Budapest
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Budapest | |||
|
|||
| Nickname(s): "Pearl of the Danube" or "Queen of the Danube", "Heart of Europe", "Capital of Freedom" |
|||
| Location of Budapest in Hungary | |||
| Coordinates: | |||
| Country | Hungary | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| County | Budapest, Capital City | ||
| Government | |||
| - Mayor | Gábor Demszky (SZDSZ) | ||
| Area | |||
| - City | 525.16 km2 (202.8 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2008) | |||
| - City | ▲ 1,702,297 | ||
| - Density | 3,241.5/km2 (8,395.4/sq mi) | ||
| - Metro | ▲ 2,475,740 | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| - Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Website | budapest.hu | ||
Budapest (pronounced /ˈb(j)u:dəˌpɛst/, also /ˈbʊ-/; Hungarian pronunciation: [ˈbudɒpɛʃt] ; names in other languages) is the capital city of Hungary.[1] As the largest city of Hungary, it serves as the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation center[2] and is considered an important hub in Central Europe.[3] In 2008, Budapest had 1,702,297 inhabitants[4], down from a mid-1980s peak of 2.1 million, with an official agglomeration of 2,451,418[5]. The city covers an area of 525 square kilometres (202.7 sq mi)[6] within the city limits. Budapest became a single city occupying both banks of the river Danube with the unification on 17 November 1873, of right-bank (west) Buda and Óbuda (Old Buda) together with Pest on the left (east) bank.[7] [6]
Aquincum, originally a Celtic settlement,[8] was the direct ancestor of Budapest,[9] becoming the Roman capital of Lower Pannonia.[8] Magyars arrived in the territory[10] in the 9th century. Their first settlement was pillaged by the Mongols in 1241-42.[11] The re-established town became one of the centers of Renaissance humanist culture[12] in the 15th century.[13] Following nearly 150 years of Ottoman rule,[14] development of the region entered a new age of prosperity in the 18th and 19th centuries, and Budapest became a global city after the 1873 unification.[15] It also became the second capital of Austria-Hungary, a great power that dissolved in 1918. Budapest was the focal point of the Hungarian Revolution of 1848, the Hungarian Soviet Republic of 1919, Operation Panzerfaust in 1944, the Battle of Budapest of 1945, and the Revolution of 1956.
Widely regarded as one of the most beautiful cities in Europe,[16][1][10][17] its World Heritage Sites include the banks of the Danube, the Buda Castle Quarter, Andrássy Avenue, and the Millennium Underground Railway, the first on the European continent.[16][18] In addition, the largest thermal water cave system in the world was discovered under Budapest in 2008.[19]
The city attracts over 20 million visitors a year.[20] The headquarters of the European Institute of Innovation and Technology (EIT) will be in Budapest.[21]
Contents |
[edit] History
The first settlement on the territory of Budapest was Ak-Ink (English: Abundant Water) built by Celts[8] before the birth of Christ. It was later occupied by the Romans. The Roman settlement - Aquincum - became the main city of Lower Pannonia[8] in 106 AD[8]. The Romans constructed roads, amphitheaters, baths and houses with heated floors in this fortified military camp[22].
The Hungarians led by Árpád settled in the territory at the end of the 9th century[23][10], and a century later officially founded the Kingdom of Hungary[10]. Research places the probable residence of the Árpáds an early place of central power near what became Budapest. [24] The Tatar invasion in the 13th century quickly proved that defence is difficult on a plain[6][10]. King Béla IV of Hungary therefore ordered the construction of reinforced stone walls around the towns[10] and set his own royal palace[11] on the top of the protecting hills of Buda. In 1361[11] it became the capital of Hungary[6].
The cultural role of Buda was particularly significant during the reign of Matthias Corvinus of Hungary[6]. The Italian Renaissance had a great influence on the city[6]. His library, the Bibliotheca Corviniana[6], was Europe's greatest collection of historical chronicles and philosophic and scientific works in the 15th century, and second only in size to the Vatican Library[6]. After the foundation of the first Hungarian university in Pécs in 1367[25] the second one was established in Óbuda in 1395[25]. The first Hungarian book was printed in Buda in 1473[26].
The Turkish occupation lasted for more than 140 years[6]. The Turks constructed some fine bathing facilities here[10]. The unoccupied western part of the country became part of the Habsburg Empire as Royal Hungary.
In 1686, two years after the unsuccessful siege of Buda, a renewed campaign was started to enter the Hungarian capital. This time, the Holy League's army was twice a large, containing over 74,000 men, including German, Croat, Dutch, Hungarian, English, Spanish, Czech, Italian, French, Burgundian, Danish and Swedish soldiers, along with other Europeans as volunteers, artilleryman, and officers, the Christian forces reconquered Buda, and in the next few years, all of the former Hungarian lands, except areas near Timişoara (Temesvár), were taken from the Turks. In the 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz these territorial changes were officially recognized, and in 1718 the entire Kingdom of Hungary was removed from Ottoman rule.
The city was destroyed during the battle[6]. Hungary was then incorporated into the Habsburg Empire[6].
The nineteenth century was dominated by the Hungarians' struggle for independence[6] and modernization. The national insurrection against the Habsburgs began in the Hungarian capital in 1848 and was defeated a little more than a year later.
1867 was the year of Reconciliation that brought about the birth of Austria-Hungary.
This made Budapest the twin capital of a dual monarchy. It was this compromise which opened the second great phase of development in the history of Budapest, lasting until World War I. In 1873 Buda and Pest were officially merged with the third part, Óbuda (Ancient Buda), thus creating the new metropolis of Budapest. The dynamic Pest grew into the country's administrative, political, economic, trade and cultural hub.

World War I brought the Golden Age to an end. In 1918 Austria-Hungary lost the war and collapsed; Hungary declared itself an independent republic. In 1920 the Treaty of Trianon finalized the country's partition, as a result, Hungary lost over two-thirds of its territory, about two-thirds of its inhabitants under the treaty including 3.3 million out of 10 million ethnic Hungarians.[27][28]
In 1944, towards the end of World War II, Budapest was partly destroyed by British and American air raids. From 24 December 1944 to 13 February 1945, the city was besieged during the Battle of Budapest. Budapest suffered major damage caused by the attacking Soviet troops and the defending German and Hungarian troops. All bridges were destroyed by the Germans. More than 38,000 civilians lost their lives during the conflict.
Between 20% and 40% of Greater Budapest's 250,000 Jewish inhabitants died through Nazi and Arrow Cross genocide during 1944 and early 1945.[29] Despite this, modern day Budapest has the highest number of Jewish citizens per capita of any European city.
In 1949, Hungary was declared a communist People's Republic. The new Communist government considered the buildings like the Buda Castle symbols of the former regime, and during the 1950s the palace was gutted and all the interiors were destroyed.
In 1956, peaceful demonstrations in Budapest led to the outbreak of the Hungarian Revolution. The Stalinist dictatorship collapsed after mass demonstrations, but Soviet tanks entered Budapest to crush the revolt. Fighting continued until early November, leaving more than 3000 dead.
From the 1960s to the late 1980s Hungary was often satirically referred to as "the happiest barrack" within the Eastern bloc, and much of the wartime damage to the city was finally repaired. Work on Erzsébet Bridge, the last to be rebuilt, was finished in 1965. In the early 1970s, Budapest Metro's East-West M2 line was first opened, followed by the M3 line in 1982. In 1987, Buda Castle and the banks of the Danube were included in the UNESCO list of World Heritage Sites. Andrassy Avenue (including the Millennium Underground Railway, Hősök tere and Városliget) was added to the UNESCO list in 2002. In the 1980s the city's population reached 2.1 million. In recent times a significant decrease in habitants occurred mainly due to a massive movement to the neighbouring agglomeration in Pest county. In the last decades of the 20th century the political changes of 1989-90 concealed changes in civil society and along the streets of Budapest. The monuments of the dictatorship were taken down from public places, into Memento Park.
[edit] Geography
The 525km2 area of Budapest lies in central Hungary surrounded by settlements of the agglomeration in Pest county. The capital extends 25 and 29 kilometers in the north-south, east-west direction respectively. The Danube enters the city from the north; later it encircles two islands, Óbuda Island and Margaret Island[6]. The third island Csepel Island is the largest of the Budapest Danube islands, however only its northernmost tip is within city limits. The river that separates the two parts of the city is only 230 m (755 ft) wide at its narrowest point in Budapest. Pest lies on the flat terrain of the Great Plain while Buda is rather hilly[6]. Pest's terrain rises with a slight eastward gradient, so the easternmost parts of the city lie at the same altitude as Buda's smallest hills, notably Gellért Hill and Castle Hill. The Buda hills consist mainly of limestone and dolomite, the water created speleothems, the most famous ones being the Pálvölgyi cave and the Szemlőhegyi cave. The hills were formed in the Triassic Era. The highest point of the hills and of Budapest is János hill, at 527 meters above sea level. The lowest point is the line of the Danube which is 96 meters above see level. The forests of Buda hills are environmentally protected.
[edit] Climate
Budapest has a temperate, transitional climate - somewhere between the mild, rainy weather of Transdanubia, the variable continental climate of the flat and open Great Plain to the east and the almost sub-Mediterranean weather of the south.[30].
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.1 (59) |
19.1 (66) |
25.4 (78) |
30.2 (86) |
34.0 (93) |
39.5 (103) |
40.7 (105) |
39.0 (102) |
35.2 (95) |
30.8 (87) |
22.6 (73) |
19.2 (67) |
|
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.1 (36) |
4.7 (40) |
10.6 (51) |
16.7 (62) |
22.0 (72) |
25.2 (77) |
27.5 (82) |
27.1 (81) |
22.6 (73) |
16.1 (61) |
8.3 (47) |
3.7 (39) |
|
| Average low °C (°F) | -2.7 (27) |
-1.3 (30) |
2.4 (36) |
6.9 (44) |
11.5 (53) |
14.6 (58) |
16.4 (62) |
15.9 (61) |
12.2 (54) |
7.5 (46) |
3.1 (38) |
-0.6 (31) |
|
| Record low °C (°F) | -21.7 (-7) |
-23.4 (-10) |
-14.1 (7) |
-4.6 (24) |
0.0 (32) |
3.0 (37) |
8.9 (48) |
7.0 (45) |
1.2 (34) |
-9.5 (15) |
-11.9 (11) |
-19.1 (-2) |
|
| Precipitation mm (inches) | 38.5 (1.52) |
36.7 (1.44) |
37.4 (1.47) |
47.2 (1.86) |
64.5 (2.54) |
69.8 (2.75) |
50.4 (1.98) |
49.5 (1.95) |
42.7 (1.68) |
46.9 (1.85) |
59.9 (2.36) |
49.3 (1.94) |
|
| Source: www.met.hu[31] 2008-09-26 | |||||||||||||
[edit] Population
| Historical populations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | %± |
| 1870 | 302,085 | — |
| 1880 | 402,706 | 33.3% |
| 1890 | 560,079 | 39.1% |
| 1900 | 861,434 | 53.8% |
| 1910 | 1,110,453 | 28.9% |
| 1920 | 1,232,026 | 10.9% |
| 1930 | 1,442,069 | 17.0% |
| 1941 | 1,712,791 | 18.8% |
| 1949 | 1,590,316 | −7.2% |
| 1960 | 1,804,606 | 13.5% |
| 1970 | 2,001,083 | 10.9% |
| 1980 | 2,059,226 | 2.9% |
| 1990 | 2,016,681 | −2.1% |
| 2001 | 1,777,921 | −11.8% |
| 2005 | 1,695,814 | −4.6% |
| 2008 | 1,702,279 | 0.4% |
[edit] Ethnic groups
Population by nationalities according to the 2001 census,[32]:
- Hungarians - 1,631,043 (91.2%)
- Germans - 18,097 (1%)
- Roma - 14,019 (0.8%)
- Others (mainly Slovaks, Greeks, Romanians) - 21,691
- No answer, unknown - 93,071
[edit] Religions
Population by denominations[33]:
- Roman Catholic - 808,460 (45.5%)
- Calvinist - 224,169 (12.6%)
- Lutheran - 46,449 (2.6%)
- Greek Catholic - 28,901 (1.6%)
- Jewish - 9,468 (0.5%)
- Atheist - 347,209 (19.5%)
- Others (mainly Christian) - 26,681
- No answer, unknown - 286,584
[edit] Historical population
In 1910 Budapest had 880,371 residents (85.9% Hungarian, 9% German, 2.3% Slovak, 2.8% other). The distribution of religions were, 59.8% Roman Catholic, 23.1% Jewish, 9.9% Calvinist, 4.9% Lutheran, 2.3% other.[34]
[edit] Districts
Originally Budapest had 10 districts after coming into existence upon the unification of the three cities in 1873. On 1 January, 1950 Budapest was united with several neighboring towns and the number of its districts was raised to 22 (Greater Budapest). At that time there were changes both in the order of districts and in their sizes. Now there are 23 districts, 6 in Buda, 16 in Pest and 1 on Csepel Island between them. Each district can be associated with one or more city parts named after former towns within Budapest.
[edit] Landmarks and monuments
The neo-Gothic Parliament, containing amongst other things the Hungarian Crown Jewels. Saint Stephen's Basilica, where the Holy Right Hand of the founder of Hungary, King Saint Stephen is on display. The Hungarian cuisine and café culture: for example, Gerbeaud Café, and the Százéves, Biarritz, Fortuna, Alabárdos, Arany Szarvas, Kárpátia and the world famous Mátyás Pince Restaurants. There are Roman remains at the Aquincum Museum, and historic furniture at the Nagytétény Castle Museum.
The Castle Hill, the River Danube embankments and the whole of Andrássy út have been officially recognized as UNESCO World Heritage Sites.

Castle Hill and the Castle District; there are three churches here, six museums, and a host of interesting buildings, streets and squares. The former Royal Palace is one of the symbols of Hungary – and has been the scene of battles and wars ever since the thirteenth century. Nowadays it houses two impressive museums and the National Széchenyi Library. The nearby Sándor Palace contains the offices and official residence of the President of Hungary. The seven-hundred year-old Matthias Church is one of the jewels of Budapest. Next to it is an equestrian statue of the first king of Hungary, King Saint Stephen, and behind that is the Fisherman's Bastion, from where opens out a panoramic view of the whole city. Statues of the Turul, the mythical guardian bird of Hungary, can be found in both the Castle District and the Twelfth District.
In Pest, arguably the most important sight is Andrássy út. As far as Kodály Körönd and Oktogon both sides are lined with large shops and flats built close together. Between there and Heroes’ Square the houses are detached and altogether grander. Under the whole runs continental Europe’s oldest Underground railway, most of whose stations retain their original appearance. Heroes’ Square is dominated by the Millenary Monument, with the Tomb of the Unknown Soldier in front. To the sides are the Museum of Fine Arts and the Palace of Arts, and behind City Park opens out, with Vajdahunyad Castle. One of the jewels of Andrássy út is the Hungarian State Opera House. Statue Park, a theme park with striking statues of the Communist era, is located just outside the main city and is accessible by public transport.
The city is home to the largest synagogue in Europe (Dohány Street Synagogue)[35], the largest medicinal bath in Europe (Széchenyi Medicinal Bath) and the third largest Parliament building in the world, once the largest in the world. The third largest church in Europe (Esztergom Basilica) and the second largest Baroque castle in the world (Gödöllő) are in the vicinity.
|
Heroes' Square with the Millenary Monument |
Saint Elisabeth Church |
||
[edit] Islands
Seven islands can be found on the Danube: Hajógyári sziget (literal translation: Shipyard Island), Margit-sziget (Margaret Island), and Csepel sziget (the northernmost part of this island belonging to Budapest is a separate district of the city, the XXI., while the other islands are parts of other districts, the III. and XIII. respectively), Palotai-sziget (in fact, it's a peninsula today), Népsziget (connected to the above, but mostly surrounded by water), Háros-sziget and Molnár-sziget.
Notable islands:
- Margit-sziget is a 2.5 km (1.6 mi) long island and 0.965 square kilometres (238 acres) in area. The island mostly consists of a park and is a popular recreational area for tourists and locals alike. The island lies between bridges Margaret Bridge (south) and Árpád Bridge (north). Dance clubs, Swimming pools, an Aqua park, athletic and fitness centres, bicycle and running tracks can be found around the Island. During the day the island is occupied by people doing sports, or just resting. In the summer (generally on the weekends) mostly young people go to the island at night to party in its terraces, or to recreate with a bottle of alcohol on a bench or on the grass (this form of entertainment is sometimes referred to as bench-partying).
- Csepel-sziget [ˈtʃɛpɛlsigɛt] or Csepel Island is the largest island of the River Danube in Hungary. It is 48 km (30 mi) long; its width is 6–8 km (3.75–5 mi) and its area comprises 257 km2 (99 sq mi), whereas only the northern tip is inside the city limits.
- Hajógyári-sziget [ˈhɒjo:ɟa:ri sigɛt] (or Óbudai-sziget) is a man built island, located in the third district. This island hosts many activities such as: wake-boarding, jet-skiing during the day, and dance clubs during the night. This is the island where the famous Sziget Festival takes place, hosting hundreds of performances per year and now around 400,000 visitors in its last edition. Many building projects are taking place to make this island into one of the biggest entertainment centres of Europe, the plan is to build Apartment buildings, hotels, casinos and a marina.
- Luppa-sziget is the smallest island of Budapest, located in the north region.
[edit] Transport
[edit] Airport
Budapest Ferihegy International Airport, which has 3 passenger terminals: Ferihegy 1, which tends to serve the many discount airlines now flying to and from Budapest, Ferihegy 2/A and Ferihegy 2/B. Terminal 2/C is planned to be built. The airport is located to the east of the centre in the XVIII. district in Pestszentlőrinc.
[edit] Roads
Budapest is the most important Hungarian road terminus; all the major highways end there. Budapest is also a major railway terminus.
Ring road M0 around Budapest is made and allows people to go around Budapest from East to West and from North to South, however there is no way from West to North - you only need to go around to the South.
[edit] Public transport
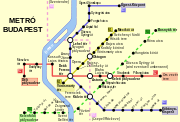
Budapest public transport is provided by BKV[36], the company operates buses, trolleybuses, trams, suburban railway lines, the metro, a boat service, a cogwheel railway and a chairlift, called Libegő.
Budapest's tram network is extensive, and reliable despite poor track infrastructure and an ageing fleet. Routes 4 and 6 combined form the busiest traditional city tram line in the world, with the world's longest passenger trams (54-metre (177 ft) long Siemens Combino) running at 60 to 90 second intervals at peak time and 3–4 minutes off-peak and usually packed with people.
Day services operate from 4:30 a.m. until 11:30 p.m. each day. Night traffic (a reduced overnight service) has a reputation for being excellent[citation needed].
There are three metro lines and a fourth is currently under construction. The Yellow line, built in 1896, is one of the oldest subway lines in the world, following London Underground and the Istanbul Metro that were built respectively in 1863 and 1875.
[edit] Special vehicles
Beside metros, suburban rails, buses, trams and boats, there are a couple of less usual vehicles in Budapest:
- trolleybus (trolibusz) on several lines in Pest
- funicular (sikló); the Castle Hill Funicular between the Chain Bridge and Buda Castle
- cyclecar (bringóhintó) for rent in Margaret Island
- chairlift (libegő)
- rack railway (fogaskerekű vasút); the Budapest Cog-wheel Railway
- children's railway (gyermekvasút)[36]
The latter three vehicles run among Buda hills.
[edit] Railway
Hungarian main-line railways are operated by MÁV. There are three main railway termini in Budapest, Keleti (eastern), Nyugati (westbound), and Déli (southbound), operating both domestic and international rail services. Budapest was one of the main stops of the Orient Express until 2001, when the service was cut back to Paris-Vienna.
There is also a suburban rail service in and around Budapest, operated under the name HÉV.
[edit] Waterways
The river Danube flows through Budapest on its way to the Black Sea. The river is easily navigable and so Budapest has historically been a major commercial port (at Csepel). In the summer months a scheduled hydrofoil service operates up the Danube to Vienna.
[edit] Education

Budapest is Hungary's main centre of education and home to many universities
- Budapest University of Technology and Economics
- Corvinus University of Budapest
- Eötvös Loránd University
- Semmelweis University (medical university)
- Szent István University, Faculty of Veterinary Science
- Budapest Business School
- Pázmány Péter Catholic University
- Károli Gáspár University of the Hungarian Reformed Church
- Jewish Theological Seminary – University of Jewish Studies
[edit] Timeline of the history of Budapest
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| B.C. | Neolithic, Chalcolithic-, bronze and iron age cultures, Celtic and Eravisci settlements on present day Budapest. |
| 1st century | Romans found the settlements known as Aquincum, Contra-Aquincum and Campona. Aquincum becomes the largest town of the Danubian region and one of the capitals of Pannonia. |
| 5th century | The Age of Huns. King Attila builds a city for himself here according to later chronicles. |
| 896 | Following the foundation of Hungary, Árpád, leader of the Hungarians, settles in the "Town of Attila", usually identified as Aquincum. |
| 10th century | Out of the seven to ten Hungarian tribes, four have settlements in the territory
of modern Budapest: Megyer, Keszi, Jenő and Nyék.[citation needed] |
| 1046 | Bishop Gellért dies at the hands of pagans on present-day Gellért Hill. |
| 1241 | During the Tatar invasions both towns are destroyed. King Béla IV builds the first royal castle on Castle Hill, Buda in 1248. The new town adopts the name of Buda from the earlier one (present day Óbuda). Pest is surrounded by city walls. |
| 1270 | Saint Margaret of Hungary dies in a cloister on the Isle of Rabbits (present day Margaret Island). |
| 1458 | The noblemen of Hungary elect Matthias Corvinus (in Latin) or Hunyadi Mátyás (in Hungarian) as king on the ice of the Danube. Under his reign Buda becomes a main hub of European Renaissance. He dies in 1490, after capturing Vienna in 1485. |
| 1541 | The beginning of Ottoman occupation. The Turkish Pashas build multiple mosques and baths in Buda. |
| 1686 | Buda and Pest are reconquered from the Turks with Habsburg leadership. Both towns are destroyed completely in the battles. |
| 1690s | Resettlement, initially only a few hundred German settlers. |
| 1773 | Election of the first Mayor of Pest. |
| 1777 | Maria Theresa of Austria moves Nagyszombat University to Castle Hill. |
| 1783 | Joseph II places the acting government (Helytartótanács) and Magyar Kamara on Buda. |
| 1795 20 May | Ignác Martinovics and other Jacobin leaders are executed on Vérmező or 'The Field of Blood'. |
| 1810 | A fire in the Tabán district. |
| 1825 | Commencement of the Reform Era. Pest becomes the cultural and economic centre of the country. The first National Theatre is built, along with the Hungarian National Museum and the Széchenyi Lánchíd. |
| 1838 | The biggest flood in recent memory in March. Pest is completely inundated. |
| 1848 15 March | Start of the Revolution and War of Independence of 1848-49. Pest replaces Pozsony (Bratislava) as the new capital of Hungary and seat of the Batthyány government and the Parliament. |
| 1849 | The Austrians occupy the city in early January, but the Hungarian Honvédsereg (Army of National Defense) reclaims it in April, taking the fortress of Buda on May 21 after an 18-day siege. In July, the Habsburg army again captures the two towns. |
| 1849 6 October | Lajos Batthyány, the first Hungarian Prime Minister is executed on the present-day Szabadság tér. |
| 1867 | Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, followed by unprecedented civic development, resulting in the style of present day Budapest. |
| 1873 | The former cities: Pest, Buda and Óbuda are united, and with that the Hungarian capital is established with the name of Budapest. |
| 1874 | The Budapest Cog-wheel Railway service is inaugurated. |
| 1878 | Electric public lighting installed in downtown. |
| 1896 | Millennium celebrations, the Millennium Underground is inaugurated, and the Ferenc József híd (today's Liberty Bridge) is opened. |
| 1909–1910 | Electric public lighting expanded to the suburbs. |
| 1910 | The census finds 880,000 people in Budapest and 55,000 in the largest suburb of Újpest (now part of Budapest). The religious make-up was 60.9% Catholic, 23.1% Jewish, 9.9% Calvinist and 5.0% Lutheran. Újpest was 65.9% Catholic, 18.4% Jewish, 9.7% Calvinist and 4.5% Lutheran. The percentage of ethnic Germans was 9.0% in Budapest and 5.7% in Újpest, while 2.3% of the population claimed to be Slovak. (Source: Történelmi Magyarország atlasza és adattára 1914, Budapest, 2001.) |
| 1918–1919 | Revolution and the 133 days of the Hungarian Soviet Republic (March-August 1919) under the leadership of Béla Kun. It is the first Communist government to be formed in Europe after the October Revolution in Russia. |
| 1924 | Hungarian National Bank is founded. |
| 1925 | Hungarian Radio commences broadcasting. |
| 1933 | Disassembly of the Tabán commences. |
| 1944 19 March | Budapest is occupied by the Germans. At the time of the occupation, there were 184,000 Jews and between 65,000 and 80,000 Christians considered Jewish in the town.
Fewer than half of them (approximately 119,000) survived the following 11 months. |
| 1944 26 December - 13 Ferbuary | Soviet and Romanian troops besiege Budapest from 15 January to 18 January. The retreating Germans destroy all Danube bridges. On 18 January, Pest and its ghetto are completely liberated. The Buda castle falls on 13 February. World War II took the lives of close to 200,000 Budapest residents and caused widespread damage to the buildings of the city. |
| 1956 23 October - 4 November | The Hungarian Revolution of 1956 breaks out, ending in the invasion of a large Soviet force. |
| 1960s | Wartime damages are largely repaired. Work on the final bridge to be repaired, the Elizabeth Bridge is finished in 1965. |
| 1970–1972 | The first phase of the East-Western Metro begins. |
| 1982 | The first phase of the North-Southern Metro begins. |
| 1987 | Castle Hill and the banks of the Danube are included in the UNESCO World Heritage Sites. |
| 1990 | The city is home to 2,016,100 residents. |
| 2002 | Andrássy Avenue is added to the list of World heritage Sites, along with the Millennium Underground railway and Heroes' Square. |
| 2006 Hungarian protests. |
[edit] Sister cities
These are the official sister cities of Budapest[37][38][39][40]:
| Country | City | County / District / Region / State | Date | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Austria | Vienna | Vienna | 1990 | |||
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Sarajevo | Sarajevo Canton | 1995 | |||
| Croatia | Zagreb | Zagreb | 1994 | |||
| Germany | Berlin | Berlin | 1992 | |||
| Germany | Frankfurt am Main | Hesse | 1990 | |||
| Israel | Tel Aviv | Tel Aviv District | 1989 | |||
| Italy | Florence | Tuscany | 2008 | |||
| Portugal | Lisbon | District of Lisbon | 1992 | |||
| United States | Fort Worth | Texas | 1990 | |||
| United States | New York City | New York | 1992 |
Some of the city's districts are also twinned to small cities or districts of other big cities, for details see the article List of districts and towns in Budapest.
[edit] Notes
- ^ a b "Beauty and the Feast". Time. 2002-03-18. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,901020325-218419,00.html. Retrieved on 2008-05-22.
- ^ "Budapest". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.. 2008. http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9106098/Budapest. Retrieved on 2008-01-30.
- ^ "Doing Business : Budapest, the soul of Central Europe". International Herald Tribune. 2004-08-04. http://www.iht.com/articles/2004/08/04/trbuda_ed3_.php. Retrieved on 2008-01-29.
- ^ "Gazetteer of the Republic of Hungary". Hungarian Central Statistical Office. 2008-01-01. http://portal.ksh.hu/pls/portal/docs/PAGE/KSHPORTAL/ADATOK/HELYSEGNEVTAR/HNK2008.PDF. Retrieved on 2008-08-16.
- ^ "Social and economic parameters of Budapest" (in Hungarian). Hungarian Central Statistical Office. 9. http://portal.ksh.hu/pls/ksh/docs/hun/xftp/idoszaki/regiok/bptarsgazdjell.pdf. Retrieved on 2007-07-13.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Török, András. "Budapest". Encarta. http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761572648/Budapest.html. Retrieved on 2008-04-06.
- ^ Molnar, A Concise History of Hungary, Chronology pp. 15
- ^ a b c d e "Aquincum". Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.. 2008. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/31272/Aquincum. Retrieved on 2008-05-22.
- ^ Sugar, Peter F.; Péter Hanák, Tibor Frank (1990). "Hungary before the Hungarian Conquest". A History of Hungary. Indiana University Press. pp. 3. ISBN 025320867X. http://books.google.com/books?id=SKwmGQCT0MAC&printsec=frontcover&hl=hu#PPA3,M1. Retrieved on 2008-05-19.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Budapest". Travel Channel. http://guides.travelchannel.com/budapest/city-guides/historical-background. Retrieved on 2008-05-22.
- ^ a b c "Budapest". 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition. http://en.wikisource.org/wiki/1911_Encyclop%C3%A6dia_Britannica/Budapest. Retrieved on 2008-01-30.
- ^ Drake, Miriam A. (2003). "Eastern Europe, England and Spain". Encyclopedia of Library and Information Science. CRC Press. pp. 2498. ISBN 0824720806. http://books.google.com/books?hl=hu&lr=&id=w1Xtjiyh9XYC&oi=fnd&pg=PA2494&ots=zKQ2JFNcOr&sig=PBqz2v48y02bWQKE_obj9N8tfis#PPA2498,M1. Retrieved on 2008-05-22.
- ^ Casmir, Fred L. (1995). "Hungarian culture in communication". Communication in Eastern Europe: The Role of History, Culture, and media in contemporary conflicts. Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. pp. 122. ISBN 0805816259. http://books.google.com/books?hl=hu&lr=&id=be2UW6NyposC&oi=fnd&pg=PA115&ots=EbQczSn6BE&sig=muxfaU71kcts3FwOQFth_M9uj3c#PPA122,M1. Retrieved on 2008-05-21.
- ^ Molnar, A Concise History of Hungary, Chronology pp. 15
- ^ Beaverstock, J. V.; R. J. Smith, P. J. Taylor (1999). A Roster of World Cities. Loughborough University. http://www.lboro.ac.uk/gawc/rb/rb5.html. Retrieved on 2008-05-22.
- ^ a b "Nomination of the banks of the Danube and the district of the Buda Castle". International Council on Monuments and Sites. http://whc.unesco.org/archive/advisory_body_evaluation/400bis.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-01-31.
- ^ "Budapest Is Stealing Some of Prague’s Spotlight". The New York Times. 2006-10-03. http://travel.nytimes.com/2006/09/03/travel/03journey.html. Retrieved on 2008-01-29.
- ^ "World Heritage Committee Inscribes 9 New Sites on the World Heritage List". Unesco World Heritage Centre. http://whc.unesco.org/en/news/156. Retrieved on 2008-01-31.
- ^ http://tvnz.co.nz/view/page/425822/2319289
- ^ "Budapest City Guide". European Rail Guide. http://www.europeanrailguide.com/destinationguides/budapest/. Retrieved on 2008-02-04.
- ^ "EU nations pick Budapest for technology institute". International Herald Tribune (The New York Times Company). 2008-06-18.
- ^ Sugar, Peter F. (1990). "Hungary before the Hungarian Conquest". A History of Hungary. pp. 5. http://books.google.com/books?hl=hu&lr=&id=SKwmGQCT0MAC&oi=fnd&pg=PR9&dq=The+Romans+roads,+amphitheaters+Aquincum+%C3%93buda&ots=mwQVAjuT18&sig=jcE_wG6ttjvPLwwagpkqKAgvHkU#PPA5,M1. Retrieved on 2008-06-03.
- ^ Molnar, A Concise History of Hungary, Chronology pp. 12
- ^ Molnar, A Concise History of Hungary, p. 14
- ^ a b Sugar, Peter F. (1990). "The Angevine State". A History of Hungary. pp. 48. http://books.google.com/books?hl=hu&lr=&id=SKwmGQCT0MAC&oi=fnd&pg=PR9&dq=Hungarian+university+1395+Buda&ots=mwQWxjoQ79&sig=UMMjYryQbpbBEiBeWIhOUqdUL8M#PPA48,M1. Retrieved on 2008-06-03.
- ^ Mona, Ilona (1974). "Hungarian Music Publication 1774–1867". Studia Musicologica Academiae Scientiarum Hungaricae (Akadémiai Kiadó) 16: 261–275. doi:. http://www.jstor.org/pss/901850. Retrieved on 2008-06-03.
- ^ Macartney, C.A. (1937). Hungary and her successors - The Treaty of Trianon and Its Consequences 1919-1937. Oxford University Press.
- ^ "East on the Danube: Hungary's Tragic Century". The New York Times. 2003-08-09. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9B07E3D91531F93AA3575BC0A9659C8B63&sec=&spon=&pagewanted=2. Retrieved on 2008-03-15.
- ^ "Budapest". United States Holocaust Memorial Museum. http://www.ushmm.org/wlc/article.php?lang=en&ModuleId=10005264. Retrieved on 2007-07-18.
- ^ "Budapest:When to go". Lonely Planet. http://www.lonelyplanet.com/worldguide/hungary/budapest/when-to-go. Retrieved on 2008-04-06.
- ^ "Monthly Averages for Budapest, Hungary (based on data from 1901–2000)". Hungarian Meteorological Service. http://www.met.hu/pages/climate/bp/index.htm. Retrieved on 2008-09-26.
- ^ "Population by nationalities". Hungarian Central Statistical Office. 2001. http://www.nepszamlalas.hu/eng/volumes/06/01/tabeng/4/load01_11_0.html. Retrieved on 2008-05-30.
- ^ "Population by religions, denominations". Hungarian Central Statistical Office. 2001. http://www.nepszamlalas.hu/eng/volumes/18/tables/load3_12.html. Retrieved on 2008-05-30.
- ^ County maps of the Hungarian Kingdom (1913)
- ^ "Out of Darkness, New Life". The New York Times. 2007-12-30. http://travel.nytimes.com/2007/12/30/travel/30dayout.html?scp=1&sq=largest+synagogue+in+Europe&st=nyt. Retrieved on 2008-03-12.
- ^ a b "36 Hours in Budapest". The New York Times. 2007-08-12. http://travel.nytimes.com/2007/08/12/travel/12hours.html?scp=10&sq=Budapest&st=nyt. Retrieved on 2008-01-29.
- ^ "Sister City - Budapest". Official website of New York City. http://www.nyc.gov/html/unccp/scp/html/sc/budapest_main.shtml. Retrieved on 2008-05-14.
- ^ "Sister cities of Budapest" (in Hungarian). Official Website of Budapest. http://www.budapest.hu/engine.aspx?page=20030224-cikk-testvervarosok. Retrieved on 2008-01-31.
- ^ "Who knows less about Budapest? A quiz with mayor candidates" (in Hungarian). Index. http://index.hu/politika/belfold/budapest/kvizkerdes74/. Retrieved on 2008-01-31.
- ^ "Hízelgő a magyar fővárosnak: Firenze testvérvárosának fogadta" (in Hungarian). Népszabadság. Ringier. 2008-05-17. http://nol.hu/budapest/cikk/492160/. Retrieved on 2008-05-30.
[edit] References
- DK Publishing, Budapest: Eyewitness Travel Guildes. DK Travel, 2007. ISBN 978-0756624354
- Annabel Barber, Visible Cities Budapest: A City Guide. Somerset, Ltd., 2004. ISBN 978-9632129860
- Krisztian Ungvary (Author), John Lukacs (Foreword), The Siege of Budapest: One Hundred Days in World War II. Yale University Press, 2006. ISBN 978-0300119855
- Molnar, Miklos (2001). A Concise History of Hungary. Cambridge Concise Histories (Fifth printing 2008 ed.). Cambridge, United Kingdom: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9780521667364.
[edit] See also
- List of cemeteries in Budapest
- List of famous people of Budapest
- Music of Budapest
- Urban and Suburban Transit Association (most of its activity is centred around Budapest)
- Budapest metropolitan area
[edit] External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: Budapest |
- Official homepage
- Budapest Tourist Office
- Public transport in Budapest
- MÁV-Start Railway Passenger Transport Co.
- Budapest travel guide from Wikitravel
|
|||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||