ajedrez color colour confusing cool couleur formagazine fun gobelins graphics illusion ilusion interesting kurios luz optica optical optical+illusions optical-illusion perception psychology visual wtf
Same color illusion
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
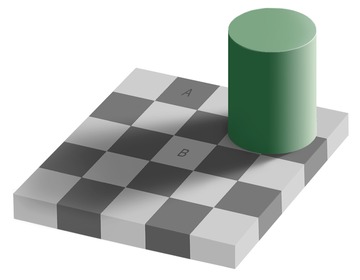
The same color illusion—also known as Adelson's checker shadow illusion, checker shadow illusion and checker shadow—is an optical illusion published by Edward H. Adelson, Professor of Vision Science at MIT in 1995.[1] The squares A and B on the illusion are the same color (or shade), although they seem to be different. This can be proven by copying the image into an art program and sampling the color of A and then of B, which will show that they are in fact the same color.
" When interpreted as a 3-dimensional scene, our visual system immediately estimates a lighting vector and uses this to judge the property of the material."[2]
[edit] See also
[edit] References
- ^ Adelson, Edward H. (2005). "Checkershadow Illusion". http://web.mit.edu/persci/people/adelson/checkershadow_illusion.html. Retrieved on 2007-04-21.
- ^ "michaelbach.de". http://www.michaelbach.de/ot/lum_adelson_check_shadow/. Retrieved on 2006-06-10.