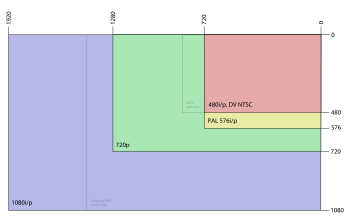
It is important to realize that the use of the word "resolution" in this context is misleading and inaccurate. The sizes given are pixel dimensions, and do not imply anything about the resolution of the display, which would be expressed in PPI (pixels per inch) or PPCM (pixels per centimeter). This explains why larger pixel dimensions do not necessarily imply that the final image will be physically larger; indeed, fitting more pixels onto the same display will produce an image the same physical size but with a higher image density and hence text and images will appear smaller.
Computer and handheld screens
| Standard |
Width |
|
Height |
DAR |
DAR |
Pixels |
| Apple II HiRes (6 color) and Apple IIe Double HiRes (16 color), grouping subpixels |
140 |
× |
192 |
35:48 |
0.729 |
26,880 |
| Nintendo Game Boy, Game Boy Color |
160 |
× |
144 |
10:9 |
1.111 |
23,040 |
| Palm (PDA) LoRES |
160 |
× |
160 |
1:1 |
1.0 |
25,600 |
| VIC-II multicolor, IBM PCjr 16-color |
160 |
× |
200 |
4:5 |
0.8 |
32,000 |
| Acorn BBC 20 column modes |
160 |
× |
256 |
5:8 |
0.625 |
40,960 |
| Nokia Series 60 smartphones (Nokia 7650, plus First and Second Edition models only) |
176 |
× |
208 |
11:13 |
0.846 |
36,608 |
| Older Java MIDP devices like Sony Ericsson K600. |
176 |
× |
220 |
4:5 |
0.8 |
38,720 |
| Nokia 5500 Sport |
208 |
× |
208 |
1:1 |
1.0 |
43,264 |
| UIQ 2.x based smartphones |
208 |
× |
320 |
13:20 |
0.65 |
66,560 |
| Nintendo Game Boy Advance |
240 |
× |
160 |
3:2 |
1.5 |
38,400 |
| TMS9918 Modes 1 (e.g. TI-99/4a) and 2, ZX Spectrum, Nintendo DS (each screen) |
256 |
× |
192 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
49,152 |
| Elektronika BK |
256 |
× |
256 |
1:1 |
1.0 |
65,536 |
| Apple II HiRes (1 bit per pixel) |
280 |
× |
192 |
35:24 |
1.458 |
53,760 |
| Atari 400/800 |
320 |
× |
192 |
5:3 |
1.667 |
61,440 |
| CGA 4-color, Atari ST 16 color, VIC-II Hires, Amiga OCS NTSC Lowres, Apple IIGS LoRes, MCGA |
320 |
× |
200 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
64,000 |
| QVGA |
320 |
× |
240 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
76,800 |
| Acorn BBC 40 column modes, Amiga OCS PAL Lowres |
320 |
× |
256 |
5:4 |
1.25 |
81,920 |
| Palm (PDA) HiRES |
320 |
× |
320 |
1:1 |
1.0 |
102,400 |
| Palm (PDA) HiRES+ |
320 |
× |
480 |
2:3 |
0.667 |
153,600 |
| Nokia Series 60 smartphones (E60, E70, N80, N90) |
352 |
× |
416 |
11:13 |
0.846 |
146,432 |
| WQVGA (common on Windows Mobile 6 handsets) |
400 |
× |
240 |
5:3 |
1.667 |
96,000 |
| Quarter SVGA (no official name, selectable in some PC shooters) |
400 |
× |
300 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
120,000 |
| WQVGA |
432 |
× |
240 |
9:5 |
1.8 |
103,680 |
| Sony PlayStation Portable |
480 |
× |
272 |
30:17 |
1.765 |
130,560 |
| HVGA, Apple iPhone |
480 |
× |
320 |
3:2 |
1.5 |
153,600 |
| Elektronika BK |
512 |
× |
256 |
2:1 |
2.0 |
131,072 |
| Black & white Macintosh (9") |
512 |
× |
342 |
3:2 |
1.5 |
175,104 |
| Macintosh LC (12")/Color Classic |
512 |
× |
384 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
196,608 |
| Apple IIe Double Hires (1 bit per pixel) |
560 |
× |
192 |
35:12 |
2.917 |
107,520 |
| (unnamed) |
600 |
× |
480 |
5:4 |
1.25 |
288,000 |
| Atari ST 4 color, CGA mono, Amiga OCS NTSC Hires, Apple IIGS HiRes, Nokia Series 80 smartphones |
640 |
× |
200 |
16:5 |
3.2 |
128,000 |
| HVGA, Handheld PC |
640 |
× |
240 |
8:3 |
2.667 |
153,600 |
| Acorn BBC 80 column modes, Amiga OCS PAL Hires |
640 |
× |
256 |
5:2 |
2.5 |
163,840 |
| Nokia Series 90 smartphones (7700, 7710) |
640 |
× |
320 |
2:1 |
2.0 |
204,800 |
| EGA |
640 |
× |
350 |
64:35 |
1.829 |
224,000 |
| QHD / nHD [2] [3] |
640 |
× |
360 |
16:9 |
1.778 |
230,400 |
| Atari ST mono, Amiga OCS NTSC Hires interlaced |
640 |
× |
400 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
256,000 |
| VGA, MCGA (in monochome), Sun-1 color |
640 |
× |
480 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
307,200 |
| Amiga OCS PAL Hires interlaced |
640 |
× |
512 |
5:4 |
1.25 |
327,680 |
| HGC |
720 |
× |
348 |
60:29 |
2.069 |
250,560 |
| MDA |
720 |
× |
350 |
72:35 |
2.057 |
252,000 |
| Apple Lisa |
720 |
× |
364 |
180:91 |
1.978 |
262,080 |
| WVGA |
768 |
× |
480 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
368,640 |
| Nokia E90 Communicator |
800 |
× |
352 |
25:11 |
2.273 |
281,600 |
| WGA or WVGA, ASUS Eee PC 700 and 701 series |
800 |
× |
480 |
5:3 |
1.667 |
384,000 |
| SVGA |
800 |
× |
600 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
480,000 |
| Apple Macintosh Half Megapixel |
832 |
× |
624 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
519,168[4] |
| WVGA |
856 |
× |
480 |
~16:9 |
1.783 |
410,880 |
| Quarter FHD |
960 |
× |
540 |
16:9 |
1.778 |
518,400 |
| (unnamed, selectable in some first/third-person shooters) |
960 |
× |
720 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
691,200 |
| WSVGA |
1024 |
× |
576 |
16:9 |
1.778 |
589,824 |
| ASUS Eee PC 900, 901, 1000 series, MSI Wind and the HP 2133 |
1024 |
× |
600 |
128:75 |
1.707 |
614,400 |
| (unnamed) |
1024 |
× |
640 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
655,360 |
| XGA |
1024 |
× |
768 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
786,432 |
| Sun-1 monochrome |
1024 |
× |
800 |
32:25 |
1.28 |
819,200 |
| Network Computing Devices |
1024 |
× |
1024 |
1:1 |
1.0 |
1,048,576 |
| NeXT MegaPixel Display |
1120 |
× |
832 |
35:26 |
1.346 |
931,840 |
| (unnamed) |
1152 |
× |
720 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
829,440 |
| Apple PowerBook G4 (original Titanium version) |
1152 |
× |
768 |
3:2 |
1.5 |
884,736 |
| XGA+ |
1152 |
× |
864 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
995,328[5] |
| Sun-2 Prime Monochrome or Color Video, also common in Sun-3 and Sun-4 workstations |
1152 |
× |
900 |
32:25 |
1.28 |
1,036,800 |
| WXGA, min. |
1280 |
× |
720 |
16:9 |
1.778 |
921,600 |
| WXGA, avg., BrightView |
1280 |
× |
768 |
5:3 |
1.667 |
983,040 |
| WXGA, avg. |
1280 |
× |
800 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
1,024,000 |
| Apple PowerBook G4 |
1280 |
× |
854 |
~3:2 |
1.499 |
1,093,120 |
| SXGA- |
1280 |
× |
960 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
1,228,800 |
| SXGA |
1280 |
× |
1024 |
5:4 |
1.25 |
1,310,720 |
| WXGA, max. (standardized HDTV 720p/1080i displays) |
1366 |
× |
768 |
~16:9 |
1.779 |
1,049,088 |
| SXGA+ |
1400 |
× |
1050 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
1,470,000 |
| WXGA+ |
1440 |
× |
900 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
1,296,000 |
| Apple PowerBook G4 (final version) |
1440 |
× |
960 |
3:2 |
1.5 |
1,382,400 |
| (unnamed) |
1440 |
× |
1080 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
1,555,200 |
| Sony VAIO Z Series laptops |
1600 |
× |
900 |
16:9 |
1.778 |
1,440,000 |
| WSXGA |
1600 |
× |
1024 |
25:16 |
1.5625 |
1,638,400 |
| UXGA |
1600 |
× |
1200 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
1,920,000 |
| WSXGA+ |
1680 |
× |
1050 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
1,764,000 |
| 1080p |
1920 |
× |
1080 |
16:9 |
1.778 |
2,073,600 |
| WUXGA |
1920 |
× |
1200 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
2,304,000 |
| TXGA |
1920 |
× |
1400 |
48:35 |
1.371 |
2,688,000 |
| (unnamed, available on some GPUs/monitors) |
1920 |
× |
1440 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
2,764,800 |
| QWXGA |
2048 |
× |
1152 |
16:9 |
1.778 |
2,359,296 |
| QXGA |
2048 |
× |
1536 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
3,145,728 |
| WQXGA |
2560 |
× |
1600 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
4,096,000 |
| QSXGA |
2560 |
× |
2048 |
5:4 |
1.25 |
5,242,880 |
| QSXGA+ |
2800 |
× |
2100 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
5,880,000 |
| WQSXGA |
3200 |
× |
2048 |
25:16 |
1.5625 |
6,553,600 |
| QUXGA |
3200 |
× |
2400 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
7,680,000 |
| QFHD aka 2160p |
3840 |
× |
2160 |
16:9 |
1.778 |
8,294,400 |
| WQUXGA |
3840 |
× |
2400 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
9,216,000 |
| HXGA |
4096 |
× |
3072 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
12,582,912 |
| WHXGA |
5120 |
× |
3200 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
16,384,000 |
| HSXGA |
5120 |
× |
4096 |
5:4 |
1.25 |
20,971,520 |
| WHSXGA |
6400 |
× |
4096 |
25:16 |
1.5625 |
26,214,400 |
| HUXGA |
6400 |
× |
4800 |
4:3 |
1.333 |
30,720,000 |
| Super Hi-Vision |
7680 |
× |
4320 |
16:9 |
1.778 |
33,177,600 |
| WHUXGA |
7680 |
× |
4800 |
8:5 |
1.6 |
36,864,000 |