds reduction of risk) when delivered in the correct dose. [52]
[edit] Prognosis
| This section does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources (ideally, using inline citations). Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (October 2007) |
A prognosis is the medical team's "best guess" in how cancer will affect a patient. There are many prognostic factors associated with breast cancer: staging, tumour size and location, grade, whether disease is systemic (has metastasized, or traveled to other parts of the body), recurrence of the disease, and age of patient.
Stage is the most important, as it takes into consideration size, local involvement, lymph node status and whether metastatic disease is present. The higher the stage at diagnosis, the worse the prognosis. The stage is raised by the invasiveness of disease to lymph nodes, chest wall, skin or beyond, and the aggressiveness of the cancer cells. The stage is lowered by the presence of cancer-free zones and close-to-normal cell behaviour (grading). Size is not a factor in staging unless the cancer invasive. Ductal Carcinoma in situ throughout the entire breast is stage zero.
Grading is based on how biopsied, cultured cells behave. The closer to normal cancer cells are, the slower their growth and the better the prognosis. If cells are not well differentiated, they will appear immature, will divide more rapidly, and will tend to spread. Well differentiated is given a grade of 1, moderate is grade 2, while poor or undifferentiated is given a higher grade of 3 or 4 (depending upon the scale used).
Younger women tend to have a poorer prognosis than post-menopausal women due to several factors. Their breasts are active with their cycles, they may be nursing infants, and may be unaware of changes in their breasts. Therefore, younger women are usually at a more advanced stage when diagnosed.
The presence of estrogen and progesterone receptors in the cancer cell, while not prognostic, is important in guiding treatment. Those who do not test positive for these specific receptors will not respond to hormone therapy.
Likewise, HER2/neu status directs the course of treatment. Patients whose cancer cells are positive for HER2/neu have more aggressive disease and may be treated with trastuzumab, a monoclonal antibody that targets this protein.
Elevated CA15-3, in conjunction with alkaline phosphatase, was shown to increase chances of early recurrence in breast cancer.[53]
[edit] Psychological aspects of diagnosis and treatment
The emotional impact of cancer diagnosis, symptoms, treatment, and related issues can be severe. Most larger hospitals are associated with cancer support groups which provide a supportive environment to help patients cope and gain perspective from cancer survivors. Online cancer support groups are also very beneficial to cancer patients, especially in dealing with uncertainty and body-image problems inherent in cancer treatment.
Not all breast cancer patients experience their illness in the same manner. Factors such as age can have a significant impact on the way a patient copes with a breast cancer diagnosis. Premenopausal women with estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer must confront the issues of early menopause induced by many of the chemotherapy regimens used to treat their breast cancer, especially those that use hormones to counteract ovarian function. [54]
On the other hand, a recent study conducted by researchers at the College of Public Health of the University of Georgia showed that older women may face a more difficult recovery from breast cancer than their younger counterparts.[55] As the incidence of breast cancer in women over 50 rises and survival rates increase, breast cancer is increasingly becoming a geriatric issue that warrants both further research and the expansion of specialized cancer support services tailored for specific age groups.[55]
[edit] Metastasis

Most people understand breast cancer as something that happens in the breast. However it can metastasize (spread) via lymphatics to nearby lymph nodes, usually those under the arm. That is why surgery for breast cancer always involves some type of surgery for the glands under the arm — either axillary clearance, sampling, or sentinel node biopsy.
Breast cancer can also spread to other parts of the body via blood vessels or the lymphatic system. So it can spread to the lungs, pleura (the lining of the lungs), liver, brain, and most commonly to the bones.[56] Seventy percent of the time that breast cancer spreads to other locations, it spreads to bone, especially the vertebrae and the long bones of the arms, legs, and ribs. Usually when breast cancer spreads to bone, it eats away healthy bone, causing weak spots, where the bones can break easily. That is why breast cancer patients are often seen wearing braces or using a wheelchair, and have aching bones.
When breast cancer is found in bones, it has usually spread to more than one site. At this stage, it is treatable, often for many years, but it is not curable. Like normal breast cells, these tumors in the bone often thrive on female hormones, especially estrogen. Therefore treatment with medicines that lower estrogen levels may be prescribed.
In 2008, scientists discovered that breast cancer becomes more invasive when a specific trio of cells are present together in the same anatomic region: an endothelial cell (a type of cell that lines the blood vessels), a perivascular macrophage (a type of immune cell found near blood vessels), and a tumor cell that produces the protein Mena [57]. This important finding could potentially alter the way in which breast cancer is treated.
[edit] Calculate the probability of nodal involvement
Below is a step-by-step approach to compute the probability of nodal involvement In invasive breast cancer in women after obtaining a clear sample of axillary lymph nodes.
Step One: Obtain the probability of nodal involvement by reference to factors such as clinical palpability, tumour size, lymphovascular invasion etc. Useful tables can be found in the medical literature. Call this probability the prior probability. See Table 6 in [58] and Table 1 below which is a modification of Table 6 of [58] by Professor Howell Tong (London School of Economics), see [59] for details.
Step Two: Obtain the probability of false negative pertaining to a sample of n nodes. We may use the following values which are based on the conservative end of the range given in Table 1 of [60].
| Number of nodes, n | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| Probability of false negative, FN(n) | 0.11 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
Step Three: Call the desired probability of nodal involvement on the basis of a pathologic analysis of the sampled nodes the posterior probability. Then apply the following formula: Posterior probability with a sample of n nodes which are all clear = FN (n) x prior probability / (1 - prior probability).
Example:
Suppose the patient's breast tumour has size 1.6 cm. with no lymphovascular invasion and she discovered it by her feeling the lump herself. Reading off from Table 1, the prior probability of nodal involvement is equal to 0.2. Suppose 5 axillary nodes have been removed from her by the surgeon and all the nodes are found to be clear. Then because FN(5) = 0.05, the posterior probability of nodal involvement = 0.05 x 0.2 / (1-0.2) = 0.0125=1.25%.
Use Table 1 to obtain a prediction before axillary sampling and then Table 2 to obtain your prediction after axillary sampling. Table 2 does not apply to samples that produce one or more positive nodes.
| Tumour Size (in mm.) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0~5 | 6~10 | 11~15 | 16~20 | 21~25 | 26~30 | 31~50 | 51~100 | |
| LVI absent Can you feel the tumour? |
||||||||
| No | 4 | 11 | 12 | 10 | 20 | 33 | 57 | 67 |
| Yes | 6 | 13 | 19 | 20 | 30 | 27 | 34 | 65 |
| Yes; axillary nodes too | 50 | 75 | 93 | 80 | 70 | 71 | 77 | 93 |
| LVI present Can you feel the tumour? |
||||||||
| No | 5 | 18 | 30 | 39 | 42 | 33 | 50 | 95 |
| Yes | 23 | 28 | 37 | 49 | 65 | 67 | 66 | 77 |
| Yes; axillary nodes too | 98 | 98 | 98 | 92 | 90 | 96 | 98 | 98 |
| Number of nodes sampled and found to be clear | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Number of patients per 100
having axillary node involvement |
||||
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 15 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 20 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 25 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 30 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
| 35 | 6 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| 40 | 7 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| 45 | 8 | 5 | 4 | 2 |
| 50 | 10 | 7 | 5 | 3 |
| 55 | 12 | 8 | 6 | 4 |
| 60 | 14 | 10 | 7 | 4 |
| 65 | 17 | 12 | 8 | 5 |
| 70 | 20 | 14 | 10 | 7 |
| 75 | 25 | 17 | 13 | 8 |
| 80 | 31 | 22 | 17 | 11 |
| 85 | 38 | 28 | 22 | 15 |
| 90 | 50 | 39 | 31 | 21 |
| 95 | 68 | 57 | 49 | 36 |
| 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
Table 2 was constructed by Professor Howell Tong (London School of Economics), see [59] for details.
[edit] Gallery
|
Woman undergoing mammogram |
|||
|
Mastectomy patient |
Breast prostheses used by some mastectomy patients |
||
|
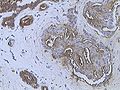
Mastectomy specimen containing a very large cancer of the breast (in this case, an invasive ductal carcinoma) |
Typical macroscopic (gross) appearance of the cut surface of a mastectomy specimen containing a cancer, in this case, an invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast, pale area at the center |
||
[edit] See also
- List of notable breast cancer patients according to occupation
- List of notable breast cancer patients according to survival status
- List of breast carcinogenic substances
- Mammary tumor for breast cancer in other animals
- Breast reconstruction
- Alcohol and cancer
- Mammography Quality Standards Act
- National Breast Cancer Coalition
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network
- Breast Cancer Action
- Breakthrough Breast Cancer
- Living Beyond Breast Cancer
- International Agency for Research on Cancer
- Susan G. Komen for the Cure
- Breast Cancer Network of Strength
- Your Disease Risk
[edit] References
- ^ a b World Health Organization International Agency for Research on Cancer (June 2003). "World Cancer Report". http://www.iarc.fr/en/Publications/PDFs-online/World-Cancer-Report/World-Cancer-Report. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ a b c World Health Organization (February 2006). "Fact sheet No. 297: Cancer". http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs297/en/index.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-26.
- ^ "Male Breast Cancer Treatment - National Cancer Institute". National Cancer Institute. 2006. http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/treatment/malebreast/healthprofessional. Retrieved on 2006-10-16.
- ^ "Breast Cancer in Men: Cancer Research UK". Cancer Research UK. 2007. http://www.cancerhelp.org.uk/help/default.asp?page=5075. Retrieved on 2007-11-06.
- ^ American Cancer Society (September 27, 2007). "What Are the Key Statistics About Breast Cancer in Men?". http://www.cancer.org/docroot/CRI/content/CRI_2_4_1X_What_are_the_key_statistics_for_male_breast_cancer_28.asp?sitearea=. Retrieved on 2008-02-03.
- ^ Giordano SH, Hortobagyi GN (2003). "Inflammatory breast cancer: clinical progress and the main problems that must be addressed". Breast Cancer Res. 5 (6): 284–8. doi:. PMID 14580242. Free Full Text.
- ^ a b c d Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy (February 2003). "Breast Disorders: Cancer". http://www.merck.com/mmhe/sec22/ch251/ch251f.html#sec22-ch251-ch251f-525. Retrieved on 2008-02-05.
- ^ a b c d American Cancer Society (2007). "Cancer Facts & Figures 2007" (PDF). http://www.cancer.org/downloads/STT/CAFF2007PWSecured.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-04-26.
- ^ eMedicine (August 23, 2006). "Breast Cancer Evaluation". http://www.emedicine.com/med/TOPIC3287.HTM. Retrieved on 2008-02-05.
- ^ National Cancer Institute (June 27, 2005). "Paget's Disease of the Nipple: Questions and Answers". http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/factsheet/Sites-Types/pagets-breast. Retrieved on 2008-02-06.
- ^ National Cancer Institute (September 1, 2004). "Metastatic Cancer: Questions and Answers". http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/factsheet/Sites-Types/metastatic. Retrieved on 2008-02-06.
- ^ Merck Manual of Diagnosis and Therapy (February 2003). "Breast Disorders: Introduction". http://www.merck.com/mmhe/sec22/ch251/ch251a.html. Retrieved on 2008-02-05.
- ^ Lane-Claypon, Janet Elizabeth (1926). A further report on cancer of the breast, with special reference to its associated antecedent conditions. London, Greater London: Her Majesty’s Stationery Office (HMSO). OCLC 14713036.
- ^ Alfredo Morabia (2004). A History of Epidemiologic Methods and Concepts. Boston: Birkhauser. pp. 301–302. ISBN 3-7643-6818-7. http://books.google.com/books?id=E-OZbEmPSTkC&pg=PA301&lpg=PA301&dq=%22lane+claypon%22+%22further+report+*+cancer%22&source=web&ots=jSQWua-Sx0&sig=3arOIXuwGU_w_Omza11lEDj2TEo#PPA301,M1. Retrieved on 2007-12-31.
- ^ Cavalieri E, Chakravarti D, Guttenplan J, et al (2006). "Catechol estrogen quinones as initiators of breast and other human cancers: implications for biomarkers of susceptibility and cancer prevention". Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1766 (1): 63–78. doi:. PMID 16675129.
- ^ Farlex (2005). ">immunological surveillance "The Free Dictionary: Immunological Surveilliance". http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/immunological+surveillance">immunological surveillance. Retrieved on 2008-02-10.
- ^ a b American Cancer Society (2005). "Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2005-2006" (PDF). http://www.cancer.org/downloads/STT/CAFF2005BrFacspdf2005.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-04-26.
- ^ Braddock, Suzanne W., Jane M. Kercher, John J. Edney, and Melanie M. Clark. Straight talk about breast cancer from diagnosis to recovery : a guide for the whole family. Omaha, Neb: Addicus Books, 1994.
- ^ Giordano, Sharon H; Cohen DS, Buzdar AU, Perkins G, Hortobagyi GN (May 2004). "Breast carcinoma in men". Cancer (American Cancer Society) 101 (1): 51–57. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/fulltext/108565241/HTMLSTART.
- ^ "Individual Risk Factors". BreastCancer.org. http://www.breastcancer.org/symptoms/understand_bc/who_gets/ind_risk.jsp. Retrieved on 2007-03-11.
- ^ Yager JD; Davidson NE (2006). "Estrogen carcinogenesis in breast cancer". New Engl J Med 354 (3): 270–82. doi:. PMID 16421368.
- ^ Chlebowski RT, Blackburn GL, Thomson CA, Nixon DW, Shapiro A, Hoy MK, et al.. "Dietary fat reduction and breast cancer outcome: interim efficacy results from the Women's Intervention Nutrition Study (WINS)". J Natl Cancer Inst 98 (24): 1767–1776. PMID 17179478.
- ^ Boffetta, Paolo; Hashibe, Mia; La Vecchia, Carlo; Zatonski, Witold; Rehm, Jürgen (2006-03-23). "The burden of cancer attributable to alcohol drinking". International Journal of Cancer (Wiley-Liss, Inc) 119 (4): 884–887. doi:. PMID 16557583. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/cgi-bin/abstract/112550783/ABSTRACT. Retrieved on 2006-10-09.
- ^ [1]
- ^ BBC report Weight link to breast cancer risk
- ^ WHO international Agency for Research on Cancer Press Release No. 180, December 2007.
- ^ Madigan MP, Ziegler RG, Benichou J, Byrne C, Hoover RN (1995). "Proportion of breast cancer cases in the United States explained by well-established risk factors". J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 87 (22): 1681–5. doi:. PMID 7473816.
- ^ Venkitaraman, AR (2002). "cancer susceptibility and the functions of BRCA1 and BRCA2". Cell 108 (2): 171–82. doi:.
- ^ Laurance, Jeremy (2006-09-29). "Breast cancer cases rise 80% since Seventies". The Independent. http://www.independent.co.uk/life-style/health-and-wellbeing/health-news/breast-cancer-cases-rise-80-since-seventies-417990.html. Retrieved on 2006-10-09.
- ^ "Breast Cancer: Statistics on Incidence, Survival, and Screening". Imaginis Corporation. 2006. http://imaginis.com/breasthealth/statistics.asp. Retrieved on 2006-10-09.
- ^ Stewart B. W. and Kleihues P. (Eds): World Cancer Report. IARCPress. Lyon 2003
- ^ Ries LAG, Eisner MP, Kosary CL, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2000. Bethesda, MD: National Cancer Institute, 2003.
- ^ a b c American Cancer Society (September 13, 2007). "What Are the Key Statistics for Breast Cancer?". http://www.cancer.org/docroot/CRI/content/CRI_2_4_1X_What_are_the_key_statistics_for_breast_cancer_5.asp. Retrieved on 2008-02-03.
- ^ Espey DK, Wu XC, Swan J, et al (2007). "Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975-2004, featuring cancer in American Indians and Alaska Natives". Cancer 110 (10): 2119–52. doi:. PMID 17939129.
- ^ Society for Women's Health Research (2005-07-07). Women's Fear of Heart Disease Has Almost Doubled in Three Years, But Breast Cancer Remains Most Feared Disease. Press release. http://www.womenshealthresearch.org/site/News2?page=NewsArticle&id=5459&news_iv_ctrl=0&abbr=press_. Retrieved on 2007-10-15.
- ^ "Leading Causes of Death for American Women 2004" (PDF). National Heart Lung and Blood Institute. http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/hearttruth/press/infograph_dressgraph.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-10-15.
- ^ In Breast Cancer Data, Hope, Fear and Confusion, By DENISE GRADY, New York Times, January 26, 1999.
- ^ Wisconsin Cancer Incidence and Mortality, 2000-2004 Wisconsin Department of Health and Family Services
- ^ a b Tammemagi CM (2007). "Racial/ethnic disparities in breast and gynecologic cancer treatment and outcomes". Curr. Opin. Obstet. Gynecol. 19 (1): 31–6. doi:. PMID 17218849.
- ^ Hirschman J, Whitman S, Ansell D (2007). "The black:white disparity in breast cancer mortality: the example of Chicago". Cancer Causes Control 18 (3): 323–33. doi:. PMID 17285262.
- ^ Breast cancer rates differ in races by Amanda Villa Wednesday, October 24, 2007. Badger Herald
- ^ Benjamin M, Reddy S, Brawley OW (2003). "Myeloma and race: a review of the literature". Cancer Metastasis Rev. 22 (1): 87–93. doi:. PMID 12716040.
- ^ Demicheli R, Retsky MW, Hrushesky WJ, Baum M, Gukas ID, Jatoi I (2007). "Racial disparities in breast cancer outcome: insights into host-tumor interactions". Cancer 110 (9): 1880–8. doi:. PMID 17876835.
- ^ Daily Mail (UK) 13 Nov 2008
- ^ Breast Cancer at Mount Sinai Hospital
- ^ lanl.gov, Better Breast Cancer Detection
- ^ Zuckerman, Diana, "Treatment Options for Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Information for Primary Care Providers", Medscape Continuing Medical Education. National Research Center for Women & Families.
- ^ Rusiecki JA, Holford TR, Zahm SH, Zheng T (2005). "Breast cancer risk factors according to joint estrogen receptor and progesterone receptor status". Cancer Detect. Prev. 29 (5): 419–26. doi:. PMID 16185815.
- ^ accessed 1/30/07 cancer.gov
- ^ "FDA Approves New Breast Cancer Test". Associated Press, February 6, 2007.
- ^ Dowlatshahi, Kambiz; Dieschbourg, Janice J.; Bloom, Kenneth J. (May 2004). "Laser Therapy of Breast Cancer with 3-Year follow up". The Breast Journal (Blackwell Publishing) 10 (3): 240–243. doi:.
- ^ Breastcancer.org Treatment Options
- ^ CA15-3 and alkaline phosphatase as predictors for breast cancer recurrence: a combined analysis of seven International Breast Cancer Study Group trials - Keshaviah et al. 18 (4): 701 - Annals of Oncology
- ^ Pritchard KI (2009). "Ovarian Suppression/Ablation in Premenopausal ER-Positive Breast Cancer Patients". Oncology 23 (1). http://www.cancernetwork.com/display/article/10165/1366719?pageNumber=1.
- ^ a b Robb C, Haley WE, Balducci L, et al (April 2007). "Impact of breast cancer survivorship on quality of life in older women". Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 62 (1): 84–91. doi:. PMID 17188505.
- ^ Lacroix M (2006). "Significance, detection and markers of disseminated breast cancer cells". Endocr Relat Cancer 13 (4): 1033–67. doi:. PMID 17158753.
- ^ Philippar U, Roussos ET, Oser M, et al (December 2008). "A Mena invasion isoform potentiates EGF-induced carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis". Dev. Cell 15 (6): 813–28. doi:. PMID 19081071.
- ^ a b Olivotto et al. (1998) “Cancer, vol. 83, No. 6, p. 953.
- ^ a b Tong, H. (2009) A SIMPLE FORMULA FOR PREDICTING AXILLARY LYMPH NODE INVOLVEMENT. Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science, University of Hong Kong, Technical report no 464, http://www.hku.hk/statistics/staff/htong/files/research-reoprt-464.pdf
- ^ G. Cserni (1999) J. Clinical Pathology, vol. 52, p.682.
- Arthur, Joyce (2002-03). "Abortion and Breast Cancer — A Forged Link". The Humanist. http://www.abortion.org.au/breastcancer.htm. Retrieved on 2007-11-03.
- Ressler, Kelly-Anne (2002-08). "Information for GPs – Alcohol and cancer risk" (PDF). Cancer Control Program. South Eastern Sydney and Illawarra Area Health Service. http://www.sesiahs.health.nsw.gov.au/publications/cancerControl/26%20Alcohol.PDF. Retrieved on 2007-11-03.
- "Surgery choices for women with early-stage Breast cancer" (PDF). National Cancer Institute. United States Department of Health and Human Services. http://www.center4research.org/pdf/booklet04bc.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-11-03.
- Napieralski, Julie A.; Carol Devine (1988-03). "Alcohol and the Risk of Breast Cancer". Program on Breast Cancer and Environmental Risk Factors in New York State. Cornell University. http://envirocancer.cornell.edu/FactSheet/Diet/fs13.alcohol.cfm. Retrieved on 2007-11-03.
- "Radiology Info - Breast Cancer". Radiological Society of North America. Radiological Society of North America. http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=breastcancer&bhcp=1. Retrieved on 2007-11-03.
- Zuckerman, Diana. "Mastectomy v. Lumpectomy: Who Decides?". National Research Center for Women & Families. National Research Center. http://www.center4research.org/bc071502.html. Retrieved on 2007-11-03.
[edit] External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Breast cancer |
| The Wikibook Sexual Health has a page on the topic of |
- Breast cancer at the Open Directory Project
- Breast cancer at the Yahoo! Directory
|
|||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||