Field-programmable gate array
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
- FPGAs should not be confused with the flip-chip pin grid array, a form of integrated circuit packaging.

A field-programmable gate array (FPGA) is a semiconductor device that can be configured by the customer or designer after manufacturing—hence the name "field-programmable". FPGAs are programmed using a logic circuit diagram or a source code in a hardware description language (HDL) to specify how the chip will work. They can be used to implement any logical function that an application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) could perform, but the ability to update the functionality after shipping offers advantages for many applications.[1]
FPGAs contain programmable logic components called "logic blocks", and a hierarchy of reconfigurable interconnects that allow the blocks to be "wired together"—somewhat like a one-chip programmable breadboard. Logic blocks can be configured to perform complex combinational functions, or merely simple logic gates like AND and XOR. In most FPGAs, the logic blocks also include memory elements, which may be simple flip-flops or more complete blocks of memory.[1]
Contents |
[edit] History
The FPGA industry sprouted from programmable read only memory (PROM) and programmable logic devices (PLDs). PROMs and PLDs both had the option of being programmed in batches in a factory or in the field (field programmable), however programmable logic was hard-wired between logic gates.[2]
Xilinx Co-Founders, Ross Freeman and Bernard Vonderschmitt, invented the first commercially viable field programmable gate array in 1985 – the XC2064.[3] The XC2064 had programmable gates and programmable interconnects between gates, the beginnings of a new technology and market.[4] The XC2064 boasted a mere 64 configurable logic blocks (CLBs), with two 3-input lookup tables (LUTs).[5] More than 20 years later, Ross was entered into the National Inventor's Hall of Fame for his invention.[6]
Some of the industry’s foundational concepts and technologies for programmable logic arrays, gates, and logic blocks are founded in patents awarded to David W. Page and LuVerne R. Peterson in 1985.[7][8]
In the late 1980s the Naval Surface Warfare Department funded an experiment proposed by Steve Casselman to develop a computer that would implement 600,000 reprogrammable gates. Casselman was successful and the system was awarded a patent in 1992.[2]
Xilinx continued unchallenged and quickly growing from 1985 to the mid-1990s, when competitors sprouted up, eroding significant market-share. By 1993, Actel was serving about 18 percent of the market.[4]
The 1990s were an explosive period of time for FPGAs, both in sophistication and the volume of production. In the early 1990s, FPGAs were primarily used in telecommunications and networking. By the end of the decade, FPGAs found their way into consumer, automotive, and industrial applications.[9]
FPGAs got a glimpse of fame in 1997, when Adrian Thompson merged genetic algorithm technology and FPGAs to create a sound recognition device. Thomson’s algorithm allowed an array of 64 x 64 cells in a Xilinx FPGA chip to decide the configuration needed to accomplish a sound recognition task.[2]
[edit] Modern developments
A recent trend has been to take the coarse-grained architectural approach a step further by combining the logic blocks and interconnects of traditional FPGAs with embedded microprocessors and related peripherals to form a complete "system on a programmable chip". This work mirrors the architecture by Ron Perlof and Hana Potash of Burroughs Advanced Systems Group which combined a reconfigurable CPU architecture on a single chip called the SB24. That work was done in 1982. Examples of such hybrid technologies can be found in the Xilinx Virtex-II PRO and Virtex-4 devices, which include one or more PowerPC processors embedded within the FPGA's logic fabric. The Atmel FPSLIC is another such device, which uses an AVR processor in combination with Atmel's programmable logic architecture.
An alternate approach to using hard-macro processors is to make use of "soft" processor cores that are implemented within the FPGA logic. (See "Soft processors" below).
As previously mentioned, many modern FPGAs have the ability to be reprogrammed at "run time," and this is leading to the idea of reconfigurable computing or reconfigurable systems — CPUs that reconfigure themselves to suit the task at hand. The Mitrion Virtual Processor from Mitrionics is an example of a reconfigurable soft processor, implemented on FPGAs. However, it does not support dynamic reconfiguration at runtime, but instead adapts itself to a specific program.
Additionally, new, non-FPGA architectures are beginning to emerge. Software-configurable microprocessors such as the Stretch S5000 adopt a hybrid approach by providing an array of processor cores and FPGA-like programmable cores on the same chip.
[edit] Gates
- 1987: 9,000 gates, Xilinx[4]
- 1992: 600,000, Naval Surface Warfare Department[2]
- Early 2000s: Millions [9]
[edit] Market size
- 1985: First commercial FPGA technology invented by Xilinx[4]
- 1987: $14 million[4]
- ~1993: >$385 million[4]
- 2005: $1.9 billion[10]
- 2010 estimates: $2.75 billion [10]
[edit] FPGA design starts
[edit] FPGA Comparisons
Historically, FPGAs have been slower, less energy efficient and generally achieved less functionality than their fixed ASIC counterparts. A combination of volume, fabrication improvements, research and development, and the I/O capabilities of new supercomputers have largely closed the performance gap between ASICs and FPGAs.[14]
Advantages include a shorter time to market, ability to re-program in the field to fix bugs, and lower non-recurring engineering costs. Vendors can also take a middle road by developing their hardware on ordinary FPGAs, but manufacture their final version so it can no longer be modified after the design has been committed.
Xilinx claims that several market and technology dynamics are changing the ASIC/FPGA paradigm:[15]
- IC costs are rising aggressively
- ASIC complexity has bolstered development time and costs
- R&D resources and headcount is decreasing
- Revenue losses for slow time-to-market are increasing
- Financial constraints in a poor economy are driving low-cost technologies
These trends make FPGAs a better alternative than ASICs for a growing number of higher-volume applications than they have been historically used for, which the company blames for the growing number of FPGA design starts (see History).[15]
The primary differences between CPLDs and FPGAs are architectural. A CPLD has a somewhat restrictive structure consisting of one or more programmable sum-of-products logic arrays feeding a relatively small number of clocked registers. The result of this is less flexibility, with the advantage of more predictable timing delays and a higher logic-to-interconnect ratio. The FPGA architectures, on the other hand, are dominated by interconnect. This makes them far more flexible (in terms of the range of designs that are practical for implementation within them) but also far more complex to design for.
Another notable difference between CPLDs and FPGAs is the presence in most FPGAs of higher-level embedded functions (such as adders and multipliers) and embedded memories, as well as to have logic blocks implement decoders or mathematical functions.
Some FPGAs have the capability of partial re-configuration that lets one portion of the device be re-programmed while other portions continue running.
[edit] Applications
Applications of FPGAs include digital signal processing, software-defined radio, aerospace and defense systems, ASIC prototyping, medical imaging, computer vision, speech recognition, cryptography, bioinformatics, computer hardware emulation and a growing range of other areas.
FPGAs originally began as competitors to CPLDs and competed in a similar space, that of glue logic for PCBs. As their size, capabilities, and speed increased, they began to take over larger and larger functions to the state where some are now marketed as full systems on chips (SoC). Particularly with the introduction of dedicated multipliers into FPGA architectures in the late 1990s, applications, which had traditionally been the sole reserve of DSPs, began to incorporate FPGAs instead.[16] [17]
FPGAs especially find applications in any area or algorithm that can make use of the massive parallelism offered by their architecture. One such area is code breaking, in particular brute-force attack, of cryptographic algorithms.
FPGAs are increasingly used in conventional high performance computing applications where computational kernels such as FFT or Convolution are performed on the FPGA instead of a microprocessor.
The inherent parallelism of the logic resources on an FPGA allows for considerable compute throughput even at a low MHz clock rates. The flexibility of the FPGA allows for even higher performance by trading off precision and range in the number format for an increased number of parallel arithmetic units. This has driven a new type of processing called reconfigurable computing, where time intensive tasks are offloaded from software to FPGAs.
The adoption of FPGAs in high performance computing is currently limited by the complexity of FPGA design compared to conventional software and the extremely long turn-around times of current design tools, where 4-8 hours wait is necessary after even minor changes to the source code.
Traditionally, FPGAs have been reserved for specific vertical applications where the volume of production is small. For these low-volume applications, the premium that companies pay in hardware costs per unit for a programmable chip is more affordable than the development resources spent on creating an ASIC for a low-volume application. Today, new cost and performance dynamics have broadened the range of viable applications.
[edit] Architecture
The most common FPGA architecture[18] consists of an array of configurable logic blocks (CLBs), I/O pads, and routing channels. Generally, all the routing channels have the same width (number of wires). Multiple I/O pads may fit into the height of one row or the width of one column in the array.
An application circuit must be mapped into an FPGA with adequate resources. While the number of CLBs and I/Os required is easily determined from the design, the number of routing tracks needed may vary considerably even among designs with the same amount of logic. (For example, a crossbar switch requires much more routing than a systolic array with the same gate count.) Since unused routing tracks increase the cost (and decrease the performance) of the part without providing any benefit, FPGA manufacturers try to provide just enough tracks so that most designs that will fit in terms of LUTs and IOs can be routed. This is determined by estimates such as those derived from Rent's rule or by experiments with existing designs.
A classic FPGA logic block consists of a 4-input lookup table (LUT), and a flip-flop, as shown below. In recent years, manufacturers have started moving to 6-input LUTs in their high performance parts, claiming increased performance.[19]
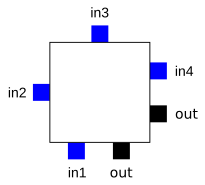
There is only one output, which can be either the registered or the unregistered LUT output. The logic block has four inputs for the LUT and a clock input. Since clock signals (and often other high-fanout signals) are normally routed via special-purpose dedicated routing networks in commercial FPGAs, they and other signals are separately managed.
For this example architecture, the locations of the FPGA logic block pins are shown below.
Each input is accessible from one side of the logic block, while the output pin can connect to routing wires in both the channel to the right and the channel below the logic block.
Each logic block output pin can connect to any of the wiring segments in the channels adjacent to it.
Similarly, an I/O pad can connect to any one of the wiring segments in the channel adjacent to it. For example, an I/O pad at the top of the chip can connect to any of the W wires (where W is the channel width) in the horizontal channel immediately below it.
Generally, the FPGA routing is unsegmented. That is, each wiring segment spans only one logic block before it terminates in a switch box. By turning on some of the programmable switches within a switch box, longer paths can be constructed. For higher speed interconnect, some FPGA architectures use longer routing lines that span multiple logic blocks.
Whenever a vertical and a horizontal channel intersect, there is a switch box. In this architecture, when a wire enters a switch box, there are three programmable switches that allow it to connect to three other wires in adjacent channel segments. The pattern, or topology, of switches used in this architecture is the planar or domain-based switch box topology. In this switch box topology, a wire in track number one connects only to wires in track number one in adjacent channel segments, wires in track number 2 connect only to other wires in track number 2 and so on. The figure below illustrates the connections in a switch box.
Modern FPGA families expand upon the above capabilities to include higher level functionality fixed into the silicon. Having these common functions embedded into the silicon reduces the area required and gives those functions increased speed compared to building them from primitives. Examples of these include multipliers, generic DSP blocks, embedded processors, high speed IO logic and embedded memories.
FPGAs are also widely used for systems validation including pre-silicon validation, post-silicon validation, and firmware development. This allows chip companies to validate their design before the chip is produced in the factory, reducing the time to market.
[edit] FPGA Design and Programming
To define the behavior of the FPGA, the user provides a hardware description language (HDL) or a schematic design. The HDL form might be easier to work with when handling large structures because it's possible to just specify them numerically rather than having to draw every piece by hand. On the other hand, schematic entry can allow for easier visualisation of a design.
Then, using an electronic design automation tool, a technology-mapped netlist is generated. The netlist can then be fitted to the actual FPGA architecture using a process called place-and-route, usually performed by the FPGA company's proprietary place-and-route software. The user will validate the map, place and route results via timing analysis, simulation, and other verification methodologies. Once the design and validation process is complete, the binary file generated (also using the FPGA company's proprietary software) is used to (re)configure the FPGA.
Going from schematic/HDL source files to actual configuration: The source files are fed to a software suite from the FPGA/CPLD vendor that through different steps will produce a file. This file is then transferred to the FPGA/CPLD via a serial interface (JTAG) or to an external memory device like an EEPROM.
The most common HDLs are VHDL and Verilog, although in an attempt to reduce the complexity of designing in HDLs, which have been compared to the equivalent of assembly languages, there are moves to raise the abstraction level through the introduction of alternative languages.
To simplify the design of complex systems in FPGAs, there exist libraries of predefined complex functions and circuits that have been tested and optimized to speed up the design process. These predefined circuits are commonly called IP cores, and are available from FPGA vendors and third-party IP suppliers (rarely free, and typically released under proprietary licenses). Other predefined circuits are available from developer communities such as OpenCores (typically free, and released under the GPL, BSD or similar license), and other sources.
In a typical design flow, an FPGA application developer will simulate the design at multiple stages throughout the design process. Initially the RTL description in VHDL or Verilog is simulated by creating test benches to simulate the system and observe results. Then, after the synthesis engine has mapped the design to a netlist, the netlist is translated to a gate level description where simulation is repeated to confirm the synthesis proceeded without errors. Finally the design is laid out in the FPGA at which point propagation delays can be added and the simulation run again with these values back-annotated onto the netlist.
[edit] Basic Process Technology Types
- SRAM - based on static memory technology. In-system programmable and re-programmable. Requires external boot devices. CMOS.
- Antifuse - One-time programmable. CMOS.
- EPROM - Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory technology. Usually one-time programmable in production because of plastic packaging. Windowed devices can be erased with ultraviolet (UV) light. CMOS.
- EEPROM - Electrically Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory technology. Can be erased, even in plastic packages. Some, but not all, EEPROM devices can be in-system programmed. CMOS.
- Flash - Flash-erase EPROM technology. Can be erased, even in plastic packages. Some, but not all, flash devices can be in-system programmed. Usually, a flash cell is smaller than an equivalent EEPROM cell and is therefore less expensive to manufacture. CMOS.
- Fuse - One-time programmable. Bipolar.
[edit] Major Manufacturers
Xilinx and Altera are the current FPGA market leaders and long-time industry rivals. Together, they control over 80 percent of the market[20], with Xilinx alone representing over 50 percent.
Xilinx also provides free Windows and Linux design software [21], while Altera provides free Windows tools; the Solaris and Linux tools are only available via a rental scheme.[22]
Other competitors include Lattice Semiconductor (flash, SRAM), Actel (antifuse, flash-based, mixed-signal), SiliconBlue Technologies (low power), Achronix (RAM based, 1.5GHz fabric speed), and QuickLogic (handheld focused CSSP, no general purpose FPGAs!).
[edit] See also
- Gate array
- PSoC
- Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC)
- Application-specific instruction-set processor (ASIP)
- Complex programmable logic device (CPLD)
- Field-programmable analog array (FPAA)
- Software Defined Silicon (SDS)
- Fpga prototype
- VHDL: VHSIC (Very High Speed Integrated Circuit) Hardware Description Language
- Verilog: Hardware Description Language
- JHDL: Just-Another Hardware Description Language
- Reconfigurable Computing
- Configware
- MyHDL Python based HDL -- generates Verilog or VHDL
- SystemC System Description Language -- C like
[edit] References
- ^ a b FPGA Architecture for the Challenge
- ^ a b c d History of FPGAs
- ^ Peter Clarke, EE Times, "Xilinx, ASIC Vendors Talk Licensing." June 22, 2001. Retrieved February 10, 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f Funding Universe. “Xilinx, Inc.” Retrieved January 15, 2009.
- ^ Clive Maxfield, Programmable Logic DesignLine, "Xilinx unveil revolutionary 65nm FPGA architecture: the Virtex-5 family. May 15, 2006. Retrieved February 5, 2009.
- ^ Press Release, "Xilinx Co-Founder Ross Freeman Honored as 2009 National Inventors Hall of Fame Inductee for Invention of FPGA"
- ^ Google Patent Search, "Re-programmable PLA". Retrieved February 5, 2009.
- ^ Google Patent Search, "Dynamic data re-programmable PLA". Retrieved February 5, 2009.
- ^ a b Clive Maxfield, book, "The Design Warrior's Guide to FPGAs".Published by Elsevier, 2004. ISBN 0750676043, 9780750676045. Retrieved February 5, 2009
- ^ a b Dylan McGrath, EE Times, "FPGA Market to Pass $2.7 Billion by '10, In-Stat Says". May 24, 2006. Retrieved February 5, 2009.
- ^ Narinder Lall, eASIC Corporation, "FPGA Judgment Day:Rise of Second Generation Structured ASICs. March, 2008. Retrieved February 5, 2009.
- ^ a b Dylan McGrath, EE Times, "Gartner Dataquest Analyst Gives ASIC, FPGA Markets Clean Bill of Health". June 13, 2005. Retrieved February 5, 2009.
- ^ Virtex-4 Family Overview
- ^ Bob Pencek, Industrial Embedded Systems, "Reconfigurable Application-Specific Computing: How Hybrid Computer Systems using FPGAs are Changing Signal Processing". No Date. Retrieved February 5, 2009.
- ^ a b Tim Erjavec, White Paper, "Introducing the Xilinx Targeted Design Platform: Fulfilling the Programmable Imperative." February 2, 2009. Retrieved February 2, 2009
- ^ FPGA/DSP Blend Tackles Telecom Apps
- ^ Xilinx aims 65-nm FPGAs at DSP applications
- ^ http://www.eecg.toronto.edu/~vaughn/challenge/fpga_arch.html
- ^ http://www.xilinx.com/bvdocs/whitepapers/wp245.pdf
- ^ Seeking Alpha, "Altera and Xilinx Report: The Battle Continues". July 17, 2008. Retrieved February 5, 2009.
- ^ "Xilinx ISE WebPACK". http://www.xilinx.com/ise/logic_design_prod/webpack.htm.
- ^ "Quartus II Web edition software". https://www.altera.com/support/software/download/altera_design/quartus_we/dnl-quartus_we.jsp.