Beowulf
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Beowulf is an Old English heroic epic poem of unknown authorship, dating as recorded in the Nowell Codex manuscript from between the 8th[1] to the early 11th century,[2] and relates events described as having occurred in what is now Denmark and Sweden. Commonly cited as one of the most important works of Anglo-Saxon literature, Beowulf has been the subject of much scholarly study, theory, speculation, discourse, and, at 3182 lines, has been noted for its length.
In the poem, Beowulf, a hero of the Geats, battles three antagonists: Grendel, who has been attacking the mead hall in Denmark called Heorot and its inhabitants; Grendel's mother; and an unnamed dragon. The last battle takes place later in life, after returning to Geatland (modern southern Sweden), where Beowulf has become king. In the final battle, Beowulf is fatally wounded. After his death he is buried in a barrow in Geatland by his retainers.
The most common English pronunciation of "Beowulf" is IPA: /ˈbeɪəwʊlf/, but the "ēo" in Bēowulf was a diphthong, and a more authentic pronunciation would be with two syllables and the stress on the first (IPA: [ˈbeːo̯wʊɫf]).[3]
Contents |
The Beowulf manuscript
Provenance
The earliest known owner is the 16th century scholar Laurence Nowell, after whom the manuscript is named, though its official designation is Cotton Vitellius A.XV because it was one of Robert Bruce Cotton's holdings in the middle of the 17th century. Kevin Kiernan argues that Nowell most likely acquired it through William Cecil, 1st Baron Burghley in 1563, when Nowell entered Cecil’s household as a tutor to his ward, Edward de Vere, 17th Earl of Oxford.[2]
It suffered damage in the Cotton Library fire at Ashburnham House in 1731. Since then, parts of the manuscript have crumbled along with many of the letters. Rebinding efforts, though saving the manuscript from much degeneration, have nonetheless covered up other letters of the poem, causing further loss. Kevin Kiernan, Professor of English at the University of Kentucky is foremost in the computer digitization and preservation of the manuscript (the Electronic Beowulf Project[4]), using fiber optic backlighting to further reveal lost letters of the poem.
The poem is known only from a single manuscript, which is estimated to date from close to AD 1000. Kiernan has argued from an examination of the manuscript that it was the author's own working copy. He dated the work to the reign of Canute the Great.[2] The poem appears in what is today called the Beowulf manuscript or Nowell Codex (British Library MS Cotton Vitellius A.xv), along with other works. The earliest extant reference to the first foliation of the Nowell Codex was made sometime between 1628 and 1650 by Franciscus Junius (the younger). [2]. The owner of the codex before Nowell remains a mystery.[2]
The Reverend Thomas Smith and Humfrey Wanley undertook the task of cataloguing the Cotton library, in which the Nowell Codex was held. Smith’s catalogue appeared in 1696, and Humfrey’s in 1705.[5] The Beowulf manuscript itself is mentioned in name for the first time in a letter in 1700 between George Hickes, Wanley’s assistant, and Wanley. In the letter to Wanley, Hickes responds to an apparent charge against Smith, made by Wanley, that Smith had failed to mention the Beowulf script when cataloguing Cotton MS. Vitellius A. XV. Hickes replies to Wanley "I can find nothing yet of Beowulph."[5] It has been theorized that Smith failed to mention the Beowulf manuscript because of his reliance on previous catalogues or because either he had no idea how to describe it or because it was temporarily out of the codex.[5]
The two scribes
The Beowulf manuscript was transcribed from an original by two scribes: Scribe A and Scribe B, the latter of whom took over at line 1939. The handwriting of the two scribes is ill-matched.[2] The script of Scribe B is archaic.[2] Both scribes proofread their work, and Scribe B even proofread the work of Scribe A.[2] The work of Scribe B bears a striking resemblance to the work of the first scribe of the Blickling homilies, and so much so that it is believed they derive from the same scriptorium.[2] In fact, for at least a century, some scholars have maintained that the description of Grendel’s mere in Beowulf was borrowed from St.Paul’s vision of Hell in Homily 16 of the Blickling homilies.[2]
Transcription
Icelandic scholar Grímur Jónsson Thorkelin made the first transcriptions of the manuscript in 1786 and published the results in 1815, working under a historical research commission of the Danish government. He made one himself, and had another done by a professional copyist who knew no Anglo-Saxon. Since that time, the manuscript has crumbled further, and the Thorkelin transcripts remain a prized secondary source for Beowulf scholars. The recovery of at least 2000 letters can be attributed to these transcripts. Their accuracy has been called into question, however (e.g., by Chauncey Brewster Tinker in The Translations of Beowulf, a comprehensive survey of 19th century translations and editions of Beowulf), and the extent to which the manuscript was actually more readable in Thorkelin's time is unclear.[citation needed]
Authorship and date
Beowulf was written in England, but is set in Scandinavia. It has variously been dated to between the 8th and the early 11th centuries. It is an epic poem told in historical perspective; a story of epic events and of great people of a heroic past. Although its author is unknown, its themes and subject matter are generally believed to have been formed through oral tradition, the passing down of stories by scops (Old English poets) and it is considered partly historical.[citation needed]
Opinion differs as to whether the composition of the poem is contemporary with its transcription, or whether the poem was composed at an earlier time and orally transmitted for many years, and then transcribed at a later date. Lord felt strongly the manuscript represents the transcription of a performance, though likely taken at more than one sitting.[citation needed] Kiernan (1996) argues on the basis of paleographical and codicological evidence, that the poem is contemporary with the manuscript.[2] Kiernan’s reasoning has in part to do with the much-discussed political context of the poem: it has been held by most scholars, until recently,[clarification needed] that the poem was composed in the 8th century or earlier on the assumption that a poem eliciting sympathy for the Danes could not have been composed by Anglo-Saxons during the Viking Ages of the 9th and 10th centuries.[2] Kiernan argues against an 8th century provenance because this would still require that the poem be transmitted by Anglo-Saxons through the Viking Age, holds that the paleographic and codicological evidence encourages the belief that Beowulf is an 11th century composite poem, and states that Scribe A and Scribe B are the authors and that Scribe B is the more poignant of the two.[2]
The 11th century date is due to scholars who argue that, rather than transcription of the tale from the oral tradition by a literate monk, Beowulf reflects an original interpretation of the story by the poet.[1][6]
Debate over oral tradition
The question of whether Beowulf was passed down through the oral tradition prior to its present manuscript form has been the subject of much debate, and involves more than the mere matter of how it was composed. Rather, given the implications of the theory of Oral-Formulaic Composition and Oral tradition, the question concerns how the poem is to be understood, and what sorts of interpretations are legitimate.
Scholarly discussion about Beowulf in the context of the oral tradition was extremely active throughout the 1960s and 1970s. The debate might be framed starkly as follows: on the one hand, we can hypothesize a poem put together from various tales concerning the hero (the Grendel episode, the Grendel's mother story, and the firedrake narrative). These fragments would be held for many years in tradition, and learned by apprenticeship from one generation of illiterate poets to the next. The poem is composed orally and extemporaneously, and the archive of tradition on which it draws is oral, pagan, Germanic, heroic, and tribal. On the other hand, one might posit a poem which is composed by a literate scribe, who acquired literacy by way of learning Latin (and absorbing Latinate culture and ways of thinking), probably a monk and therefore profoundly Christian in outlook. On this view, the pagan references would be a sort of decorative archaizing.[7][8]
M. H. Abrams and Stephen Greenblatt assert in their introduction to Beowulf in the Norton Anthology of English Literature that, "The poet was reviving the heroic language, style, and pagan world of ancient Germanic oral poetry [...] it is now widely believed that Beowulf is the work of a single poet who was a Christian and that his poem reflects well-established Christian tradition."[9] However, scholars such as D.K. Crowne, have proposed the idea that the poem was passed down from reciter to reciter under the theory of Oral-Formulaic Composition, which hypothesizes that epic poems were (at least to some extent) improvised by whoever was reciting them. In his landmark work, The Singer of Tales, Albert Lord refers to the work of Francis P. Magoun and others, saying “the documentation is complete, thorough and accurate. This exhaustive analysis is in itself sufficient to prove that Beowulf was composed orally.”[10]
Examination of Beowulf and other Anglo-Saxon poetry for evidence of oral-formulaic composition has met with mixed response. While "themes" (inherited narrative subunits for representing familiar classes of event, such as the "arming the hero",[11] or the particularly well-studied "hero on the beach" theme[12]) do exist across Anglo-Saxon and other Germanic works, some scholars conclude that Anglo-Saxon poetry is a mix of oral-formulaic and literate patterns, arguing that the poems both were composed on a word-by-word basis and followed larger formulae and patterns.[13]
Larry Benson argued that the interpretation of Beowulf as an entirely formulaic work diminishes the ability of the reader to analyze the poem in a unified manner, and with due attention to the poet’s creativity. Instead, he proposed that other pieces of Germanic literature contain "kernels of tradition" from which Beowulf borrows and expands upon.[14][15] A few years later, Ann Watts published a book in which she argued against the imperfect application of traditional, Homeric, oral-formulaic theory to Anglo-Saxon poetry. She also argued that the two traditions are not comparable and should not be regarded as such.[16][15] Thomas Gardner agreed with Watts, in a paper published four years later which argued that the Beowulf text is of too varied a nature to be completely constructed from formulae and themes.[17][15]
John Miles Foley held, specifically with reference to the “Beowulf” debate,[18] that while comparative work was both necessary and valid, it must be conducted with a view to the particularities of a given tradition; Foley argued with a view to developments of oral traditional theory that do not assume, or depend upon, finally unverifiable assumptions about composition, and that discard the oral/literate dichotomy focused on composition in favor of a more fluid continuum of traditionality and textuality.[19] [20][21][22]
Finally, in the view of Ursula Schaefer, the question of whether the poem was "oral" or "literate" becomes something of a red herring.[23] In this model, the poem is created, and is interpretable, within both noetic horizons. Schaefer’s concept of "vocality" offers neither a compromise nor a synthesis of the views which see the poem as on the one hand Germanic, pagan, and oral and on the other Latin-derived, Christian, and literate, but, as stated by Monika Otter: "…a 'tertium quid', a modality that participates in both oral and literate culture yet also has a logic and aesthetic of its own."[24]
Dialect
The poem mixes the West Saxon and Anglian dialects of Old English, though they are predominantly West Saxon, as are other Old English poems copied at the time.[citation needed]
There is a bewildering array of linguistic forms in the Beowulf manuscript. It is this fact that leads some scholars to believe that Beowulf has endured a long and complicated transmission through all the main dialect areas.[2] The poem retains a complicated mix of the following dialectical forms: Mercian, Northumbrian, Early West Saxon, Kentish and Late West Saxon.[2] Kiernan argues that it is virtually impossible that there could have been a process of transmission which could have sustained the complicated mix of forms from dialect to dialect, from generation to generation, and from scribe to scribe.[2]
Kiernan’s argument against an early dating based on a mixture of forms is long and involved, but he concludes that the mixture of forms points to a comparatively straightforward history of the written text as:
... an 11th-century MS; an 11-th century Mercian poet using an archaic poetic dialect; and 11th-century standard literary dialect that contained early and late, cross-dialectical forms, and admitted spelling variations; and (perhaps) two 11th century scribes following slightly different spelling practices.[2]
According to this view, Beowulf can largely be seen to be the product of antiquarian interests and that it tells readers more about "an 11th century Anglo-Saxon’s notions about Denmark, and its pre-history, than it does about the age of Bede and a 7th or 8th century Anglo-Saxon’s notions about his ancestors’ homeland."[2]
Form and metre
An Old English poem such as Beowulf is very different from modern poetry. Anglo-Saxon poets typically used alliterative verse, a form of verse that uses alliteration as the principal structuring device to unify lines of poetry, as opposed to other devices such as rhyme. This is a technique in which the first half of the line (the a-verse) is linked to the second half (the b-verse) through similarity in initial sound. In addition, the two halves are divided by a caesura:
| “ | Oft Scyld Scefing \\ sceaþena þreatum | ” |
The poet has a choice of epithets or formulae to use in order to fulfill the alliteration. When speaking or reading Old English poetry, it is important to remember for alliterative purposes that many of the letters are not pronounced the same way as they are in modern English. The letter "h", for example, is always pronounced (Hroðgar: HROTH-gar), and the digraph "cg" is pronounced like "dj", as in the word "edge". Both f and s vary in pronunciation depending on their phonetic environment. Between vowels or voiced consonants, they are voiced, sounding like modern v and z, respectively. Otherwise they are unvoiced, like modern f in "fat" and s in "sat". Some letters which are no longer found in modern English, such as thorn, þ, and eth, ð — representing both pronunciations of modern English "th", as in "cloth" and "clothe" — are used extensively both in the original manuscript and in modern English editions. The voicing of these characters echoes that of f and s. Both are voiced (as in "clothe") between other voiced sounds: oðer, laþleas, suþern. Otherwise they are unvoiced (as in "cloth"): þunor, suð, soþfæst.
Kennings are also a significant technique in Beowulf. They are evocative poetic descriptions of everyday things, often created to fill the alliterative requirements of the metre. For example, a poet might call the sea the "swan-road" or the "whale-road"; a king might be called a "ring-giver." There are many kennings in Beowulf, and the device is typical of much of classic poetry in Old English, which is heavily formulaic. The poem also makes extensive use of elided metaphors.[25]
J.R.R. Tolkien argued that the poem is an elegy. [1]
Story
The main protagonist, whose name is Beowulf, a hero of the Geats, comes to the aid of Hroðgar, the king of the Danes, whose great hall, Heorot is plagued by the monster Grendel. Beowulf kills both Grendel and Grendel's mother, the latter with the help of a magical sword, which he uses when his own sword Hrunting is rendered powerless.
Later in his life, Beowulf is himself king of the Geats, and finds his realm terrorized by a dragon whose treasure had been stolen from his hoard in a burial mound. He attacked the dragon with his thegns, but they did not succeed. Beowulf decided to follow the dragon into its lair, at Earnanæs, but only his young Swedish relative Wiglaf dared join him. Beowulf finally slays the dragon, but is mortally wounded. He is buried in a barrow by the sea.
As an epic
Beowulf is considered an epic poem in that the main character is a hero who travels great distances to prove his strength at impossible odds against supernatural demons and beasts. The poet who composed Beowulf, while objective in telling the tale, nonetheless utilizes a certain style to maintain excitement and adventure within the story. An elaborate history of characters and their lineages are spoken of, as well as their interactions with each other, debts owed and repaid, and deeds of valor.[citation needed]
Historical background

The events described in the poem take place in the late 5th century, after the Anglo-Saxons had begun migration and settlement in England, and before the beginning of the 7th century, a time when the Saxons were either newly arrived or in close contact with their fellow Germanic kinsmen in Scandinavia and Northern Germany. The poem could have been transmitted in England by people of Geatish origins.[26] It has been suggested that Beowulf was first composed in the 7th century at Rendlesham in East Anglia,[27] as Sutton Hoo also shows close connections with Scandinavia, and also that the East Anglian royal dynasty, the Wuffings, were descendants of the Geatish Wulfings.[28] Others have associated this poem with the court of King Alfred, or with the court of King Canute.[2]
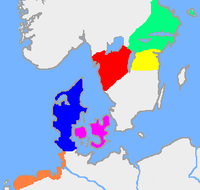
The poem deals with legends, i.e., it was composed for entertainment and does not separate between fictional elements and real historic events, such as the raid by King Hygelac into Frisia, ca. 516. Scholars generally agree that many of the personalities of Beowulf also appear in Scandinavian sources,[29] but this does not only concern people (e.g., Healfdene, Hroðgar, Halga, Hroðulf, Eadgils and Ohthere), but also clans (e.g., Scyldings, Scylfings and Wulfings) and some of the events (e.g., the Battle on the Ice of Lake Vänern). The Scandinavian sources are notably Ynglinga saga, Gesta Danorum, Hrólfr Kraki's saga and the Latin summary of the lost Skjöldunga saga. As far as Sweden is concerned, the dating of the events in the poem has been confirmed by archaeological excavations of the barrows indicated by Snorri Sturluson and by Swedish tradition as the graves of Ohthere (dated to c. 530) and his son Eadgils (dated to c. 575) in Uppland, Sweden.[30][31][32] In Denmark, recent archaeological excavations at Lejre, where Scandinavian tradition located the seat of the Scyldings, i.e., Heorot, have revealed that a hall was built in the mid-6th century, exactly the time period of Beowulf.[33] Three halls, each about 50 metres long, were found during the excavation.[33]
The majority view appears to be that people such as King Hroðgar and the Scyldings in Beowulf are based on real people in 6th century Scandinavia.[34] Like the Finnsburg Fragment and several shorter surviving poems, Beowulf has consequently been used as a source of information about Scandinavian personalities such as Eadgils and Hygelac, and about continental Germanic personalities such as Offa, king of the continental Angles.

Nineteenth-century archeological evidence may confirm elements of the Beowulf story. Eadgils was buried at Uppsala, according to Snorri Sturluson. When Eadgils' mound (to the left in the photo) was excavated in 1874, the finds supported Beowulf and the sagas. They showed that a powerful man was buried in a large barrow, c 575, on a bear skin with two dogs and rich grave offerings. These remains include a Frankish sword adorned with gold and garnets and a tafl game with Roman pawns of ivory. He was dressed in a costly suit made of Frankish cloth with golden threads, and he wore a belt with a costly buckle. There were four cameos from the Middle East which were probably part of a casket. This would have been a burial fitting a king who was famous for his wealth in Old Norse sources. Ongenþeow's barrow (to the right in the photo) has not been excavated.[30][31]
Structured by battles
Jane Chance (Professor of English, Rice University) in her 1980 article "The Structural Unity of Beowulf: The Problem of Grendel's Mother" argued that there are two standard interpretations of the poem: one view which suggests a two-part structure (i.e., the poem is divided between Beowulf's battles with Grendel and with the dragon) and the other, a three-part structure (this interpretation argues that Beowulf's battle with Grendel's mother is structurally separate from his battle with Grendel).[35] Chance stated that, "this view of the structure as two-part has generally prevailed since its inception in J. R. R. Tolkien's Beowulf: The Monsters and the Critics in Proceedings of the British Academy 22 (1936)."[35] In contrast, she argued that the three-part structure has become "increasingly popular."[35]
First battle: Grendel
Beowulf begins with the story of King Hroðgar, who built the great hall Heorot for his people. In it he, his wife Wealhþeow, and his warriors spend their time singing and celebrating, until Grendel, an outcast from society who is angered by the singing, attacks the hall and kills and devours many of Hroðgar's warriors while they sleep. But Grendel dares not touch the throne of Hroðgar, because he is described as protected by a powerful god. Hroðgar and his people, helpless against Grendel's attacks, abandon Heorot.
Beowulf, a young warrior from Geatland, hears of Hroðgar's troubles and with his king's permission leaves his homeland to help Hroðgar.
Beowulf and his men spend the night in Heorot. After they fall asleep, Grendel enters the hall and attacks, devouring one of Beowulf's men. Beowulf, who bears no weapon as this would be an unfair advantage over the unarmed beast, has been feigning sleep, and leaps up and clenches Grendel's hand. The two battle until it seems as though the hall might collapse. Beowulf's retainers draw their swords and rush to his aid, but their blades do not pierce Grendel's skin because he is magically immune to human weapons. Finally, Beowulf tears Grendel's arm from his body at the shoulder and Grendel runs to his home in the marshes to die.
Second battle: Grendel's mother
The next night, after celebrating Grendel's death, Hroðgar and his men sleep in Heorot. Grendel's mother appears, however, and attacks the hall. She kills Hroðgar's most trusted warrior, Æschere, in revenge for Grendel's death.
Hroðgar, Beowulf, and their men track Grendel's mother to her lair under an eerie lake. Beowulf prepares himself for battle; he is presented with a sword, Hrunting, by a warrior called Unferth. After stipulating a number of conditions (upon his death) to Hroðgar (including the taking in of his kinsmen, and the inheritance by Unferth of Beowulf's estate), Beowulf dives into the lake. There, he is swiftly detected and attacked by Grendel's mother. Unable to harm Beowulf through his armor, Grendel's mother drags him to the bottom of the lake. There, in a cavern containing Grendel's body and the remains of many men that the two have killed, Grendel's mother and Beowulf engage in fierce combat.
Grendel's mother at first prevails, after Beowulf, finding that the sword (Hrunting) given to him by Unferð cannot harm his foe, discards it in fury. Again, Beowulf is saved from the effects of his opponent's attack by his armor and, grasping a mighty sword from Grendel's mother's armory (which, the poem tells us, no other man could have hefted in battle), Beowulf beheads her. Travelling further into the lair, Beowulf discovers Grendel's corpse; he severs the head. Beowulf then returns to the surface and to his men at the "ninth hour" (l. 1600, "nōn", about 3pm).[36] He returns to Heorot, where Hroðgar gives Beowulf many gifts, including the sword Nægling, his family's heirloom.
Third battle: The dragon
Beowulf returns home and eventually becomes king of his own people. One day, late in Beowulf's life, a slave steals a golden cup from the lair of an unnamed dragon (sometimes referred to as Sua) at Earnaness. When the dragon sees that the cup has been stolen, it leaves its cave in a rage, burning up everything in sight. Beowulf and his warriors come to fight the dragon, but only one of the warriors, a brave young man named Wiglaf, stays to help Beowulf, because the rest are too afraid. Beowulf kills the dragon with Wiglaf's help, but Beowulf dies from the wounds he has received.
After he is cremated, Beowulf is buried in Geatland on a cliff overlooking the sea, where sailors are able to see his barrow. The dragon's treasure is buried with him, rather than distributed to his people, as was Beowulf's wish, because of the curse associated with the hoard, and also accordance with Germanic and Scandinavian burial practices.
Structured by funerals
It is widely accepted that there are three funerals in Beowulf. [37] These funerals help to outline changes in the poem’s story as well as the audiences’ views on earthly possessions, battle and glory. The funerals are also paired with the three battles described above. [37] The three funerals share similarities regarding the offerings for the dead and the change in theme through the description of each funeral. Gale Owen-Crocker (Professor of Anglo-Saxon, University of Manchester) in The Four Funerals in Beowulf (2000) argues that a passage in the poem, commonly known as “The Lay of the Last Survivor” (lines 2247-66), is an additional funeral.[37] The funerals are themselves involved in the ritual of hoarding: the deposition of sacrificial objects with both religious and socio-economic functions.[38] .
Scyld Scefing (lines 1–52)
The first funeral in the poem is of Scyld Scefing (translated in some versions as "Shield Shiefson") the king of the Danes. [39] The first fitt helps the poet illustrate the settings of the poem by introducing Hrothgar’s lineage. The funeral leads to the introduction of the hero, Beowulf and his confrontation with the first monster, Grendel. This passage begins by describing Scyld’s glory as a “scourge of many tribes, a wrecker of mead-benches.” [39] Scyld’s glory and importance is shown by the prestigious death he obtains through his service as the king of the Danes. [37] His importance is proven once more by the grand funeral given to him by his people: his funeral at sea with many weapons and treasures shows he was a great soldier and an even greater leader to his people. [37] The poet introduces the concepts of a heroic society through Scyld. The possessions buried with the king are elaborately described to emphasize the importance of such items. [37] The importance of these earthly possessions are then used to establish this dead king’s greatness in respect to the treasure. [37] Scyld’s funeral helps the poet to elaborate on the glory of battle in a heroic society and how earthly possessions help define a person‘s importance. This funeral also helps the poet to develop the plot to lead into the confrontation between the protagonist, Beowulf, and the main antagonist, Grendel.
Hildeburg’s kin (lines 1107–24)
The second funeral in the poem is that of Hildeburg’s kin and is the second fitt of this poem. [39] The funeral is sung in Heorot to celebrate Beowulf's victory over Grendel. It also signifies the beginning of the protagonist’s battle against Grendel's mother. The death of Hildeburg’s brother, son(s), and husband are the results of battle. The battle also leads to Scyld’s death and mirrors the use of funeral offerings for the dead with extravagant possessions. [39] As with the Dane’s king, Hildeburg’s relatives are buried with their armor and gold to signify their importance. [37] However, the relatives’ funeral differs from the first as it was a cremation ceremony. Furthermore, the poet focuses on the strong emotions of those who died while in battle. [39] The gory details of “heads melt[ing], gashes [springing] open…and the blood [springing] out from the body’s wounds” [39] describes war as a horrifying event instead of one of glory. [37] Although the poet maintains the theme of possessions as important even in death, the glory of battle is challenged by the vicious nature of war. The second funeral displays different concepts from the first and a change of direction in the plot that leads to Beowulf's fight against Grendel's Mother.
Lay of the Last Survivor (lines 2247–66)
"The Lay of the Last Survivor" is arguably an addition to the other three funerals in Beowulf because of the striking similarities that define the importance of the other burials.[37] The parallels that identify this passage with the other three funerals are the similar burial customs, changes in setting and plot, and changes of theme. The lament appears to be a funeral because of the Last Survivor’s description of burial offerings that are also found in the funerals of Scyld Scefing, Hildeburg’s kin, and Beowulf.[37] The Last Survivor describes the many treasures left for the dead such as the weapons, armour and gold cups [39] that have strong parallels to Scyld’s “well furbished ship…,bladed weapons and coats of mail,”[39] Hildeburg’s Kin’s “blood-plastered coats of mail [and] boar-shaped helmets”[39] and Beowulf's treasure from the dragon.[39]
An additional argument towards viewing this passage as a funeral lies in the statement, “tumbling hawk [and] swift horse”[39] mentioned in the poem. This is an animal offering which was a burial custom during the era of the poem.[37] Moreover this passage, like the other funerals, signifies changes in setting and plot. [37] One can also argue that it is the 3rd part to the poem since it describes the settings during the time lapse for the final battle between Beowulf and the Dragon. The poet also describes death in battle as horrifying, a concept continued from the second part of the poem, through the Last Survivor’s eyes.[37]
Beowulf’s funeral (lines 3137–82)
The fourth and final funeral of the poem is Beowulf's funeral. After the final battle against the dragon, Beowulf receives fatal wounds and dies. The greatness of Beowulf's life is demonstrated through this funeral, particularly through the many offerings of his people. [37] In addition, the immense hoard of the dragon is buried with the hero. The poet also bestows on Beowulf more significance than the others through his description of the cremation. [37] “Weohstan’s son(pause) commanded it be announced to many men(pause) that they should fetch from afar wood for the pyre.” [39] for their leader’s funeral. The dragon’s remains are thrown into the sea, a parallel to Scyld’s burial in his ship. Beowulf's funeral is the fourth fitt of the poem and acts as an epilogue for the hero who is the, “most gracious and fair-minded, kindest to his people and keenest to win fame.” [39]
Interpretation and criticism
In historical terms, the poem's characters would have been Norse pagans (the historical events of the poem took place before the Christianization of Scandinavia), yet the poem was recorded by Christian Anglo-Saxons who had largely converted from their native Anglo-Saxon paganism around the 7th century - both Anglo-Saxon paganism and Norse paganism share a common origin as both are forms of Germanic paganism. Beowulf thus depicts a Germanic warrior society, in which the relationship between the lord of the region and those who served under him was of paramount importance. M. H. Abrams and Stephen Greenblatt note that:
Although Hrothgar and Beowulf are portrayed as morally upright and enlightened Pagans, they fully espouse and frequently affirm the values of Germanic heroic poetry. In the poetry depicting warrior society, the most important of human relationships was that which existed between the warrior - the thane - and his lord, a relationship based less on subordination of one man's will to another's than on mutual trust and respect. When a warrior vowed loyalty to his lord, he became not so much his servant as his voluntary companion, one who would take pride in defending him and fighting in his wars. In return, the lord was expected to take care of his thanes and to reward them richly for their valor.[40]
This society was strongly defined in terms of kinship; if someone was killed, it was the duty of surviving kin to exact revenge either with their own lives or through weregild, a payment of reparation. [40]
Stanley B. Greenfield (Professor of English, University of Oregon) has suggested that references to the human body throughout Beowulf emphasize the relative position of thanes to their lord. He argues that the term “shoulder-companion” could refer to both a physical arm as well as a thane (Aeschere) who was very valuable to his lord (Hrothgar). With Aeschere's death, Hrothgar turns to Beowulf as his new "arm." [41] In addition Greenfield argues, the foot is used for the opposite effect, only appearing four times in the poem. It is used in conjunction with Unferth (a man described by Beowulf as weak, traitorous, and cowardly). Greenfield notes that Unferth is described as “at the king’s feet” (line 499). Unferth is also a member of the foot troops, who, throughout the story, do nothing and “generally serve as backdrops for more heroic action.” [42]
At the same time, Richard North (Professor of English, University College London) argues that the Beowulf poet interpreted "Danish myths in Christian form" (as the poem would have served as a form of entertainment for a Christian audience), and states: "As yet we are no closer to finding out why the first audience of Beowulf liked to hear stories about people routinely classified as damned. This question is pressing, given [...] that Anglo-Saxons saw the Danes as 'heathens' rather than as foreigners."[43] Grendel's mother and Grendel are described as descendants of Cain, a fact which some scholars link to The Cain Tradition. [44]
Allen Cabaniss argues that there are several similarities between Beowulf and the Bible. First he argues, for similarities between Beowulf and Jesus: both are brave and selfless in overcoming the evils that oppose them, and both are kings that die to save their people. [45] Secondly, he argues for a similarity between part of The Book of Revelation (“shall have their part in the lake which burneth with fire and brimstone: which is the second death." Revelation 21:8) and the home of Grendel and Grendel's mother. [46] Third, he compares the words of Jesus in the Gospel of Luke (when he pardons those who call for his crucifixion) to the portion of the poem when (before plunging into the perilous lake) Beowulf forgives his enemy, Unferth. [46]
Scholars disagree, however, as to the meaning and nature of the poem: is it a Christian work set in a Germanic pagan context? The questions suggests that the conversion from the Germanic pagan beliefs to Christian ones was a very slow and gradual process over several centuries, and it remains unclear the ultimate nature of the poem's message in respect to religious belief at the time it was written. Robert F. Yeager (Professor of literature, University of North Carolina at Asheville) notes the facts that form the basis for these questions:
That the scribes of Cotton Vitellius A.XV were Christian is beyond doubt; and it is equally certain that Beowulf was composed in a Christianized England, since conversion took place in the sixth and seventh centuries. Yet the only Biblical references in Beowulf are to the Old Testament, and Christ is never mentioned. The poem is set in pagan times, and none of the characters is demonstrably Christian. In fact, when we are told what anyone in the poem believes, we learn that they are pagans. Beowulf’s own beliefs are not expressed explicitly. He offers eloquent prayers to a higher power, addressing himself to the “Father Almighty” or the “Wielder of All.” Were those the prayers of a pagan who used phrases the Christians subsequently appropriated? Or, did the poem’s author intend to see Beowulf as a Christian Ur-hero, symbolically refulgent with Christian virtues?[47]
Translations and glossaries
In 1805 Sharon Turner translated selected verses into English. [48] This was followed in 1814 by John Josias Conybeare who published an edition "in English paraphrase and Latin verse translation." [48] In 1815, Grímur Jónsson Thorkelin published the first complete edition in Latin. [48] Nikolaj Frederik Severin Grundtvig reviewed this edition in 1815 and created the first complete verse translation in Danish in 1820. [48] In 1837, J. M. Kemble created an important literal translation in English. [48] In 1895, William Morris & A. J. Wyatt's published the ninth English translation. [48]
During the early 20th century, Frederick Klaeber's Beowulf and The Fight at Finnsburg (which included the poem in Old English, an extensive glossary of Old English terms, and general background information) became the "central source used by graduate students for the study of the poem and by scholars and teachers as the basis of their translations."[49] In 1999, Nobel Laureate Seamus Heaney's edition of Beowulf was published by Faber & Faber and includes "Northern Irish diction and turns of phrase." In 2000, W.W. Norton added it to the Norton Anthology of English Literature. [48]

Artistic adaptations
The Beowulf epic has been adapted in a number of films, Beowulf & Grendel (2005), Grendel (2007), Beowulf (2007), and Beowulf: Prince of the Geats (2008), besides numerous references in popular culture more loosely connected with the poem.
J. R. R. Tolkien's The Hobbit adapts some features of the dragon episode in Beowulf. John Gardner in his 1971 Grendel retells the story from Grendel's point of view.
Bibliography
Dictionaries
- Cameron, Angus, et al. Dictionary of Old English (Microfiche). Toronto: Published for the Dictionary of Old English Project Centre for Medieval Studies University of Toronto by the Pontifical Institute of Medieval Studies, 1986/1994.
Text
Hypertext editions:
- Breeden, David. The Adventures of Beowulf: an Adaptation from the Old English.
- Klaeber, Frederick, ed. Beowulf and the Fight at Finnsburg. Third ed. Boston: Heath, 1950.
- Lancashire, Ian (for the Department of English, University of Toronto). Beowulf: Representative Poetry Online.
- McMaster University. Beowulf in hypertext.
- Northern Virginia Community College. Comparison of various English translations.
- Ringler, Dick (University of Wisconsin-Madison). Beowulf: A New Translation For Oral Delivery.
- Slade, Benjamin. Beowulf on Steorarume (Beowulf in Cyberspace).
- University of Virginia. Audio reading of Beowulf in Old English.
Modern English translations:
- Alexander, Michael. Beowulf : A Verse Translation. Penguin Classics;. Rev. ed. London: New York, 2003.
- Anderson, Sarah M., Alan Sullivan, and Timothy Murphy. Beowulf. A Longman Cultural Edition;. New York: Pearson/Longman, 2004.
- Crossley-Holland, Kevin; Mitchell, Bruce. Beowulf: A New Translation. London: Macmillan, 1968
- Donaldson, E. Talbot, and Nicholas Howe. Beowulf : A Prose Translation : Backgrounds and Contexts, Criticism. A Norton Critical Edition. 2nd ed. New York: Norton, 2002.
- Garmonsway, George Norman, et al. Beowulf and Its Analogues. (Revised 1980). ed. London: Dent, 1980.
- Gummere, Frances. 'Beowulf'. St Petersburg, Florida:Red and Black Publishers, 2007. ISBN 978-0-979-1813-1-3.
- Heaney, Seamus Beowulf: A New Verse Translation. New York: W.W. Norton, 2001. ISBN 0-393-32097-9
- Lehmann, Ruth. Beowulf : An Imitative Translation. 1st ed. Austin: University of Texas Press, 1988.
- R. M. Liuzza. Beowulf: A New Verse Translation. Orchard Park, NY: Broadview Press, 2000.
- Osborn, Marijane. Annotated List of Beowulf Translations.
- Raffel, Burton. Beowulf. New York: Signet Classic, 1999.
- Ringler, Dick. Beowulf: A New Translation For Oral Delivery. Hackett Publishing Company, Inc., 2007. ISBN 978-0-87220-893-3
- Swanton, Michael (ed.). Beowulf (Manchester Medieval Studies). Manchester: University, 1997.
- Szobody, Michelle L. & Justin Gerard (Illustrator) Beowulf, Book I: Grendel the Ghastly. Greenville, SC: Portland Studios, 2007. ISBN-13 9780979718304
Old English and modern English:
- I. Chickering, Howell D. Beowulf: a dual-language edition.New York: Anchor books ed., 1977,1989 ISBN 0-385-06213-3
- Heaney, Seamus Beowulf: A New Verse Translation. New York: W.W. Norton, 2001. ISBN 0-393-32097-9
Old English with glossaries:
- Alexander, Michael. Beowulf: A Glossed Text. Second ed. Penguin: London, 2000.
- Jack, George. Beowulf : A Student Edition. Oxford University Press: New York, 1997.
- Klaeber, Frederick, ed. Beowulf and the Fight at Finnsburg. Third ed. Boston: Heath, 1950.
- Mitchell, Bruce, et al. Beowulf: An Edition with Relevant Shorter Texts. Oxford, UK: Malden Ma., 1998.
- Porter, John. Beowulf: text and translation. Anglo-Saxon Books, 1991.
- Rebsamen, Frederick R. Beowulf : A Verse Translation. 1st ed. New York, NY: Icon Editions, 1991.
- Wrenn, C.L., ed. Beowulf with the Finnesburg Fragment. 3rd ed. London: Harrap, 1973.
Audio
- Ringler, Dick & Norman Gilliland. Beowulf: The Complete Story—A Drama. Madison, WI: NEMO Productions, 2006. ISBN ISBN 0-9715093-2-8
- P. Baker. Readings from Beowulf. In Old English.
Scholarship
- M.H. Abrams and Stephen Greenblatt. Norton Anthology of English Literature: The Middle Ages (Vol 1), Beowulf. New York: W.W. Norton, 2000. 29-32.
- Alfano, Christine. "The Issue of Feminine Monstrosity: A Re-evaluation of Grendel's Mother." Comitatus 23 (1992): 1-16.
- Battaglia, Frank. "The Germanic Earth Goddess in Beowulf." Mankind Quarterly 31.4 (Summer 1991): 415-46.
- Chadwick, Nora K. "The Monsters and Beowulf." The Anglo-Saxons: Studies in Some Aspects of Their History. Ed. Peter ed Clemoes. London: Bowes & Bowes, 1959. 171-203.
- Chance, Jane. "The Structural Unity of Beowulf: The Problem of Grendel's Mother." New Readings on Women in Old English Literature. Eds. Helen Damico and Alexandra Hennessey Olsen. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 1990. 248-61.
- Creed, Robert P. Reconstructing the Rhythm of Beowulf.
- Damico, Helen. Beowulf's Wealhtheow and the Valkyrie Tradition. Madison, Wis.: University of Wisconsin Press, 1984.
- Drout, Michael. Beowulf and the Critics.
- Gillam, Doreen M. "The Use of the Term 'Aeglaeca' in Beowulf at Lines 893 and 2592." Studia Germanica Gandensia 3 (1961): 145-69.
- Grigsby, John. Beowulf & Grendel: The Truth Behind England's Oldest Legend. Watkins Publishing. London, 2005. (2006 reprint edition distributed by Sterling Publishing).
- The Heroic Age, Issue 5. "Anthropological and Cultural Approaches to Beowulf." Summer/Autumn 2001.
- Horner, Shari. The Discourse of Enclosure: Representing Women in Old English Literature. New York: SUNY Press, 2001.
- Nicholson, Lewis E. (Ed.). An Anthology of Beowulf Criticism. (1963), Notre Dame: University of Notre Dame Press. ISBN 0-268-00006-9
- North, Richard. Origins of Beowulf: From Vergil to Wiglaf. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2006.
- Orchard, Andy. A Critical Companion to Beowulf. Cambridge: D.S. Brewer, 2003.
- ---. Pride and Prodigies: Studies in the Monsters of the Beowulf-Manuscript. Toronto: University of Toronto Press, 2003.
- Owen-Crocker, Gale (2000). The Four Funerals in Beowulf: And the Structure of the Poem. New York: Manchester University Press.
- Stanley, E.G. "Did Beowulf Commit 'Feaxfeng' against Grendel's Mother." Notes and Queries 23 (1976): 339-40.
- Tolkien, J.R.R.. Beowulf: The Monsters and the Critics (1983). London: George Allen & Unwin. ISBN 0-0480-9019-0
- Trask, Richard M. "Preface to the Poems: Beowulf and Judith: Epic Companions." Beowulf and Judith : Two Heroes. Lanham, Md.: University Press of America, 1998. 11-14.
References
- ^ a b c Tolkien, J.R.R. (1958). Beowulf: the Monsters and the Critics. London: Oxford University Press. p. 127.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Kiernan, Kevin (1996). Beowulf and the Beowulf manuscript. Ann Arbor, MI: University of Michigan. footnote 69 pg 162, 90, 258, 257,171, xix-xx, xix, 3 , 4 , 277-278 , 23-34, 29, 29, 60, 62, footnote 69 162.
- ^ Mitchell, Bruce; Fred C. Robinson (1986). "Diphthongs". A Guide to Old English. Blackwell. p. 14-15.
- ^ "Electronic Beowulf". The University of Kentucky. http://www.uky.edu/~kiernan/eBeowulf/guide.htm. Retrieved on 2007-11-06.
- ^ a b c Joy, Eileen A (2005). "Thomas Smith, Humfrey Wanley, and the Little-Known Country of the Cotton Library" (PDF). Electronic British Library Journal. 2, 24, 24, footnote 24. http://www.bl.uk/eblj/2005articles/pdf/article1.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-03-03.
- ^ Heaney, Seamus (2000). Beowulf: A New Verse Translation. New York: Norton.
- ^ "The Christian Coloring of Beowulf" (F. A. Blackburn, PMLA 12 (1897), 210-17
- ^ "The Pagan Coloring of Beowulf" (Larry D. Benson, in Old English Poetry: fifteen essays. R.P. Creed, ed. Providence (Rhode Island): Brown University Press, 1967: 193-213).
- ^ Abrams, M.H.; Greenblatt, Stephen (2000), The Norton Anthology of English Literature: The Middle Ages (Vol 1), Beowulf, New York: W.W. Norton, pp. 29
- ^ Lord, Albert. The Singer of Tales. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1960. p. 198
- ^ Zumthor, Paul. “The Text and the Voice.” Transl. Marilyn C. Englehardt. New Literary History 16(1984):67-92
- ^ Crowne, D.K. 'The Hero on the Beach: An Example of Composition by Theme in Anglo-Saxon Poetry', Neuphilologische Mitteilungen, 61 (1960)
- ^ Benson, Larry D. "The Literary Character of Anglo-Saxon Formulaic Poetry" Publications of the Modern Language Association 81 (1966):, 334-41
- ^ Benson, Larry. "The Originality of Beowulf" The Interpretation of Narrative. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1970. pp 1-44
- ^ a b c Foley, John M. Oral-Formulaic Theory and Research: An Introduction and Annotated Bibliography. New York: Garland Publishing, Inc., 1985. p.126
- ^ Watts, Ann C. The Lyre and the Harp: A Comparative Reconsideration of Oral Tradition in Homer and Old English Epic Poetry. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1969. p. 124, et al.
- ^ Gardner, Thomas. "How Free Was the Beowulf Poet?" Modern Philology. 1973. p. 111-27.
- ^ Foley, John Miles. The Theory of Oral Composition: History and Methodology. Bloomington: IUP, 1991, pp. 109 f.
- ^ Bäuml, Franz H. "Varieties and Consequences of Medieval Literacy and Illiteracy", in Speculum, Vol. 55, No. 2 (1980), pp.243-244.
- ^ Havelock, Eric Alfred. Preface to Plato. Vol. 1 A History of the Greek Mind, Belknap Press of Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA: 1963.
- ^ Curschmann, Michael. The Concept of the Formula as an Impediment to Our Understanding of Medieval Oral Poetry” Medievalia et Humanistica, n.s. 8(1977):63-76
- ^ Zumthor, Paul. “The Text and the Voice.” Transl. Marilyn C. Englehardt. New Literary History 16(1984):67-92
- ^ Schaefer, Ursula. Vokalitat: Altenglische Dichtung zwischen Mundlichkeit und Schriftlichkeit, ScriptOralia 39 (Tubingen: Gunter Narr Verlag, 1992
- ^ http://serials.infomotions.com/bmcr/bmcr-9404-otter-vokalitaet.txt
- ^ "Beowulf." Norton Anthology of English Literature. ed. Stephen Greenblatt. 8th Edition. pp 29-33
- ^ The Norton Anthology of English Literature. W. W. Norton and Co., Ltd. 1986. p. 19. ISBN 0393954722.
- ^ Beowulf: a Dual-Language Edition. New York, NY: Doubleday. 1977.
- ^ Newton, Sam (1993). The Origins of Beowulf and the Pre-Viking Kingdom of East Anglia. Woodbridge, Suffolk, England: Boydell & Brewer Ltd.. ISBN 0 85991 361 9.
- ^ Shippey, T. A. (Summer 2001). "Wicked Queens and Cousin Strategies in Beowulf and Elsewhere, Notes and Bibliography". In the Heroic Age (5).
- ^ a b Klingmark, Elisabeth (in Swedish). Gamla Uppsala, Svenska kulturminnen 59. Riksantikvarieämbetet.
- ^ a b Nerman, Birger (1925). Det svenska rikets uppkomst. Stockholm.
- ^ "Ottar's Mound". Swedish National Heritage Board. http://www.raa.se/cms/extern/en/places_to_visit/our_historical_sites/ottar_s_mound.html. Retrieved on 2007-10-01.
- ^ a b Niles, John D. (October 2006). "Beowulf's Great Hall". History Today 56 (10): 40–44. http://www.historytoday.com/MainArticle.aspx?m=31861&amid=30234433.
- ^ Anderson, Carl Edlund (1999). "Formation and Resolution of Ideological Contrast in the Early History of Scandinavia (Ph.D. thesis)" (PDF). University of Cambridge, Department of Anglo-Saxon, Norse & Celtic (Faculty of English). p. 115. http://www.carlaz.com/phd/cea_phd_chap4.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-10-01.
- ^ a b c Chance, Jane (1990). Helen Damico and Alexandra Hennessey Olsen. ed. The Structural Unity of Beowulf: The Problem of Grendel's Mother. Bloomington, Indiana: Indiana University Press. pp. 248.
- ^ Jack, George. Beowulf: A Student Edition. Oxford University Press, USA. p. 123.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Owen-Crocker, Gale (2000). The Four Funerals in Beowulf: And the Structure of the Poem. New York: Manchester University Press. p. 1-5, 23, 31, 34, 44, 52, 65-69, 84-86, 104-105.
- ^ Tarzia, Wade (1989). 'The Hoarding Ritual in Germanic Epic Tradition.'. The Journal of Folklore Research 26:2. p. 99-121.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Greenblatt, Stephen; M.H. Abrahams (2006). The Norton Anthology of English Literature: Volume A: Middle Ages. New York: Norton & Company. p. 34-35, 57-58, 81, 99-100.
- ^ a b Abrams, M.H.; Greenblatt, Stephen (2000), The Norton Anthology of English Literature: The Middle Ages (Vol 1), Beowulf, New York: W.W. Norton, pp. 30
- ^ Greenfield, Stanley. (1989) Hero and Exile. London: Hambleton Press, 59
- ^ Greenfield, Stanley. (1989) Hero and Exile. London: Hambleton Press, 61
- ^ Richard North, "The King's Soul: Danish Mythology in Beowulf," in the Origins of Beowulf: From Vergil to Wiglaf, (New York: Oxford University Press, 2006), 195
- ^ Williams, David:"Cain and Beowulf: A Study in Secular Allegory. University of Toronto Press, 1982
- ^ Cabaniss, A: "Liturgy and Literature", page 101. University of Alabama Press, 1970
- ^ a b Cabaniss, A: "Liturgy and Literature", page 102. University of Alabama Press, 1970
- ^ Yeager, Robert F.. "Why Read Beowulf?". National Endowement For The Humanities. http://www.neh.gov/news/humanities/1999-03/yeager.html. Retrieved on 2007-10-02.
- ^ a b c d e f g Osborn, Marijane, Annotated List of Beowulf Translations, http://www.asu.edu/clas/acmrs/web_pages/online_resources/online_resources_annotated_beowulf_bib.html, retrieved on 2007-11-21
- ^ "Bloomfield, Josephine. Benevolent Authoritarianism in Klaeber's Beowulf: An Editorial Translation of Kingship" (PDF). Modern Language Quarterly 60 (2). June 1999. http://muse.jhu.edu/journals/modern_language_quarterly/v060/60.2bloomfield.pdf.
- ^ Ewald, Gustav (1950). "Är Skalunda hög kung Beowulfs grav?" (in Swedish). Västgöta-Bygden 1: 335–336.(Om *Birger Nermans och °Carl Otto Fasts idéer angående hednatima kungars gravplats.)
External links
| Wikiquote has a collection of quotations related to: Beowulf |
- Comparison of various English translations
- Resources for the Study of Beowulf - University of Nevada
- Beowulf resources
- Beowulf manuscript in The British Library's Online Gallery
- Beowulf Full text and audio.
- Full summary of Beowulf
- Simple Plot Summary of Beowulf - At Literapedia
- Beowulf at Project Gutenberg — 1910 Translation by Francis B. Gummere
|
||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






