Geology
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
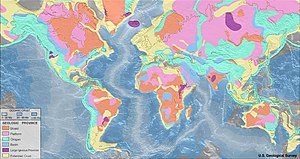
Oceanic crust 0-20 Ma 20-65 Ma >65 Ma Continental Crust Shield Platform Orogen Basin Large igneous province Extended crust
Geology (from Greek: γη, gê, "earth"; and λόγος, logos, "speech" lit. to talk about the earth) is the science and study of the solid and liquid matter that constitutes the Earth. The field of geology encompasses the study of the composition, structure, physical properties, dynamics, and history of Earth materials, and the processes by which they are formed, moved, and changed. The field is a major academic discipline, and is also important for mineral and hydrocarbon extraction, knowledge about and mitigation of natural hazards, some engineering fields, and understanding past climates and environments with reference to present-day climate change.
Contents |
[edit] Etymology
The word "geology" was first used by Jean-André Deluc in the year 1778 and introduced as a fixed term by Horace-Bénédict de Saussure in the year 1779. The science was not included in Encyclopædia Britannica's third edition completed in 1797, but had a lengthy entry in the fourth edition completed by 1809.[1] An older meaning of the word was first used by Richard de Bury to distinguish between earthly and theological jurisprudence.
[edit] History

The work Peri Lithon (On Stones) by the ancient Greek scholar Theophrastus (372-287 BC), a student of ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle, remained authoritative for millennia. Peri Lithon was translated into Latin and some other foreign languages. Its interpretation of fossils was the most dominant theory in classical Antiquity and the early Middle Ages, until it was replaced by Avicenna's theory of petrifying fluids (succus lapidificatus) in the late Middle Ages.[2][3] In the Roman period, Pliny the Elder produced a very extensive discussion of many more minerals and metals then widely used for practical ends. He is among the first to correctly identify the origin of amber as a fossilized resin from pine trees by the observation of insects trapped within some pieces. He also laid the basis of crystallography by recognising the octahedral habit of diamond.
Some modern scholars, such as Fielding H. Garrison, are of the opinion that modern geology began in the medieval Islamic world.[4] Abu al-Rayhan al-Biruni (973-1048 AD) was one of the earliest Muslim geologists, whose works included the earliest writings on the geology of India, hypothesizing that the Indian subcontinent was once a sea.[5] Ibn Sina (Avicenna, 981-1037), in particular, made significant contributions to geology and the natural sciences (which he called Attabieyat) along with other natural philosophers such as Ikhwan AI-Safa and many others. He wrote an encyclopaedic work entitled “Kitab al-Shifa” (the Book of Cure, Healing or Remedy from ignorance), in which Part 2, Section 5, contains his essay on Mineralogy and Meteorology, in six chapters: Formation of mountains, The advantages of mountains in the formation of clouds; Sources of water; Origin of earthquakes; Formation of minerals; The diversity of earth’s terrain. These principles were later known in the Renaissance of Europe as the law of superposition of strata, the concept of catastrophism, and the doctrine of uniformitarianism. These concepts were also embodied in the Theory of the Earth by James Hutton in the Eighteenth century C.E. Academics such as Toulmin and Goodfield (1965), commented on Avicenna's contribution: "Around A.D. 1000, Avicenna was already suggesting a hypothesis about the origin of mountain ranges, which in the Christian world, would still have been considered quite radical eight hundred years later".[6] Avicenna's scientific methodology of field observation was also original in the Earth sciences, and remains an essential part of modern geological investigations.[3]
In China, the polymath Shen Kua (1031-1095) formulated a hypothesis for the process of land formation: based on his observation of fossil animal shells in a geological stratum in a mountain hundreds of miles from the ocean, he inferred that the land was formed by erosion of the mountains and by deposition of silt.

Georg Agricola (1494-1555), a physician, wrote the first systematic treatise about mining and smelting works, De re metallica libri XII, with an appendix Buch von den Lebewesen unter Tage (Book of the Creatures Beneath the Earth). He covered subjects like wind energy, hydrodynamic power, melting cookers, transport of ores, extraction of soda, sulfur and alum, and administrative issues. The book was published in 1556.
Nicolas Steno (1638-1686) is credited with the law of superposition, the principle of original horizontality, and the principle of lateral continuity: three defining principles of stratigraphy. Previous attempts at such statements met accusations of heresy from the Church.[citation needed]
By the 1700s Jean-Étienne Guettard and Nicolas Desmarest hiked central France and recorded their observations on geological maps; Guettard recorded the first observation of the volcanic origins of this part of France.
William Smith (1769-1839) drew some of the first geological maps and began the process of ordering rock strata (layers) by examining the fossils contained in them.[7]
James Hutton is often viewed as the first modern geologist.[8] In 1785 he presented a paper entitled Theory of the Earth to the Royal Society of Edinburgh. In his paper, he explained his theory that the Earth must be much older than had previously been supposed in order to allow enough time for mountains to be eroded and for sediments to form new rocks at the bottom of the sea, which in turn were raised up to become dry land. Hutton published a two-volume version of his ideas in 1795 (Vol. 1, Vol. 2).

Followers of Hutton were known as Plutonists because they believed that some rocks were formed by vulcanism which is the deposition of lava from volcanoes, as opposed to the Neptunists, who believed that all rocks had settled out of a large ocean whose level gradually dropped over time.
In 1811 Georges Cuvier and Alexandre Brongniart published their explanation of the antiquity of the Earth, inspired by Cuvier's discovery of fossil elephant bones in Paris. To prove this, they formulated the principle of stratigraphic succession of the layers of the earth. They were independently anticipated by William Smith's stratigraphic studies on England and Scotland.
Sir Charles Lyell first published his famous book, Principles of Geology[9], in 1830. Lyell continued to publish new revisions until he died in 1875. The book, which influenced the thought of Charles Darwin, successfully promoted the doctrine of uniformitarianism. This theory states that slow geological processes have occurred throughout the Earth's history and are still occurring today. In contrast, catastrophism is the theory that Earth's features formed in single, catastrophic events and remained unchanged thereafter. Though Hutton believed in uniformitarianism, the idea was not widely accepted at the time.

19th-century geology revolved around the question of the Earth's exact age. Estimates varied from a few 100,000 to billions of years.[10] The most significant advance in 20th century geology has been the development of the theory of plate tectonics in the 1960s. Plate tectonic theory arose out of two separate geological observations: seafloor spreading and continental drift. The theory revolutionized the Earth sciences.
The theory of continental drift was proposed by Frank Bursley Taylor in 1908, expanded by Alfred Wegener in 1912 and by Arthur Holmes, but wasn't broadly accepted until the late 1960s when the theory of plate tectonics was developed.
[edit] Important principles in the development of geology
There are a number of important principles that were developed near the beginning of geology as a formal science. Many of these involve the ability to provide the relative ages of strata or the manner in which they were formed. These principles are still often used today as a means to provide information about geologic history and the timing of geologic events.
The principle of intrusive relationships concerns crosscutting intrusions. In geology, when an igneous intrusion cuts across a formation of sedimentary rock, it can be determined that the igneous intrusion is younger than the sedimentary rock. There are a number of different types of intrusions, including stocks, laccoliths, batholiths, sills and dikes.
The principle of cross-cutting relationships pertains to the formation of faults and the age of the sequences through which they cut. Faults are younger than the rocks they cut; accordingly, if a fault is found that penetrates some formations but not those on top of it, then the formations that were cut are older than the fault, and the ones that are not cut must be younger than the fault. Finding the key bed in these situations may help determine whether the fault is a normal fault or a thrust fault.[11]
The principle of inclusions and components states that, with sedimentary rocks, if inclusions (or clasts) are found in a formation, then the inclusions must be older than the formation that contains them. For example, in sedimentary rocks, it is common for gravel from an older formation to be ripped up and included in a newer layer. A similar situation with igneous rocks occurs when xenoliths are found. These foreign bodies are picked up as magma or lava flows, and are incorporated, later to cool in the matrix. As a result, xenoliths are older than the rock which contains them.
The principle of uniformitarianism states that the geologic processes observed in operation that modify the Earth's crust at present have worked in much the same way over geologic time.[12] A fundamental principle of geology advanced by the 18th century Scottish physician and geologist James Hutton, is that "the present is the key to the past." In Hutton's words: "the past history of our globe must be explained by what can be seen to be happening now."[citation needed]
The principle of original horizontality states that the deposition of sediments occurs as essentially horizontal beds. Observation of modern marine and non-marine sediments in a wide variety of environments supports this generalization (although cross-bedding is inclined, the overall orientation of cross-bedded units is horizontal).[11]
The principle of superposition states that a sedimentary rock layer in a tectonically undisturbed sequence is younger than the one beneath it and older than the one above it. Logically a younger layer cannot slip beneath a layer previously deposited. This principle allows sedimentary layers to be viewed as a form of vertical time line, a partial or complete record of the time elapsed from deposition of the lowest layer to deposition of the highest bed.[11]
The principle of faunal succession is based on the appearance of fossils in sedimentary rocks. As organisms exist at the same time period throughout the world, their presence or (sometimes) absence may be used to provide a relative age of the formations in which they are found. Based on principles laid out by William Smith almost a hundred years before the publication of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution, the principles of succession were developed independently of evolutionary thought. The principle becomes quite complex, however, given the uncertainties of fossilization, the localization of fossil types due to lateral changes in habitat (facies change in sedimentary strata), and that not all fossils may be found globally at the same time[13]
[edit] Modern geology
[edit] Radioactive decay and the age of the Earth
A large advance in geology in the advent of the 20th century was the ability to use ratios of radioactive isotopes to find the amount of time that has passed since a rock passed through a particular temperature. These methods work by measuring the time since a particular mineral grain cooled through its closure temperature, at which point the different radiometric isotopes stop diffusing out of the crystal lattice.[14][15]
The advent of isotopic dating changed the understanding of geologic time. Before, geologists could only use fossils to date sections of rock relative to one another. With isotopic dates, absolute dating became possible, and these absolute dates could be applied fossil sequences in which there was datable material, converting the old relative ages into new absolute ages.
Geologists have used radioactive decay to establish the age of the Earth at about 4.54 billion (4.5x109) years[16][17] and the age of the oldest planetary material (Carbonaceous Chondrite meteorites) at 4.567 billion years.[18]

[edit] Plate tectonics
In the 1960s, a series of discoveries, the most important of which was seafloor spreading[19][20], showed that the Earth's lithosphere, which includes the crust and rigid uppermost portion of the upper mantle, is separated into a number of tectonic plates that move across the plastically-deforming, solid, upper mantle, which is called the asthenosphere. There is an intimate coupling between the movement of the plates on the surface and the convection of the mantle: plate motions and mantle convection currents always move in the same direction. This coupling between rigid plates moving on the surface of the Earth and the convecting mantle is called plate tectonics.

The development of plate tectonics provided a physical basis for many observations of the solid Earth. Long linear regions of geologic features could be explained as plate boundaries.[21] Mid-ocean ridges, high regions on the seafloor where hydrothermal vents and volcanoes exist, were explained as divergent boundaries, where two plates move apart. Arcs of volcanoes and earthquakes were explained as convergent boundaries, where one plate subducts under another. Transform boundaries, such as the San Andreas fault system, resulted in widespread powerful earthquakes. Plate tectonics also provided a mechanism for Alfred Wegener's theory of continental drift[22], in which the continents move across the surface of the Earth over geologic time. They also provided a driving force for crustal deformation, and a new setting for the observations of structural geology. The power of the theory of plate tectonics lies in its ability to combine all of these observations into a single theory of how the lithosphere moves over the convecting mantle.
[edit] Earth structure
Advances in seismology, computer modeling, and mineralogy and crystallography at high temperatures and pressures give insights into the internal composition and structure of the Earth.
Seismologists can use the arrival times of seismic waves in reverse to image the interior of the Earth. Early advances in this field showed the existence of a liquid outer core (where shear waves were not able to propagate) and a dense solid inner core. These advances led to the development of a layered model of the Earth, with a crust and lithosphere on top, the mantle below (separated within itself by seismic discontinuities at 410 and 660 kilometers), and the outer core and inner core below that. More recently, seismologists have been able to create detailed images of wave speeds inside the earth in the same way a doctor images a body in a CT scan. These images have led to a much more detailed view of the interior of the Earth, and have replaced the simplified layered model with a much more dynamic model.
Mineralogists have been able to use the pressure and temperature data from the seismic and modelling studies alongside knowledge of the elemental composition of the Earth at depth to reproduce these conditions in experimental settings and measure changes in crystal structure. These studies explain the chemical changes associated with the major seismic discontinuities in the mantle, and show the crystallographic structures expected in the inner core of the Earth.
[edit] Planetary geology
With the advent of space exploration in the twentieth century, geologists have begun to look at other planetary bodies in the same way as the Earth. This led to the establishment of the field of planetary geology, sometimes known as Astrogeology, in which geologic principles are applied to other bodies of the solar system.
Although the Greek-language-origin prefix geo refers to Earth, "geology" is often used in conjunction with the names of other planetary bodies when describing their composition and internal processes: examples are "the geology of Mars" and "Lunar geology". Specialised terms such as selenology (studies of the moon), areology (of Mars), etc., are also in use.
Although planetary geologists are interested in all aspects of the planets, a significant focus is in the search for past or present life on other worlds. This has led to many missions whose purpose (or one of their purposes) is to examine planetary bodies for evidence of life. One of this is the Phoenix lander, which analyzed Martian polar soil for water and chemical and mineralogical constituents related to biological processes.
[edit] Geologic time

The geologic time-scale encompasses the history of the Earth, from solar system formation at 4.567 Ga (gigaannum: billion years ago) to present.[23]
[edit] Important milestones
- 4.567 Ga: Solar system formation[18]
- 4.54 Ga: Accretion of Earth[16][17]
- c. 4 Ga: End of Late Heavy Bombardment, first life
- c. 3.5 Ga: Start of photosynthesis
- c. 2.3 Ga: Oxygenated atmosphere, first snowball Earth
- 730-635 Ma (megaannum: million years ago): two snowball Earths
- 542± 0.3 Ma: Cambrian explosion - vast multiplication of hard-bodied life; first abundant fossils; start of the Paleozoic
- c. 380 Ma: First vertebrate land animals
- 250 Ma: Permian-Triassic extinction - 90% of all land animals die. End of Paleozoic and beginning of Mesozoic
- 65 Ma: Cretaceous-Tertiary extinction - Dinosaurs die; end of Mesozoic and beginning of Cenozoic
- c. 7 Ma - Present: Hominins
- c. 7 Ma: First hominins appear
- 3.9 Ma: First Australopithecus, direct ancestor to modern Homo sapiens, appear
- 200 ka (kiloannum: thousand years ago): First modern Homo sapiens appear in East Africa
[edit] Brief time-scale
The second and third timelines are each subsections of their preceding timeline as indicated by asterisks.


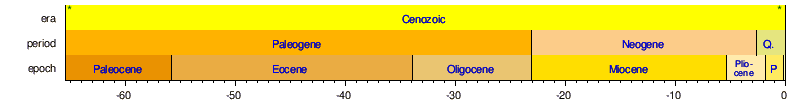
The Holocene (the latest epoch) is too small to be shown clearly on this timeline.
[edit] Geological evolution of an area

The geology of an area evolves through time as rock units are deposited and inserted and deformational processes change their shapes and locations.
Rock units are first emplaced either by deposition onto the surface or intrusion into the overlying rocks. Deposition can occur when sediments settle onto the surface of the Earth and later lithify into sedimentary rock, or when as volcanic material such as volcanic ash or lava flows, blanket the surface. Igneous intrusions such as batholiths, laccoliths, dikes, and sills, push upwards into the overlying rock, and crystallize as they intrude.
After the initial sequence of rocks has been deposited, the rock units can be deformed and/or metamorphosed. Deformation typically occurs as a result of horizontal shortening, horizontal extension, or side-to-side (strike-slip) motion. These structural regimes broadly relate to convergent boundaries, divergent boundaries, and transform boundaries, respectively, between tectonic plates.
When rock units are placed under horizontal compression, they shorten and become thicker. Because rock units, other than muds, do not significantly change in volume, this is accomplished in two primary ways: through faulting and folding. In the shallow crust, where brittle deformation can occur, thrust faults form, which cause deeper rock to move on top of shallower rock. Because deeper rock is often older, as noted by the principle of superposition, this can result in older rocks moving on top of younger ones. Movement along faults can result in folding, either because the faults are not planar, or because the rock layers are dragged along, forming drag folds, as slip occurs are along the fault. Deeper in the Earth, rocks behave plasticly, and fold instead of faulting. These folds can either be those where the material in the center of the fold buckles upwards, creating "antiforms", or where it buckles downwards, creating "synforms". If the tops of the rock units within the folds remain pointing upwards, they are called anticlines and synclines, respectively. If some of the units in the fold are facing downward, the structure is called an overturned anticline or syncline, and if all of the rock units are overturned or the correct up-direction is unknown, they are simply called by the most general terms, antiforms and synforms.
Even higher pressures and temperatures during horizontal shortening can cause both folding and metamorphism of the rocks. This metamorphism causes changes in the mineral composition of the rocks; creates a foliation, or planar surface, that is related to mineral growth under stress; and can remove signs of the original textures of the rocks, such as bedding in sedimentary rocks, flow features of lavas, and crystal patterns in crystalline rocks.
Extension causes the rock units as a whole to become longer and thinner. This is primarily accomplished through normal faulting and through the ductile stretching and thinning. Normal faults drop rock units that are higher below those that are lower. This typically results in younger units being placed below older units. Stretching of units can result in their thinning; in fact, there is a location within the Maria Fold and Thrust Belt in which the entire sedimentary sequence of the Grand Canyon can be seen over a length of less than a meter. Rocks at the depth to be ductily stretched are often also metamorphosed. These stretched rocks can also pinch into lenses, known as boudins, after the French word for "sausage", because of their visual similarity.
Where rock units slide past one another, strike-slip faults develop in shallow regions, and become shear zones at deeper depths where the rocks deform ductily.

The addition of new rock units, both depositionally and intrusively, often occurs during deformation. Faulting and other deformational processes result in the creation of topographic gradients, causing material on the rock unit that is increasing in elevation to be eroded by hillslopes and channels. These sediments are deposited on the rock unit that is going down. Continual motion along the fault maintains the topographic gradient in spite of the movement of sediment, and continues to create accommodation space for the material to deposit. Deformational events are often also associated with volcanism and igneous activity. Volcanic ashes and lavas accumulate on the surface, and igneous intrusions enter from below. Dikes, long, planar igneous intrusions, enter along cracks, and therefore often form in large numbers in areas that are being actively deformed. This can result in the emplacement of dike swarms, such as those that are observable across the Canadian shield, or rings of dikes around the lava tube of a volcano.
All of these processes do not necessarily occur in a single environment, and do not necessarily occur in a single order. The Hawaiian Islands, for example, consist almost entirely of layered basaltic lava flows. The sedimentary sequences of the mid-continental United States and the Grand Canyon in the southwestern United States contain almost-undeformed stacks of sedimentary rocks that have remained in place since Cambrian time. Other areas are much more geologically complex. In the southwestern United States, sedimentary, volcanic, and intrusive rocks have been metamorphosed, faulted, foliated, and folded. Even older rocks, such as the Acasta gneiss of the Slave craton in northwestern Canada, the oldest known rock in the world have been metamorphosed to the point where their origin is undiscernable without laboratory analysis. In addition, these processes can occur in stages. In many places, the Grand Canyon in the southwestern United States being a very visible example, the lower rock units were metamorphosed and deformed, and then deformation ended and the upper, undeformed units were deposited. Although any amount of rock emplacement and rock deformation can occur, and they can occur any number of times, these concepts provide a guide to understanding the geological history of an area.
[edit] Methods of geology
Geologists use a number of field, laboratory, and numerical modeling methods to decipher Earth history and understand the processes that occur on and in the Earth. In typical geological investigations, geologists use primary information related to petrology (the study of rocks), stratigraphy (the study of sedimentary layers), and structural geology (the study of positions of rock units and their deformation). In many cases, geologists also study modern soils, rivers, landscapes, and glaciers; investigate past and current life and biogeochemical pathways, and use geophysical methods to investigate the subsurface.
[edit] Field methods


Geological field work varies depending on the task at hand. Typical fieldwork could consist of:
- Geological mapping
- Structural mapping: the locations of the major rock units and the faults and folds that led to their placement there.
- Stratigraphic mapping: the locations of sedimentary facies (lithofacies and biofacies) or the mapping of isopachs of equal thickness of sedimentary rock
- Surficial mapping: the locations of soils and surficial deposits
- Surveying of topographic features
- Creation of topographic maps
- Work to understand change across landscapes, including:
- Patterns of erosion and deposition
- River channel change through migration and avulsion
- Hillslope processes
- Subsurface mapping through geophysical methods.
- These methods include:
- Shallow seismic surveys
- Ground-penetrating radar
- Electrical resistivity tomography
- They are used for:
- These methods include:
- High-resolution stratigraphy
- Measuring and describing stratigraphic sections on the surface
- Well drilling and logging
- Biogeochemistry and geomicrobiology
- Collecting samples to:
- Determine biochemical pathways
- Identify new species of organisms. These organisms may help to show:
- Identify new chemical compounds
- And to use these discoveries to
- Understand early life on Earth and how it functioned and metabolized
- Find important compounds for use in pharmaceuticals.
- Collecting samples to:
- Paleontology: excavation of fossil material
- Collection of samples for geochronology and thermochronology
- Glaciology: measurement of characteristics of glaciers and their motion
[edit] Laboratory methods

[edit] Petrology
In addition to the field identification of rocks, petrologists identify rock samples in the laboratory. Two of the primary methods for identifying rocks in the laboratory are through optical microscopy and by using an electron microprobe. In an optical mineralogy analysis, thin sections of rock samples are analyzed through a petrographic microscope, where the minerals can be identified through their different properties in plane-polarized and cross-polarized light, including their birefringence, pleochroism, twinning, and interference properties with a conoscopic lens.[24] In the electron microprobe, individual locations are analyzed for their exact chemical compositions and variation in composition within individual crystals.[25] Stable[26] and radioactive isotope[27] studies provide insight into the geochemical evolution of rock units.
Petrologists use fluid inclusion data[28] and perform high temperature and pressure physical experiments[29] to understand the temperatures and pressures at which different mineral phases appear, and how they change through igneous[30] and metamorphic processes. This research can be extrapolated to the field to understand metamorphic processes and the conditions of crystallization of igneous rocks.[31] This work can also help to explain processes that occur within the Earth, such as subduction and magma chamber evolution.
[edit] Structural geology

Structural geologists use microscopic analysis of oriented thin sections of geologic samples to observe the fabric within the rocks which gives information about strain within the crystal structure of the rocks. They also plot and combine measurements of geological structures in order to better-understand the orientations of faults and folds in order to reconstruct the history of rock deformation in the area. In addition, they perform analog and numerical experiments of rock deformation in large and small settings.
The analysis of structures is often accomplished by plotting the orientations various features onto stereonets. A stereonet is a stereographic projection of a sphere onto a plane, in which planes are projected as lines and lines are projected as points. These can be used to find the locations of fold axes, relationships between several faults, and relationships between other geologic structures.
Among the most well-known experiments in structural geology are those involving orogenic wedges, which are zones in which mountains are built along convergent tectonic plate boundaries.[32] In the analog versions of these experiments, horizontal layers of sand are pulled along a lower surface into a back stop, which results in realistic-looking patterns of faulting and the growth of an critically-tapered (all angles remain the same) orogenic wedge.[33] Numerical models work in the same way as these analog models, though they are often more sophisticated and can include patterns of erosion and uplift in the mountain belt.[34] This helps to show the relationship between erosion and the shape of the mountain range. These studies can also give useful information about pathways for metamorphism through pressure, temperature, space, and time.[35]
[edit] Stratigraphy

In the laboratory, stratigraphers analyze samples of stratigraphic sections that can be returned from the field, such as those from drill cores.[36] Stratigraphers also analayze data from geophysical surveys that show the locations of stratigraphic units in the subsurface.[37] Geophysical data and well logs can be combined to produce a better view of the subsurface, and stratigraphers often use computer programs to do this in three dimensions.[38] Stratigraphers can then use these data to reconstruct ancient processes occurring on the surface of the Earth,[39] interpret past environments, and locate areas for water and hydrocarbon extraction.
In the laboratory, biostratigraphers analyze rock samples from outcrop and drill cores for the fossils found in them.[40] These fossils help scientists to date the core and to understand the depositional environment in which the rock units formed. Geochronologists precisely date rocks within the stratigraphic section in order to provide better absolute bounds on the timing and rates of deposition.[41] Magnetic stratigraphers look for signs of magnetic reversals in igneous rock units within the drill cores.[40] Other scientists perform stable isotope studies on the rocks to gain information about past climate.[40]
[edit] Applied geology
[edit] Economic geology
Economic geologists help locate and manage the Earth's natural resources, such as petroleum and coal, as well as mineral resources, which include metals such as iron, copper, and uranium.
[edit] Mining geology
Mining geology consists of the extractions of mineral resources from the Earth. Some resources of economic interests include gemstones, metals, and many minerals such as asbestos, perlite, mica, phosphates, zeolites, clay, pumice, quartz, and silica, as well as elements such as sulfur, chlorine, and helium.
[edit] Petroleum geology
Petroleum geologists study locations of the subsurface of the Earth which can contain extractable hydrocarbons, especially petroleum and natural gas. Because many of these reservoirs are found in sedimentary basins[42], they study the formation of these basins, as well as their sedimentary and tectonic evolution and the present-day positions of the rock units.
[edit] Soil mechanics and geotechnical engineering
In the field of civil engineering, geological principles and analyses are used in order to ascertain the mechanical principles of the material on which structures are built. This allows tunnels to be built without collapsing, bridges and skyscrapers to be built with sturdy foundations, and buildings to be built that will not settle in clay and mud.[43]
[edit] Hydrology and environmental issues
Geology and geologic principles can be applied to various environmental problems, such as stream restoration, the restoration of brownfields, and the understanding of the interactions between natural habitat and the geologic environment. Groundwater hydrology, or hydrogeology, is used to locate groundwater,[44] which can often provide a ready supply of uncontaminated water and is especially important in arid regions,[45] and to monitor the spread of contaminants in groundwater wells.[46][47]
Geologists also obtain data through stratigraphy, boreholes, core samples, and ice cores. Ice cores[48] and sediment cores[49] are used to for paleoclimate reconstructions, which tell geologists about past and present temperature, precipitation, and sea level across the globe. These data are our primary source of information on global climate change outside of instrumental data.[50]
[edit] Natural hazards
Geologists and geophysicists study natural hazards in order to enact safe building codes and warning systems that are used to prevent loss of property and life.[51] Examples of important natural hazards that are pertinent to geology (as opposed those that are mainly or only pertinent to meteorology) are:
- Avalanches
- Earthquakes
- Floods and river channel migration and avulsion
- Landslides and debris flows
- Liquefaction
- Sinkholes
- Subsidence
- Tsunamis
- Volcanoes
[edit] Fields or related disciplines

An illustrated depiction of a syncline and anticline commonly studied in Structural geology and Geomorphology.
|
[edit] Regional geology
[edit] By mountain range
- Geology of the Alps
- Geology of the Andes
- Geology of the Appalachians
- Geology of the Himalaya
- Geology of the Rocky Mountains
[edit] By nations
|
|
[edit] By planet
[edit] References
- ^ Winchester, Simon (2001). The Map that Changed the World. HarperCollins Publishers. pp. 25. ISBN 0-06-093180-9
- ^ Rudwick, M. J. S. (1985), The Meaning of Fossils: Episodes in the History of Palaeontology, University of Chicago Press, p. 24, ISBN 0226731030
- ^ a b Munim M. Al-Rawi and Salim Al-Hassani (November 2002). "The Contribution of Ibn Sina (Avicenna) to the development of Earth sciences". FSTC. http://www.muslimheritage.com/uploads/ibnsina.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-07-01.
- ^ Fielding H. Garrison wrote in the History of Medicine:
"The Saracens themselves were the originators not only of algebra, chemistry, and geology, but of many of the so-called improvements or refinements of civilization, such as street lamps, window-panes, fireworks, stringed instruments, cultivated fruits, perfumes, spices, etc."
- ^ Abdus Salam (1984), "Islam and Science". In C. H. Lai (1987), Ideals and Realities: Selected Essays of Abdus Salam, 2nd ed., World Scientific, Singapore, p. 179-213.
- ^ Toulmin, S. and Goodfield, J. (1965), ’The Ancestry of science: The Discovery of Time’, Hutchinson & Co., London, p. 64 (see also The Contribution of Ibn Sina to the development of Earth sciences)
- ^ a b Simon Winchester ; (2002). The map that changed the world : William Smith and the birth of modern geology. New York, NY: Perennial. ISBN 0060931809.
- ^ James Hutton: The Founder of Modern Geology, American Museum of Natural History
- ^ Charles Lyell. (1991). Principles of geology.. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.. ISBN 9780226497976.
- ^ England, Philip (2007). "John Perry's neglected critique of Kelvin's age for the Earth: A missed opportunity in geodynamics". GSA Today 17: 4. doi:.
- ^ a b c Olsen, Paul E. (2001). "Steno's Principles of Stratigraphy" (in English). Dinosaurs and the History of Life. Columbia University. http://rainbow.ldeo.columbia.edu/courses/v1001/steno.html. Retrieved on 2009-03-14.
- ^ Reijer Hooykaas, Natural Law and Divine Miracle: The Principle of Uniformity in Geology, Biology, and Theology, Leiden: EJ Brill, 1963.
- ^ As recounted in Simon Winchester, The Map that Changed the World (New York: HarperCollins, 2001), pp. 59-91.
- ^ Hugh R. Rollinson (1996). Using geochemical data evaluation, presentation, interpretation. Harlow: Longman. ISBN 9780582067011.
- ^ Gunter Faure. (1998). Principles and applications of geochemistry : a comprehensive textbook for geology students. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall. ISBN 9780023364501.
- ^ a b Patterson, C., 1956. “Age of Meteorites and the Earth.” Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 10: p. 230-237.
- ^ a b G. Brent Dalrymple (1994). The age of the earth. Stanford, Calif.: Stanford Univ. Press. ISBN 0804723311.
- ^ a b Amelin, Y; Krot, An; Hutcheon, Id; Ulyanov, Aa (Sep 2002). "Lead isotopic ages of chondrules and calcium-aluminum-rich inclusions.". Science (New York, N.Y.) 297 (5587): 1678–83. doi:. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 12215641.
- ^ H. H. Hess, "History Of Ocean Basins" (November 1, 1962). IN: Petrologic studies: a volume in honor of A. F. Buddington. A. E. J. Engel, Harold L. James, and B. F. Leonard, editors. [New York?]: Geological Society of America, 1962. pp. 599-620.
- ^ Kious, Jacquelyne; Tilling, Robert I. (February 1996). "Developing the Theory" (in English). This Dynamic Earth: The Story of Plate Tectonics. Kiger, Martha, Russel, Jane (Online ed.). Reston, Virgina, USA: United States Geological Survey. ISBN 0-16-048220-8. http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html. Retrieved on 13 March 2009.
- ^ Kious, Jacquelyne; Tilling, Robert I. (February 1996). "Understanding Plate Motions" (in English). This Dynamic Earth: The Story of Plate Tectonics. Kiger, Martha, Russel, Jane (Online ed.). Reston, Virgina, USA: United States Geological Survey. ISBN 0-16-048220-8. http://pubs.usgs.gov/gip/dynamic/understanding.html. Retrieved on 13 March 2009.
- ^ Origin of continents and oceans. S.l.: Dover Pub. 1999. ISBN 0486617084.
- ^ International Commission on Stratigraphy
- ^ William D. Nesse. (1991). Introduction to optical mineralogy. New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0195060245.
- ^ Morton, ANDREW C. (1985). "A new approach to provenance studies: electron microprobe analysis of detrital garnets from Middle Jurassic sandstones of the northern North Sea". Sedimentology 32: 553. doi:.
- ^ Zheng, Y (2003). "Stable isotope geochemistry of ultrahigh pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie–Sulu orogen in China: implications for geodynamics and fluid regime". Earth-Science Reviews 62: 105. doi:.
- ^ Condomines, M (1995). "Magma dynamics at Mt Etna: Constraints from U-Th-Ra-Pb radioactive disequilibria and Sr isotopes in historical lavas". Earth and Planetary Science Letters 132: 25. doi:.
- ^ T.J. Shepherd, A.H. Rankin, D.H.M. Alderton. (1985). A practical guide to fluid inclusion studies. Glasgow: Blackie. ISBN 0412006014.
- ^ Sack, Richard O. (1987). "Experimental petrology of alkalic lavas: constraints on cotectics of multiple saturation in natural basic liquids". Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology 96: 1. doi:.
- ^ Alexander R. McBirney. (2007). Igneous petrology. Boston: Jones and Bartlett Publishers. ISBN 9780763734480.
- ^ Frank S. Spear (1995). Metamorphic phase equilibria and pressure-temperature-time paths. Washington, DC: Mineralogical Soc. of America. ISBN 9780939950348.
- ^ Dahlen, F A (1990). "Critical Taper Model of Fold-And-Thrust Belts and Accretionary Wedges". Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 18: 55. doi:.
- ^ Gutscher, M (1998). "Material transfer in accretionary wedges from analysis of a systematic series of analog experiments". Journal of Structural Geology 20: 407. doi:.
- ^ Koons, P O (1995). "Modeling the Topographic Evolution of Collisional Belts". Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences 23: 375. doi:.
- ^ Dahlen, F. A., Suppe, J. & Davis, D. J. geophys. Res. 89, 10087−10101 (1983).
- ^ Hodell, David A. (1994). "Magnetostratigraphic, Biostratigraphic, and Stable Isotope Stratigraphy of an Upper Miocene Drill Core from the Salé Briqueterie (Northwestern Morocco): A High-Resolution Chronology for the Messinian Stage". Paleoceanography 9: 835. doi:.
- ^ edited by A.W. Bally. (1987). Atlas of seismic stratigraphy. Tulsa, Okla., U.S.A.: American Association of Petroleum Geologists. ISBN 0891810331.
- ^ Fernández, O. (2004). "Three-dimensional reconstruction of geological surfaces: An example of growth strata and turbidite systems from the Ainsa basin (Pyrenees, Spain)". AAPG Bulletin 88: 1049. doi:.
- ^ Poulsen, Chris J. (1998). "Three-dimensional stratigraphic evolution of the Miocene Baltimore Canyon region: Implications for eustatic interpretations and the systems tract model". Geological Society of America Bulletin 110: 1105. doi:.
- ^ a b c Hodell, David A. (1994). "Magnetostratigraphic, Biostratigraphic, and Stable Isotope Stratigraphy of an Upper Miocene Drill Core from the Salé Briqueterie (Northwestern Morocco): A High-Resolution Chronology for the Messinian Stage". Paleoceanography 9: 835. doi:.
- ^ Toscano, M (1999). "Submerged Late Pleistocene reefs on the tectonically-stable S.E. Florida margin: high-precision geochronology, stratigraphy, resolution of Substage 5a sea-level elevation, and orbital forcing.". Quaternary Science Reviews 18: 753. doi:.
- ^ Richard C. Selley. (1998). Elements of petroleum geology. San Diego: Academic Press. ISBN 0-12-636370-6.
- ^ Braja M. Das. (2006). Principles of geotechnical engineering.. England: THOMSON LEARNING (KY). ISBN 0534551440.
- ^ Hamilton, Pixie A. (1995). "Effects of Agriculture on Ground-Water Quality in Five Regions of the United States". Ground Water 33: 217. doi:.
- ^ Seckler, David (1999). "Water Scarcity in the Twenty-first Century". International Journal of Water Resources Development 15: 29. doi:.
- ^ Welch, Alan H. (1988). "Arsenic in Ground Water of the Western United States". Ground Water 26: 333. doi:.
- ^ Hamilton, Pixie A. (1995). "Effects of Agriculture on Ground-Water Quality in Five Regions of the United States". Ground Water 33: 217. doi:.
- ^ Barnola, J. M. (1987). "Vostok ice core provides 160,000-year record of atmospheric CO2". Nature 329: 408. doi:.
- ^ Colman, S.M. (1990). "Holocene paleoclimatic evidence and sedimentation rates from a core in southwestern Lake Michigan". Journal of Paleolimnology 4. doi:.
- ^ Jones, P. D. (2004). "Climate over past millennia". Reviews of Geophysics 42: RG2002. doi:.
- ^ USGS Natural Hazards Gateway
[edit] See also
- Agrogeology
- Geochemistry
- Geologic modeling
- Geologic time scale
- Geologist
- Glossary of geology terms
- Important publications in geology
- International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS)
- List of fossil sites (with link directory)
- List of geology topics
- List of minerals
- List of rock textures
- List of rock types
- List of soil topics
- Mineral
- Paleorrota
- Timeline of geology
[edit] External links
- James Hutton's Theory of the Earth
- James Hutton's Theory of the Earth & Abstract of the Theory of the Earth
- Charles Lyell's Elements of Geology
- Charles Lyell's Principles of Geology, or the Modern Changes of the Earth and its Inhabitants, Considered as Illustrative of Geology
- American Geophysical Union
- European Geosciences Union
- Geological Society of America
- Earth Science News, Maps, Dictionary, Articles, Jobs
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||






