Maxima (software)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
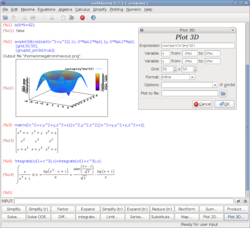 wxMaxima screenshot |
|
| Developed by | Macsyma group at Project MAC and volunteer contributors |
|---|---|
| Latest release | 5.17.1 / 2008-12-15 |
| Written in | Common Lisp |
| OS | Cross-platform |
| Type | Mathematical software |
| License | GPL |
| Website | maxima.sourceforge.net |
- For other meanings of Maxima, see Maxima
Maxima is a complete computer algebra system based on a 1982 version of Macsyma. It is written in Common Lisp and runs on all POSIX platforms such as Mac OS X, Unix, BSD, and Linux as well as under Microsoft Windows. It is free software released under the terms of the GNU General Public License.
Contents |
[edit] History
Maxima is based on a 1982 version of Macsyma, which was developed at MIT with funding from the United States Department of Energy and other government agencies. A version of Macsyma was maintained by Bill Schelter from 1982 until his death in 2001. In 1998 Schelter obtained permission from the Department of Energy to release his version under the GPL. That version, now called Maxima, is maintained by an independent group of users and developers. Maxima does not include any of the many modifications and enhancements made to the commercial version of Macsyma during 1982–1999. Though the core functionality remains similar, code depending on these enhancements may not work on Maxima, and bugs which were fixed in Macsyma may still be present in Maxima, and vice-versa.
[edit] Features
Maxima includes a complete programming language with ALGOL-like syntax but Lisp-like semantics. It is written in Common Lisp, and can be accessed programmatically and extended, as the underlying Lisp can be called from Maxima. It uses Gnuplot for drawing.
[edit] Numeric calculations
Maxima is a full-featured CAS (computer algebra system) that specializes in symbolic operations but it also offers numerical capabilities such as arbitrary-precision arithmetic: integers and rational numbers which can grow to sizes limited only by machine memory, and floating point numbers whose precision can be set arbitrarily large ("bfloats").
For calculations which use floating point and arrays heavily, Maxima offers the possibility of generating code in other programming languages (notably Fortran) which may execute more efficiently.
Maxima is a general-purpose system, and special-case calculations such as factorization of large numbers, manipulation of extremely large polynomials, etc. are sometimes better done in specialized systems.
[edit] Interfaces
Various graphical user interfaces are available for Maxima. wxMaxima is a cross-platform GUI based on wxWidgets. The GNU TeXmacs and LyX mathematical editor programs can be used to provide an interactive GUI for Maxima, as can Sage. Other options include the Imaxima front end as well as an Emacs interaction mode.
[edit] See also
| Wikibooks has a book on the topic of |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: category:Created with Maxima (software) |
[edit] External links
- The official Maxima website
- wxMaxima
- irc.freenode.net port 6667 channel#maxima
- Maxima Beginner's FAQ
- Maxima 10 Minute Tutorial
- The HTML Maxima Manual in English
- dynamicalsystems: collection of several Maxima programs to create various graphical representations of discrete dynamical systems and fractals
- Short list of useful examples
- comparison of Maxima vs. MuPAD, includes a very long list of examples
- Imaxima, Emacs front end that includes typesetting.
- (Japanese) Various plotting examples
- A Maxima-Gnuplot interface- drawing examples
- (French) The SYM package for Maxima
- (Portuguese) Dynamical Systems textbook at the University of Porto (Portugal), with examples in Maxima
- DragMath, an open-source online equation editor that can export Maxima, and other formats.
- Tutorial A lot of tips und tricks using maxima.
|
||||||||||||||

