History of Ireland
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| History of Ireland | |
 This article is part of a series |
|
| Chronological | |
|---|---|
| Timeline | |
| Prehistoric and Early Ireland (before 400CE) | |
| Early Christian Ireland (400–800) | |
| Early medieval era (800–1168) | |
| Norman Ireland (1169–1536) | |
| Early modern era (1536–1691) | |
| Protestant Ascendancy (1691–1801) | |
| Union with Britain (1801–1922) | |
| Republic (1919–present) | |
| Northern Ireland (1921–present) | |
| Topical | |
| Battles · Tribes · States | |
| Gaelic monarchs · British monarchs | |
| Economic history | |
| Irish language | |
|
Ireland Portal |
The history of Ireland began with the first known settlement in Ireland around 8000 BC, when hunter-gatherers arrived from continental Europe, probably via a land bridge.[1] Few archaeological traces remain of this group, but their descendants and later Neolithic arrivals, particularly from the Iberian Peninsula, were responsible for major Neolithic sites such as Newgrange.[2][3] Following the arrival of Saint Patrick and other Christian missionaries in the early to mid-5th century AD, Christianity subsumed the indigenous pagan religion by the year 600.
From around AD 800, more than a century of Viking invasions brought havoc upon the monastic culture and on the island's various regional dynasties, yet both of these institutions proved strong enough to survive and assimilate the invaders. The coming of Cambro-Norman mercenaries under Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, nicknamed Strongbow, in 1169 marked the beginning of more than 700 years of direct Norman and, later, English involvement in Ireland. The English crown did not begin asserting full control of the island until after the English Reformation, when questions over the loyalty of Irish vassals provided the initial impetus for a series of military campaigns between 1534 and 1691. This period was also marked by an English policy of plantation which led to the arrival of thousands of English and Scottish Protestant settlers. As the military and political defeat of Gaelic Ireland became more clear in the early seventeenth century, the role of religion as a new division in Ireland became more pronounced. From this period on, sectarian conflict became a recurrent theme in Irish history.
The overthrow, in 1613, of the Catholic majority in the Irish parliament was realised principally through the creation of numerous new boroughs, all of which were Protestant-dominated. By the end of the seventeenth century all Catholics, representing some 85% of Ireland's population then, were banned from the Irish parliament. Political power rested entirely in the hands of a British settler-colonial, and more specifically Anglican, minority while the Catholic population suffered severe political and economic privations. In 1801, this colonial parliament was abolished and Ireland became an integral part of a new United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland under the Act of Union. Catholics were still banned from sitting in that new parliament until Catholic Emancipation was attained in 1829, the principal condition of which was the removal of the poorer, and thus more radical, Irish freeholders from the franchise.
The Irish Parliamentary Party strove from the 1880s to attain Home Rule self-government through the parliamentary constitutional movement eventually winning the Home Rule Act 1914, though suspended on the outbreak of World War I. In 1922, after the Irish War of Independence, Ireland seceded from the United Kingdom (UK) to become the independent Irish Free State — and after 1948, the Republic of Ireland. The six north eastern counties, known as Northern Ireland, later rejoined the UK. The history of Northern Ireland has been dominated by sporadic sectarian conflict between (mainly Catholic) Nationalists and (mainly Protestant) Unionists. This conflict erupted into the Troubles in the late 1960s, until an uneasy peace thirty years later.
[edit] Early history (8000 BC – 400 AD)
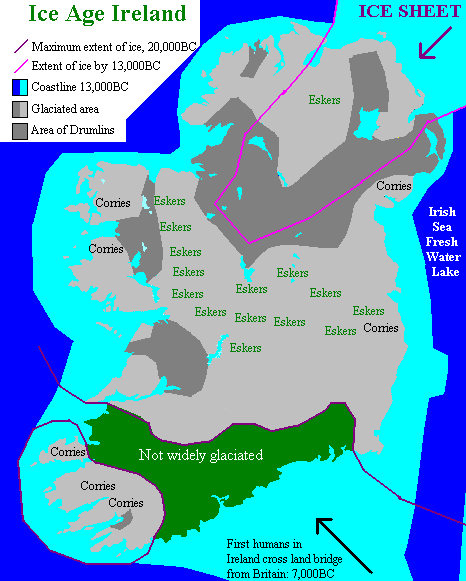
What little is known of pre-Christian Ireland comes from a few references in Roman writings, Irish poetry and myth, and archaeology. The earliest inhabitants of Ireland, people of a mid-Stone Age, or Mesolithic, culture, arrived sometime after 8000 BC, when the climate had become more hospitable following the retreat of the polar icecaps. About 4000 BC agriculture was introduced from the South West continent, leading to the establishment of a high Neolithic culture, characterized by the appearance of pottery, polished stone tools, rectangular wooden houses and communal megalithic tombs, some of which are huge stone monuments like the Passage Tombs of Newgrange, Knowth and Dowth, many of them astronomically aligned (most notably, Newgrange). Four main types of megalithic tomb have been identified: Portal Tombs, Court Tombs, Passage Tombs and Wedge Tombs. In Leinster and Munster individual adult males were buried in small stone structures, called cists, under earthen mounds and were accompanied by distinctive decorated pottery. This culture apparently prospered, and the island became more densely populated. Towards the end of the Neolithic new types of monuments developed, such as circular embanked enclosures and timber, stone and post and pit circles.
The Bronze Age properly began once copper was alloyed with tin to produce true bronze artifacts; this took place around 2000 BC, when some Ballybeg flat axes and associated metalwork was produced. The period preceding this, in which Lough Ravel and most Ballybeg axes were produced, and is known as the Copper Age or Chalcolithic, commenced about 2500 BC. This period also saw the production of elaborate gold and bronze ornaments, weapons and tools. There was a movement away from the construction of communal megalithic tombs to the burial of the dead in small stone cists or simple pits, which could be situated in cemeteries or in circular earth or stone built burial mounds known respectively as barrows and cairns. As the period progressed inhumation burial gave way to cremation and by the Middle Bronze Age cremations were often placed beneath large burial urns.
The Iron Age in Ireland began about 600 BC. By the historic period (AD 431 onwards) the main over-kingdoms of In Tuisceart, Airgialla, Ulaid, Mide, Laigin, Mumhain, Cóiced Ol nEchmacht began to emerge (see Kingdoms of ancient Ireland). Within these kingdoms a rich culture flourished. The society of these kingdoms was dominated by an upper class, consisting of aristocratic warriors and learned people, possibly including druids.
Linguists realised from the 17th century onwards that the language spoken by these people, the Goidelic languages, was a branch of the Celtic languages. This was originally explained as a result of invasions by Celts from the continent. However, research during the 20th century indicated otherwise, and in the later years of the century the conclusion drawn was that culture developed gradually and continuously, and that the introduction of Celtic language and elements of Celtic culture was a result of cultural exchange with Celtic groups on South West continental Europe from the neolithic to the Bronze Age.[1] [2] Little archaeological evidence was found for large intrusive groups of Celtic immigrants in Ireland. The hypothesis that the native Late Bronze Age inhabitants gradually absorbed Celtic influences has since been supported by some recent genetic research.[4]
The Romans referred to Ireland as Hibernia. Ptolemy in AD 100 records Ireland's geography and tribes. Ireland was never formally a part of the Roman Empire but Roman influence was often projected well beyond formal borders. Tacitus writes that an exiled Irish prince was with Agricola in Britain and would return to seize power in Ireland. Juvenal tells us that Roman "arms had been taken beyond the shores of Ireland". In recent years, some experts have hypothesized that Roman-sponsored Gaelic forces (or perhaps even Roman regulars) mounted some kind of invasion around 100,[5] but the exact relationship between Rome and the dynasties and peoples of Hibernia remains unclear.
Irish confederations attacked and settled in Britain during the Great Conspiracy of 367.
[edit] Early Christian Ireland (400–800)
The middle centuries of the first millennium AD marked great changes in Ireland.
Niall Noigiallach (died c.450/455) laid the basis for the Uí Néill dynasty's hegemony over much of western, northern and central Ireland. Politically, the former emphasis on tribal affiliation had been replaced by the 700s by that of patrilineal and dynastic background. Many formerly powerful kingdoms and peoples disappeared. Irish pirates struck all over the coast of western Britain in the same way that the Vikings would later attack Ireland. Some of these founded entirely new kingdoms in Pictland, Wales and Cornwall. The Attacotti of south Leinster may even have served in the Roman military in the mid-to-late 300s.[6]
Perhaps it was some of the latter returning home as rich mercenaries, merchants, or slaves stolen from Britain or Gaul, that first brought the Christian faith to Ireland. Some early sources claim that there were missionaries active in southern Ireland long before St. Patrick. Whatever the route, and there were probably many, this new faith was to have the most profound effect on the Irish.
Tradition maintains that in AD 432, St. Patrick arrived on the island and, in the years that followed, worked to convert the Irish to Christianity. On the other hand, according to Prosper of Aquitaine, a contemporary chronicler, Palladius was sent to Ireland by the Pope in 431 as "first Bishop to the Irish believing in Christ", which demonstrates that there were already Christians living in Ireland. Palladius seems to have worked purely as Bishop to Irish Christians in the Leinster and Meath kingdoms, while Patrick — who may have arrived as late as 461 — worked first and foremost as a missionary to the Pagan Irish, converting in the more remote kingdoms located in Ulster and Connacht.
Patrick is traditionally credited with preserving the tribal and social patterns of the Irish, codifying their laws and changing only those that conflicted with Christian practices. He is also credited with introducing the Roman alphabet, which enabled Irish monks to preserve parts of the extensive Celtic oral literature. The historicity of these claims remains the subject of debate and there is no direct evidence linking Patrick with any of these accomplishments. The myth of Patrick, as scholars refer to it, was developed in the centuries after his death.[7]
The druid tradition collapsed, first in the face of the spread of the new faith, and ultimately in the aftermath of famine and plagues due to the climate changes of 535–536. Irish scholars excelled in the study of Latin learning and Christian theology in the monasteries that flourished shortly thereafter. Missionaries from Ireland to England and Continental Europe spread news of the flowering of learning, and scholars from other nations came to Irish monasteries. The excellence and isolation of these monasteries helped preserve Latin learning during the Early Middle Ages. The period of Insular art, mainly in the fields of illuminated manuscripts, metalworking, and sculpture flourished and produced such treasures as the Book of Kells, the Ardagh Chalice, and the many carved stone crosses that dot the island. Insular style was to be a crucial ingredient in the formation of the Romanesque and Gothic styles throughout Western Europe. Sites dating to this period include clochans, ringforts and promontory forts.
The first English involvement in Ireland took place in this period. In 684 AD an English expeditionary force sent by Northumbrian King Ecgfrith invaded Ireland in the summer of that year. The English forces managed to seize a number of captives and booty, but they apparently did not stay in Ireland for long. The next English involvement in Ireland would take place a little more than half a millennium later in 1169 AD when the Normans invaded the country.
[edit] Early medieval and Viking era (800–1168)

The first recorded Viking raid in Irish history occurred in 795 when Vikings from Norway looted the island. Early Viking raids were generally small in scale and quick. These early raids interrupted the golden age of Christian Irish culture starting the beginning of two hundred years of intermittent warfare, with waves of Viking raiders plundering monasteries and towns throughout Ireland. Most of the early raiders came from the fjords of western Norway.
The Vikings were expert sailors, who travelled in Longships, and by the early 840s, had begun to establish settlements along the Irish coasts and to spend the winter months there. Vikings founded settlements in several places; most famously in Dublin. Written accounts from this time (early to mid 840s) show that the Vikings were moving further inland to attack (often using rivers) and then retreating to their coastal headquarters.
In 852, the Vikings landed in Dublin Bay and established a fortress. After several generations a group of mixed Irish and Norse ethnic background arose (the so-called Gall-Gaels, Gall then being the Irish word for "foreigners").
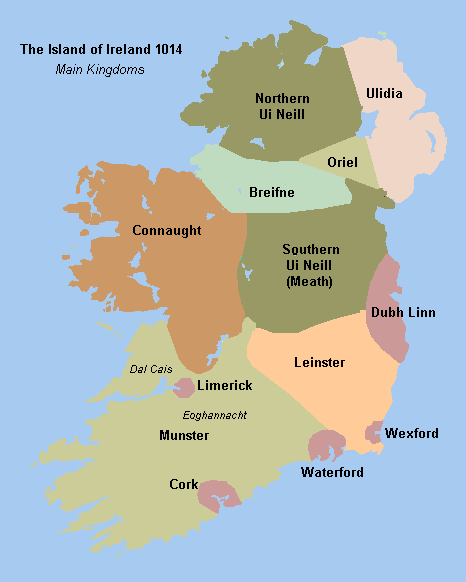
However, the Vikings never achieved total domination of Ireland, often fighting for and against various Irish kings. The Battle of Clontarf in 1014 marked the beginning of the decline of Viking power in Ireland. However the towns that the Vikings had founded continued to flourish and trade became an important part of the Irish economy.
[edit] Norman Ireland (1168–1536)
[edit] Arrival of the Normans

By the 12th century, Ireland was divided politically into a shifting hierarchy of petty kingdoms and over-kingdoms. Power was exercised by the heads of a few regional dynasties vying against each other for supremacy over the whole island. One of these men, King Diarmait Mac Murchada of Leinster was forcibly exiled by the new High King, Ruaidri mac Tairrdelbach Ua Conchobair of the Western kingdom of Connacht. Fleeing to Aquitaine, Diarmait obtained permission from Henry II to recruit Norman knights to regain his kingdom. The first Norman knight landed in Ireland in 1167, followed by the main forces of Normans, Welsh and Flemings. Several counties were restored to the control of Diarmait, who named his son-in-law, the Norman Richard de Clare, known as Strongbow, heir to his kingdom. This caused consternation to King Henry II of England, who feared the establishment of a rival Norman state in Ireland. Accordingly, he resolved to establish his authority.
With the authority of the papal bull Laudabiliter from Adrian IV, Henry landed with a large fleet at Waterford in 1171, becoming the first King of England to set foot on Irish soil. Henry awarded his Irish territories to his younger son John with the title Dominus Hiberniae ("Lord of Ireland"). When John unexpectedly succeeded his brother as King John, the "Lordship of Ireland" fell directly under the English Crown.
[edit] The Lordship of Ireland
Initially the Normans controlled the entire east coast, from Waterford up to eastern Ulster and penetrated far west in the country. The counties were ruled by many smaller kings. The first Lord of Ireland was King John, who visited Ireland in 1185 and 1210 and helped consolidate the Norman controlled areas, while at the same time ensuring that the many Irish kings swore fealty to him.
Throughout the thirteenth century the policy of the English Kings was to weaken the power of the Norman Lords in Ireland. For example King John encouraged Hugh de Lacy to destabilise and then overthrow the Lord of Ulster, before creating him to the Earl of Ulster. The Hiberno-Norman community suffered from a series of invasions that ceased the spread of their settlement and power. Politics and events in Gaelic Ireland served to draw the settlers deeper into the orbit of the Irish.
[edit] Gaelic resurgence, Norman decline

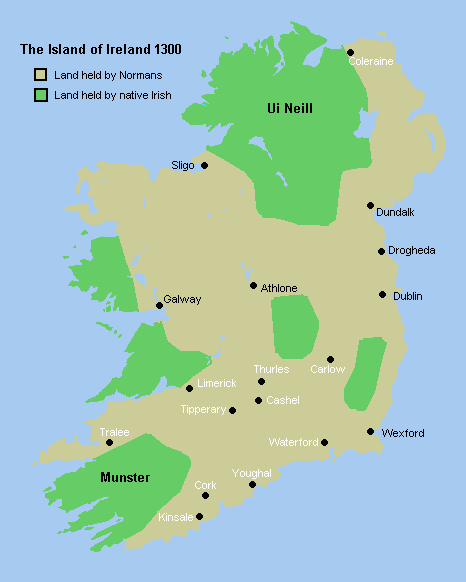
By 1261 the weakening of the Normans had become manifest when Fineen MacCarthy defeated a Norman army at the Battle of Callann. The war continued between the different lords and earls for about 100 years and the wars caused a great deal of destruction, especially around Dublin. In this chaotic situation, local Irish lords won back large amounts of land that their families had lost since the conquest and held them after the war was over.
The Black Death arrived in Ireland in 1348. Because most of the English and Norman inhabitants of Ireland lived in towns and villages, the plague hit them far harder than it did the native Irish, who lived in more dispersed rural settlements. After it had passed, Gaelic Irish language and customs came to dominate the country again. The English-controlled territory shrunk back to a fortified area around Dublin (the Pale), and had little real authority outside (beyond the Pale).
By the end of the 15th century, central English authority in Ireland had all but disappeared. England's attentions were diverted by the Wars of the Roses. The Lordship of Ireland lay in the hands of the powerful Fitzgerald Earl of Kildare, who dominated the country by means of military force and alliances with lords and clans around Ireland. Around the country, local Gaelic and Gaelicised lords expanded their powers at the expense of the English government in Dublin but the power of the Dublin government was seriously curtailed by the introduction of Poynings Law in 1494. According to this act the Irish parliament was essentially put under the control of the Westminster parliament.
[edit] Early Modern Ireland (1536–1691)
[edit] Re-conquest and rebellion
From 1536, Henry VIII decided to re-conquer Ireland and bring it under crown control. The Fitzgerald dynasty of Kildare, who had become the effective rulers of Ireland in the 15th century, had become very unreliable allies of the Tudor monarchs. They had invited Burgundian troops into Dublin to crown the Yorkist pretender, Lambert Simnel as King of England in 1487. Again in 1536, Silken Thomas Fitzgerald went into open rebellion against the crown. Having put down this rebellion, Henry VIII resolved to bring Ireland under English government control so the island would not become a base for future rebellions or foreign invasions of England. In 1541, Henry upgraded Ireland from a lordship to a full Kingdom. Henry was proclaimed King of Ireland at a meeting of the Irish Parliament that year. This was the first meeting of the Irish Parliament to be attended by the Gaelic Irish chieftains as well as the Hiberno-Norman aristocracy. With the institutions of government in place, the next step was to extend the control of the English Kingdom of Ireland over all of its claimed territory. This took nearly a century, with various English administrations in the process either negotiating or fighting with the independent Irish and Old English lords. The Spanish Armada in Ireland suffered heavy losses during an extraordinary season of storms in the autumn of 1588. Among the survivors was Captain Francisco de Cuellar, who gave a remarkable account of his experiences on the run in Ireland.[8]
The re-conquest was completed during the reigns of Elizabeth and James I, after several extremely brutal conflicts. (See the Desmond Rebellions (1569–1573 and 1579–1583 and the Nine Years War 1594–1603, for details). After this point, the English authorities in Dublin established real control over Ireland for the first time, bringing a centralised government to the entire island, and successfully disarmed the native lordships. However, the English were not successful in converting the Catholic Irish to the Protestant religion and the brutal methods used by crown authority (including resorting to martial law) to pacify the country heightened resentment of English rule.
From the mid-16th and into the early 17th century, crown governments carried out a policy of colonisation known as Plantations. Scottish and English Protestants were sent as colonists to the provinces of Munster, Ulster and the counties of Laois and Offaly (see also Plantations of Ireland). These settlers, who had a British and Protestant identity, would form the ruling class of future British administrations in Ireland. A series of Penal Laws discriminated against all faiths other than the established (Anglican) Church of Ireland. The principal victims of these laws were Catholics and later Presbyterians.
[edit] Civil wars and penal laws
The 17th century was perhaps the bloodiest in Ireland's history. Two periods of civil war (1641-53 and 1689-91) caused huge loss of life and resulted in the final dispossession of the Irish Catholic landowning class and their subordination under the Penal Laws.
In the mid-17th century, Ireland was convulsed by eleven years of warfare, beginning with the Rebellion of 1641, when Irish Catholics rebelled against English and Protestant domination, in the process killing thousands of Protestant settlers. The Catholic gentry briefly ruled the country as Confederate Ireland (1642-1649) against the background of the Wars of the Three Kingdoms until Oliver Cromwell re-conquered Ireland in 1649-1653 on behalf of the English Commonwealth. Cromwell's conquest was the most brutal phase of a brutal war. By its close, up to a third of Ireland's pre-war population was dead or in exile. As punishment for the rebellion of 1641, almost all lands owned by Irish Catholics were confiscated and given to British settlers. Several hundred remaining native landowners were transplanted to Connacht.
Ireland became the main battleground after the Glorious Revolution of 1688, when the Catholic James II left London and the English Parliament replaced him with William of Orange. The wealthier Irish Catholics backed James to try to reverse the remaining Penal Laws and land confiscations, whereas Protestants supported William to preserve their property in the country. James and William fought for the Kingdom of Ireland in the Williamite War, most famously at the Battle of the Boyne in 1690, where James's outnumbered forces were defeated. Jacobite resistance was finally ended after the Battle of Aughrim in July 1691. The Penal Laws that had been relaxed somewhat after the English Restoration were re-enacted more thoroughly after this war, as the Protestant élite wanted to ensure that the Irish Catholic landed classes would not be in a position to repeat their rebellions of the 17th century.
[edit] Protestant Ascendancy (1691–1801)
Subsequent Irish antagonism towards England was aggravated by the economic situation of Ireland in the 18th century. Some absentee landlords managed some of their estates inefficiently, and food tended to be produced for export rather than for domestic consumption. Two very cold winters, and consecutive years of potato blight led directly to the Great Irish Famine (1740-1741), which killed about 400,000 people and caused over 150,000 of the Irish to emigrate; all of Europe was affected. In addition, Irish exports were reduced by the Navigation Acts from the 1660s, which placed tariffs on Irish products entering England, but exempted English goods from tariffs on entering Ireland. However most of the 18th century was relatively peaceful in comparison with the preceding two hundred years, and the population doubled to over four million.
By the late 18th century, many of the Anglo-Irish ruling class had come to see Ireland as their native country. A Parliamentary faction led by Henry Grattan agitated for a more favourable trading relationship with England and for greater legislative independence for the Parliament of Ireland. However, reform in Ireland stalled over the more radical proposals to enfranchise Irish Catholics. This was enabled in 1793, but Catholics could not yet enter parliament or become government officials. Some were attracted to the more militant example of the French Revolution of 1789. They formed the Society of the United Irishmen to overthrow British rule and found a non-sectarian republic. Their activity culminated in the Irish Rebellion of 1798, which was bloodily suppressed. Largely in response to this rebellion, Irish self-government was abolished altogether by the Act of Union in 1801.
[edit] Union with Great Britain (1801–1912)
In 1800, after the Irish Rebellion of 1798, the British and the Irish parliaments enacted the Act of Union, which merged the Kingdom of Ireland and the Kingdom of Great Britain (itself a union of "England" (Wales had been incorporated into England by the Act of Union of 1536), and Scotland, created almost 100 years earlier), to create the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. Part of the deal for the union was that Catholic Emancipation would be conceded to remove discrimination against Catholics, Presbyterians, and others. However, King George III controversially blocked any change.
In 1823, an enterprising Catholic lawyer, Daniel O'Connell, known as "The Liberator" began a successful campaign to achieve emancipation, which was finally conceded in 1829. However, the continuing obligation of Catholics to fund the Church of Ireland led to the Tithe War of 1831-38. One condition was the removal of the poorer Irish freeholders from the franchise. He later led the Repeal Association in a campaign to undo the Act of Union 1800.[9]
The second of Ireland's "Great Famines", An Gorta Mór struck the country severely in the period 1845-1849, with potato blight leading to mass starvation and emigration. (See Great Irish Famine.) The impact of emigration in Ireland was severe; the population dropped from over 8 million before the Famine to 4.4 million in 1911. Gaelic once the spoken language of the entire island, declined in use sharply in the nineteenth century as a result of the Famine and the creation of the National School education system, as well as hostility to the language from leading Irish politicians of the time; it was largely replaced by English.
Outside mainstream nationalism, a series of violent rebellions by Irish republicans took place in 1803, under Robert Emmet; in 1848 a rebellion by the Young Irelanders, most prominent among them, Thomas Francis Meagher; and in 1867, another insurrection by the Irish Republican Brotherhood. All failed, but physical force nationalism remained an undercurrent in the nineteenth century.
The late 19th century also witnessed major land reform, spearheaded by the Land League under Michael Davitt demanding what became known as the 3 Fs; Fair rent, free sale, fixity of tenure. From 1870 and as a result of the Land War agitations and subsequent Plan of Campaign of the 1880s, various British governments introduced a series of Irish Land Acts - William O'Brien playing a leading role by winning the greatest piece of social legislation Ireland had yet seen, the Wyndham Land Purchase Act (1903) which broke up large estates and gradually gave rural landholders and tenants ownership of the lands. It effectively ended absentee landlordism, solving the age-old Irish Land Question
In the 1870s the issue of Irish self-government again became a major focus of debate under Protestant landowner, Charles Stewart Parnell and the Irish Parliamentary Party of which he was founder. British prime minister William Ewart Gladstone made two unsuccessful attempts to introduce Home Rule in 1886 and 1893. Parnell's controversial leadership eventually ended when he was implicated in a divorce scandal, when it was revealed that he had been living in family relationship with Katherine O'Shea, the long separated wife of a fellow Irish MP, with whom he was father of three children.
After the introduction of the Local Government (Ireland) Act 1898 which broke the power of the landlord dominated "Grand Juries", passing for the first time absolute democratic control of local affairs into the hands of the people through elected Local County Councils, the debate over full Home Rule led to tensions between Irish nationalists and Irish unionists (those who favoured maintenance of the union). Most of the island was predominantly nationalist, Catholic and agrarian. The northeast, however, was predominantly unionist, Protestant and industrialised. Unionists feared a loss of political power and economic wealth in a predominantly rural, nationalist, Catholic home-rule state. Nationalists believed that they would remain economically and politically second class citizens without self-government. Out of this division, two opposing sectarian movements evolved, the Protestant Orange Order and the Catholic Ancient Order of Hibernians.
[edit] Home Rule, Easter Rising and War of Independence (1912–1922)
Home Rule became certain when in 1910 the Irish Parliamentary Party (IPP) under John Redmond held the balance of power in the Commons and the third Home Rule Bill was introduced in 1912. Unionist resistance was immediate with the formation of the Ulster Volunteers. In turn the Irish Volunteers were established to oppose them and enforce the introduction of self-government.
In September 1914, just as the First World War broke out, the UK Parliament finally passed the Third Home Rule Act to establish self-government for Ireland, but was suspended for the duration of the war. In order to ensure the implementation of Home Rule after the war, nationalist leaders and the IPP under Redmond supported the British and Allied war effort against the Central Powers. The core of the Irish Volunteers were against this decision, but the majority left to form the National Volunteers who enlisted in Irish regiments of the 10th and 16th (Irish) Divisions. Before the war ended, Britain made two concerted efforts to implement Home Rule, one in May 1916 and again with the Irish Convention during 1917-1918, but the Irish sides (Nationalist, Unionist) were unable to agree terms for the temporary or permanent exclusion of Ulster from its provisions.
The period from 1916-1921 was marked by political violence and upheaval, ending in the partition of Ireland and independence for 26 of its 32 counties. A failed attempt was made to gain separate independence for Ireland with the 1916 Easter Rising, an insurrection in Dublin. Though support for the insurgents was small, the violence used in its suppression led to a swing in support of the rebels. In addition, the unprecedented threat of Irishmen being conscripted to the British Army in 1918 (for service on the Western Front as a result of the German Spring Offensive) accelerated this change. (See: Conscription Crisis of 1918). In the December 1918 elections Sinn Féin, the party of the rebels, won a majority of three-quarters of all seats in Ireland, MPs of which assembled in Dublin on 21 January 1919, to form a thirty-two county Irish Republic parliament, the first Dáil Éireann unilaterally declaring sovereignty over the entire island.
| Irish parliaments |
|---|

Leinster House, home of the Ireland's parliament since 1922.
|
Unwilling to negotiate any understanding with Britain short of complete independence, the Irish Republican Army — the army of the newly declared Irish Republic — waged a guerilla war (the Irish War of Independence) from 1919 to 1921. In the course of the fighting and amid much acrimony, the Fourth Government of Ireland Act 1920 implemented Home Rule while separating the island into what the British government's Act termed "Northern Ireland" and "Southern Ireland". In July 1921, the Irish and British governments agreed a truce that halted the war. In December 1921, representatives of both governments signed an Anglo-Irish Treaty. The Irish delegation was led by Arthur Griffith and Michael Collins. This abolished the Irish Republic and created the Irish Free State, a self-governing Dominion of the British Empire in the manner of Canada and Australia. Under the Treaty, Northern Ireland could opt out of the Free State and stay within the United Kingdom: it promptly did so. In 1922, both parliaments ratified the Treaty, formalising independence for the twenty-six county Irish Free State (which went on to re-name itself Ireland in 1937 and declare itself a republic in 1949); while the six county Northern Ireland, gaining Home Rule for itself, remained part of the United Kingdom. For most of the next 75 years, each territory was strongly aligned to either Catholic or Protestant ideologies, although this was more marked in the six counties of Northern Ireland.
[edit] Free State and Republic (1922–present)
Main articles: History of the Republic of Ireland; Irish Free State, Republic of Ireland; Names of the Irish state
The treaty to sever the Union divided the republican movement into anti-Treaty (who wanted to fight on until an Irish Republic was achieved) and pro-Treaty supporters (who accepted the Free State as a first step towards full independence and unity). Between 1922 and 1923 both sides fought the bloody Irish Civil War. The new Irish Free State government defeated the anti-Treaty remnant of the Irish Republican Army. This division among nationalists still colours Irish politics today, specifically between the two leading Irish political parties, Fianna Fáil and Fine Gael.
The new Irish Free State (1922–37) existed against the backdrop of the growth of dictatorships in mainland Europe and a major world economic downturn in 1929. In contrast with many contemporary European states it remained a democracy. Testament to this came when the losing faction in the Irish civil war, Eamon de Valera's Fianna Fáil, was able to take power peacefully by winning the 1932 general election. Nevertheless, up until the mid 1930s, considerable parts of Irish society saw the Free State through the prism of the civil war, as a repressive, British imposed state. It was only the peaceful change of government in 1932 that signalled the final acceptance of the Free State on their part. In contrast to many other states in the period, the Free State remained financially solvent as a result of low government expenditure. However, unemployment and emigration were high. The population declined to a low of 2.7 million recorded in the 1961 census.
The Roman Catholic Church had a powerful influence over the Irish state for much of its history. The clergy's influence meant that the Irish state had very conservative social policies, banning, for example, divorce, contraception, abortion, pornography as well as encouraging the censoring of many books and films. In addition the Church largely controlled the State's hospitals, schools and remained the largest provider of many other social services.
With the partition of Ireland in 1922, 92.6% of the Free State's population were Catholic while 7.4% were Protestant.[10] By the 1960s, the Protestant population had fallen by half. Although emigration was high among all the population, due to a lack of economic opportunity, the rate of Protestant emigration was disproportionate in this period. Many Protestants left the country in the early 1920s, either because they felt unwelcome in a predominantly Catholic and nationalist state, because they were afraid due to the burning of Protestant homes (particularly of the old landed class) by republicans during the civil war, because they regarded themselves as British and did not wish to live in an independent Irish state, or because of the economic disruption caused by the recent violence. The Catholic Church had also issued a decree, known as Ne Temere, whereby the children of marriages between Catholics and Protestants had to be brought up as Catholics. From 1945, the emigration rate of Protestants fell and they became less likely to emigrate than Catholics - indicating their integration into the life of the Irish State.
In 1937, a new Constitution of Ireland re-established the state as Ireland (or Éire in Irish). The state remained neutral throughout World War II (see Irish neutrality) and this saved it from much of the horrors of the war, although tens of thousands volunteered to serve in the British forces. Ireland was also hit badly by rationing of food, and coal in particular (peat production became a priority during this time). Though nominally neutral, recent studies have suggested a far greater level of involvement by the South with the Allies than was realised, with D Day's date set on the basis of secret weather information on Atlantic storms supplied by Ireland. For more detail on 1939–45, see main article The Emergency.
In 1949 the state was formally declared a republic and it left the British Commonwealth.
In the 1960s, Ireland underwent a major economic change under reforming Taoiseach (prime minister) Seán Lemass and Secretary of the Department of Finance T.K. Whitaker, who produced a series of economic plans. Free second-level education was introduced by Donnchadh O'Malley as Minister for Education in 1968. From the early 1960s, Ireland sought admission to the European Economic Community but, because 90% of exports were to the United Kingdom market, it did not do so until the UK did, in 1973.
Global economic problems in the 1970s, augmented by a set of misjudged economic policies followed by governments, including that of Taoiseach Jack Lynch, caused the Irish economy to stagnate. The Troubles in Northern Ireland discouraged foreign investment. Devaluation was enabled when the Irish Pound, or Punt, was established in as a truly separate currency in 1979, breaking the link with the UK's sterling. However, economic reforms in the late 1980s, helped by investment from the European Community, led to the emergence of one of the world's highest economic growth rates, with mass immigration (particularly of people from Asia and Eastern Europe) as a feature of the late 1990s. This period came to be known as the Celtic Tiger and was focused on as a model for economic development in the former Eastern Bloc states, which entered the European Union in the early 2000s. Property values had risen by a factor of between four and ten between 1993 and 2006, in part fuelling the boom.
Irish society also adopted relatively liberal social policies during this period. Divorce was legalised, homosexuality decriminalised, while abortion in limited cases was allowed by the Irish Supreme Court in the X Case legal judgement. Major scandals in the Roman Catholic Church, both sexual and financial, coincided with a widespread decline in religious practice, with weekly attendance at Roman Catholic Mass halving in twenty years. A series of tribunals set up from the 1990s have investigated alleged malpractices by politicians, the Catholic clergy, judges, hospitals and the Gardaí (police).
[edit] Northern Ireland
[edit] "A Protestant State" (1921–1972)
From 1921 to 1972, Northern Ireland was governed by a Unionist government, based at Stormont in east Belfast. The first Prime Minister, James Craig, declared that it would be "a Protestant State for a Protestant People" (in response to the "Catholic nation" of De Valera in the south). Discrimination against the minority nationalist community in jobs and housing, and their total exclusion from political power due to the majoritarian electoral system, led to the emergence of the Northern Ireland Civil Rights Association in the late 1960s, inspired by Martin Luther King's civil rights movement in the United States of America. A violent counter-reaction from conservative unionists led to civil disorder, notably the Battle of the Bogside and the Northern Ireland riots of August 1969. To restore order, British troops were deployed to the streets of Northern Ireland at this time.
Tensions came to a head with the events of Bloody Sunday and Bloody Friday, and the worst years (early 1970s) of what became known as the Troubles resulted. The Stormont parliament was prorogued in 1972 and abolished in 1973. Paramilitary private armies such as the Provisional Irish Republican Army, the Official IRA, the Irish National Liberation Army, the Ulster Defence Association and the Ulster Volunteer Force fought each other and the British army and the (largely Protestant) RUC, resulting in the deaths of well over three thousand men, women and children, civilians and military. Most of the violence took place in Northern Ireland, but some also spread to England and across the Irish border.
| Irish Police forces |
|---|
| ---Defunct Irish Police Forces--- |
| Royal Irish Constabulary (1822—1922) |
| Dublin Metropolitan Police (1836—1925) |
| Irish Republican Police (Irish Republic 1920—1922) |
| Royal Ulster Constabulary (1922—2001) |
| ---Current Irish Police Forces--- |
| Northern Ireland |
| Belfast Harbour Police (1847) |
| Larne Harbour Police (1847) |
| Royal Military Police (1946) |
| Belfast International Airport Constabulary (1994) |
| Police Service of Northern Ireland (2001) |
| Ministry of Defence Police (2004) |
| Republic of Ireland |
| Garda Síochána (1922) |
| Póilíní Airm (1922) |
| Garda Síochána Reserve (2006) |
[edit] Direct rule (1972–1999)
For the next 27½ years, with the exception of five months in 1974, Northern Ireland was under "direct rule" with a Secretary of State for Northern Ireland in the British Cabinet responsible for the departments of the Northern Ireland government. Principal acts were passed by the Parliament of the United Kingdom in the same way as for much of the rest of the UK, but many smaller measures were dealt with by Order in Council with minimal parliamentary scrutiny. Throughout this time the aim was to restore devolution, but three attempts - the power-sharing executive established by the Northern Ireland Constitution Act and the Sunningdale Agreement, the 1975 Northern Ireland Constitutional Convention and Jim Prior's 1982 assembly - all failed to either reach consensus or operate in the longer term.
During the 1970s British policy concentrated on defeating the Provisional Irish Republican Army (IRA) by military means including the policy of Ulsterisation (requiring the RUC and British Army reserve Ulster Defence Regiment to be at the forefront of combating the IRA). Although IRA violence decreased it was obvious that no military victory was on hand in either the short or medium terms. Even Catholics that generally rejected the IRA were unwilling to offer support to a state that seemed to remain mired in sectarian discrimination, and the Unionists plainly were not interested in Catholic participation in running the state in any case. In the 1980s the IRA attempted to secure a decisive military victory based on massive arms shipments from Libya. When this failed - probably because of MI5's penetration of the IRA's senior commands[citation needed] - senior republican figures began to look to broaden the struggle from purely military means. In time this began a move towards military cessation. In 1986 the British and Irish governments signed the Anglo Irish Agreement signalling a formal partnership in seeking a political solution. Socially and economically Northern Ireland suffered the worst levels of unemployment in the UK and although high levels of public spending ensured a slow modernisation of public services and moves towards equality, progress was slow in the 1970s and 1980s, only in the 1990s when progress towards peace became tangible, did the economic situation brighten. By then, too, the demographics of Northern Ireland had undergone significant change, and more than 40% of the population was Catholic.
[edit] Devolution and direct rule (1999–present)
More recently, the Belfast Agreement ("Good Friday Agreement") of 10 April 1998 brought - on 2 December 1999 - a degree of power sharing to Northern Ireland, giving both unionists and nationalists control of limited areas of government. However, both the power-sharing Executive and the elected Assembly were suspended between January and May 2000, and from October 2002 until April 2007, following breakdowns in trust between the political parties involving outstanding issues, including "decommissioning" of paramilitary weapons, policing reform and the removal of British army bases. In new elections in 2003, the moderate Ulster Unionist and (nationalist) Social Democrat and Labour parties lost their dominant positions to the more hard-line Democratic Unionist and (nationalist) Sinn Féin parties. On 28 July 2005, the Provisional IRA announced the end of its armed campaign and on 25 September 2005 international weapons inspectors supervised the full disarmament of the PIRA. Eventually, devolution was restored in April 2007.
[edit] Flags in Ireland

The national flag of the Ireland is a tricolour of green, white and orange. This flag, which bears the colours green for Roman Catholics, orange for Protestants, and white for the desired peace between them, dates back to the middle of the 19th century.[11]
The tricolour was first unfurled in public by Young Irelander Thomas Francis Meagher who, using the symbolism of the flag, explained his vision as follows: "The white in the centre signifies a lasting truce between the "Orange" and the "Green," and I trust that beneath its folds the hands of the Irish Protestant and the Irish Catholic may be clasped in generous and heroic brotherhood". Fellow nationalist John Mitchel said of it: "I hope to see that flag one day waving as our national banner."
After its use in the 1916 Rising it became widely accepted by nationalists as the national flag, as was used officially by the Irish Republic (1919-21) and the Irish Free State (1922-37).
In 1937 when the Constitution of Ireland was introduced, the tricolour was formally confirmed as the national flag: "The national flag is the tricolour of green, white and orange." While the tricolour today is the official flag of Ireland, it is not an official flag in Northern Ireland although it is sometimes used unofficially.
The only official flag representing Northern Ireland is the Union Flag of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Ulster Banner is sometimes used unofficially as a de facto regional flag for Northern Ireland.
Since Partition, there has been no universally-accepted flag to represent the entire island. As a provisional solution for certain sports fixtures, the Flag of the Four Provinces enjoys a certain amount of general acceptance and popularity.
Historically a number of flags have been used, including:
- Saint Patrick's Flag (St Patrick's Saltire, St Patric's Cross) which represented Ireland on the Union Flag after the Act of Union,
- a green flag with a harp (used by most nationalists in the 19th century and which is also the flag of Leinster),
- a blue flag with a harp used from the 18th century onwards by many nationalists (now the standard of the President of Ireland), and
- the Irish tricolour.
St Patrick's Saltire was formerly used to represent the island of Ireland by the all-island Irish Rugby Football Union (IRFU), before adoption of the four-provinces flag. The Gaelic Athletic Association (GAA) uses the tricolour to represent the whole island.
[edit] See also
- Timeline of Irish history
- History of Belfast
- History of Cork
- History of Derry
- History of Dublin
- History of Galway
- History of Limerick
- History of Waterford
- History of rail transport in Ireland
- History of the United Kingdom
- Irish Historians
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
[edit] Footnotes
- ^ Moody, T.W. & Martin, F.X., eds. (1995). The Course of Irish History. Roberts Rinehart. pp. 31–32. ISBN 1-56833-175-4.
- ^ History news netwok2004-09-09. Retrieved 2007-04-01.
- ^ Myths of British ancestry Stephen Oppenheimer. October 2006, Special report. Retrieved 2007-04-01.
- ^ Y-chromosome variation and Irish origins (pdf)
- ^ "Yes, the Romans did invade Ireland". British Archaeology. http://www.britarch.ac.uk/BA/ba14/ba14feat.html.
- ^ *Philip Rance, ‘Attacotti, Déisi and Magnus Maximus: the Case for Irish Federates in Late Roman Britain’, Britannia 32 (2001) 243-270
- ^ *Carmel McCaffrey, Leo Eaton "In Search of Ancient Ireland" Ivan R Dee (2002)PBS 2002
- ^ 'The Wild Irish are Barbarous and Most Filthy in their Diet', bbc.co.uk
- ^ Kee, Robert. The Green Flag. London, Weidenfeld and Nicholson, 1972. pp. 187-243
- ^ M.E.Collins, Ireland 1868-1966, (1993) p431)
- ^ The Irish State www.irlgov.ie
[edit] References
- Irish History, Séamus Mac Annaidh, Bath: Paragon, 1999, ISBN 0-76256-139-1
- Irish Kings and High Kings, Francis John Byrne, Dublin, 1973, ISBN 0-71341-304-2
- A New History of Ireland: I - PreHistoric and Early Ireland, ed. Daibhi O Croinin. 2005, ISBN 0-19821-737-4
- A New History of Ireland: II- Medieval Ireland 1169-1534, ed. Art Cosgrove. 1987.
- Braudel, Fernand, The Perspective of the World, vol III of Civilization and Capitalism (1979, in English 1985), ISBN 0-06015-317-2
- Plumb, J.H., England in the 18th Century, 1973: "The Irish Empire"
[edit] Further reading
- S. J. Connolly (editor) The Oxford Companion to Irish History (Oxford University Press, 2000)
- Tim Pat Coogan De Valera (Hutchinson, 1993)
- Norman Davies The Isles: A History (Macmillan, 1999)
- Nancy Edwards, The archaeology of early medieval Ireland (London, Batsford 1990).
- R. F. Foster Modern Ireland, 1600-1972
- J. J. Lee The Modernisation of Irish Society 1848-1918 (Gill and Macmillan)
- F. S. L. Lyons Ireland Since the Famine
- Dorothy McCardle The Irish Republic
- T. W. Moody and F. X. Martin "The Course of Irish History" Fourth Edition (Lanham, Maryland: Roberts Rinehart Publishers, 2001).
- James H. Murphy Abject Loyalty: Nationalism and Monarchy in Ireland During the Reign of Queen Victoria (Cork University Press, 2001)
- http://www.ucc.ie/celt/published/E900003-001/ - the 1921 Treaty debates online.
- John A. Murphy Ireland in the Twentieth Century (Gill and Macmillan)
- Frank Pakenham, (Lord Longford) Peace by Ordeal
- Alan J. Ward The Irish Constitutional Tradition: Responsible Government & Modern Ireland 1782-1992 (Irish Academic Press, 1994)
- Robert Kee The Green Flag Volumes 1-3 (The Most Distressful Country, The Bold Fenian Men, Ourselves Alone)
- Carmel McCaffrey and Leo Eaton In Search of Ancient Ireland: the origins of the Irish from Neolithic Times to the Coming of the English (Ivan R Dee, 2002)
- Carmel McCaffrey In Search of Ireland's Heroes: the Story of the Irish from the English Invasion to the Present Day (Ivan R Dee, 2006)
- Hugh F. Kearney Ireland:Contested Ideas of Nationalism and History (NYU Press, 2007)]
- Nicholas Canny "The Elizabethan Conquest of Ireland"(London, 1976) ISBN 0-85527-034-9.
[edit] External links
- http://hnn.us/roundup/entries/7406.html
- http://www.prospect-magazine.co.uk/article_details.php?id=7817
- http://www.pbs.org/wnet/ancientireland/
- History of Ireland: Primary Documents
- History of Ireland guide
- Ireland Under Coercion - "The diary of an American", by William Henry Hurlbert, published 1888, from Project Gutenberg
- The Story of Ireland by Emily Lawless, 1896 (Project Gutenberg)
- Timeline of Irish History 1840-1916 (1916 Rebellion Walking Tour)
- A Concise History of Ireland by P. W. Joyce